Table of Contents
Overview
Backend development has long stood as one of software engineering’s most persistent bottlenecks—complex infrastructure management, tedious API configuration, database optimization headaches, and the constant tension between development speed and production-grade quality. Traditional approaches force teams to choose between rapid no-code prototyping that eventually hits scaling walls, or code-heavy custom development that consumes months before delivering value. Xano 2.0, officially launched on October 22, 2025, fundamentally reimagines this paradigm by converging three previously separate development approaches into a unified platform: visual no-code building for speed, full code-level control through XanoScript and IDE integration for flexibility, and AI-assisted development through Logic Assistant for intelligence.
This represents not merely an incremental improvement but a architectural transformation in how teams build production backends. Whether you approach backend development through visual drag-and-drop workflows, prefer writing code directly in Visual Studio Code with full Git integration, or leverage AI to generate logic from natural language descriptions, Xano 2.0 provides a first-class experience for each paradigm while ensuring they interoperate seamlessly. The platform delivers complete backend infrastructure—PostgreSQL database, API generation, authentication, serverless functions, real-time capabilities, and enterprise compliance—all deployed on auto-scaling, secure infrastructure without DevOps overhead.
Key Features
Xano 2.0 distinguishes itself through a comprehensive feature ecosystem engineered to support diverse developer workflows while maintaining production-grade quality and security.
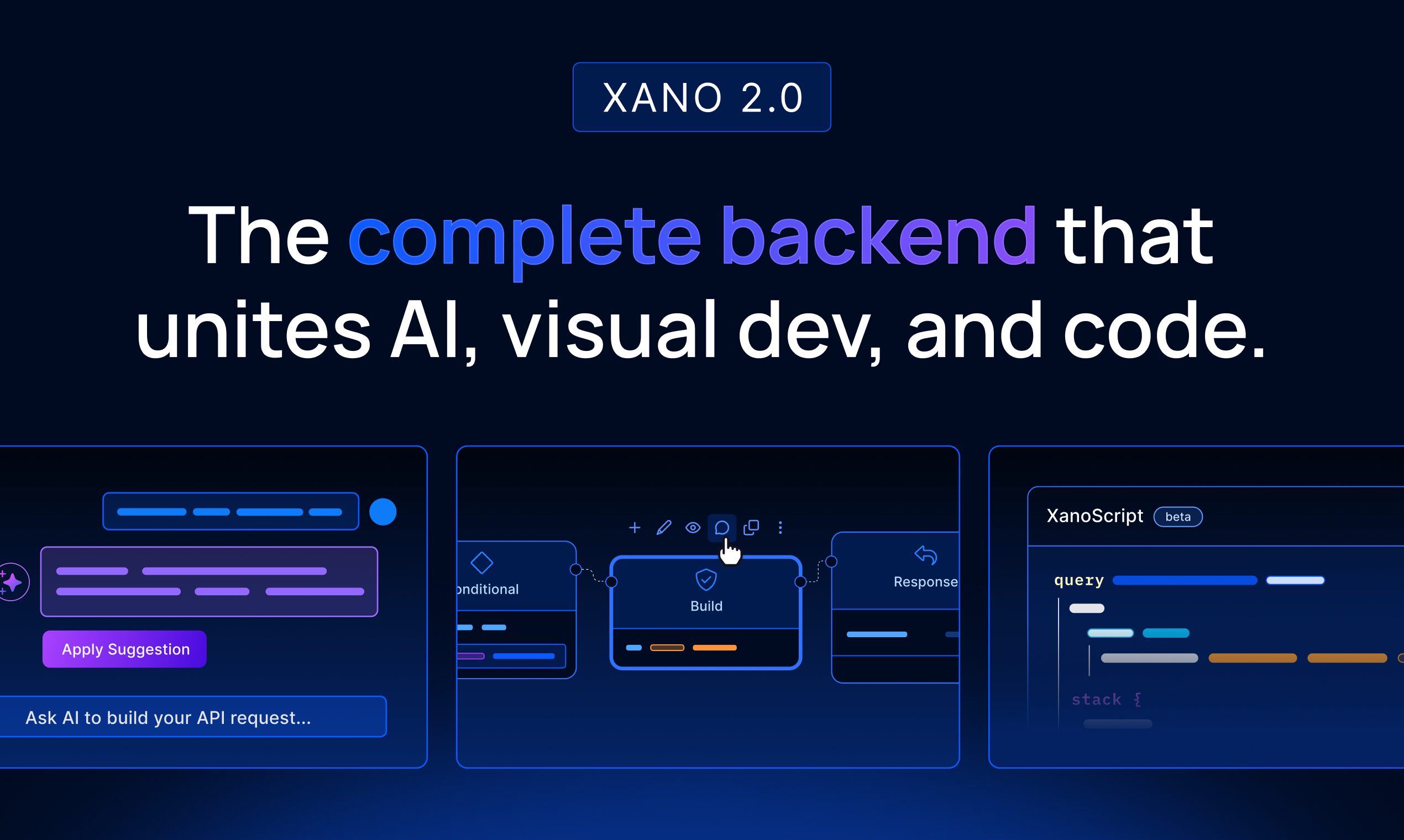
- Three-Way Development Paradigm: Build your backend through visual Canvas or Function Stack builders for rapid iteration, write XanoScript directly in the integrated editor or your preferred IDE for granular control, or describe logic in natural language and let the Logic Assistant generate implementation. Seamlessly switch between approaches as your needs evolve, with changes synchronized instantly across all views.
- XanoScript Language: A purpose-built scripting language designed specifically for backend data transformation and business logic, providing familiar syntax with backend-optimized constructs. XanoScript features a dedicated language server enabling intelligent autocomplete, real-time error detection, inline documentation, and refactoring capabilities within Xano’s interface or external IDEs.
- Visual Canvas Builder: A node-based, workflow-oriented visual editor that represents logic as interconnected story flows rather than linear function lists. The Canvas view excels for developers who think spatially and want to visualize data flow, decision trees, and dependencies graphically, making complex logic comprehension and debugging more intuitive.
- Function Stack Builder: Xano’s original visual development interface presenting backend logic as ordered, executed function sequences. This hybrid approach between traditional code views and visual builders appeals to developers preferring structured, procedural clarity while maintaining no-code accessibility.
- AI Logic Assistant: A conversational interface enabling plain language logic description that generates XanoScript implementations. The assistant iteratively refines code based on feedback, explains generated logic, and suggests optimizations—dramatically accelerating development for both non-technical builders and experienced engineers prototyping rapidly.
- VS Code Extension and IDE Integration: Native Visual Studio Code extension providing direct Xano backend connection, enabling developers to build entirely within their preferred IDE environment. The extension supports Cursor, Windsurf, and other VS Code-compatible editors, with full integration for IDE-native AI copilots like GitHub Copilot to assist with Xano-specific backend development patterns.
- Git Sync Integration: One-way push functionality automatically exporting workspace as XanoScript to Git repositories upon publish, enabling version control, code review workflows, collaborative development practices, and integration into existing CI/CD pipelines. Frontend static hosting can pull code from selected Git repositories for coordinated deployment.
- Comprehensive Backend Services: Complete infrastructure including scalable PostgreSQL database with visual schema design, automatic REST API generation with Swagger documentation, JWT-based authentication with role-based access control, serverless Lambda functions supporting custom Node.js packages including private NPM registries, file storage with transformation capabilities, real-time capabilities through webhooks and Agents, and message queuing for asynchronous processing.
- AI Agents and Automation: Orchestrate intelligent workflows and autonomous decision-making through Xano Agents, supporting long-running tasks, event-driven architectures, and complex multi-step automations. Agents receive limited free Gemini credits for initial experimentation without requiring external API keys.
- XanoScript Diff Viewer: Git-style diff experience enabling comparison of backend changes before publishing, merging across branches, deploying to production, or reverting modifications. This transparency ensures confidence in changes and facilitates collaborative review processes.
- Metadata API and MCP Support: Enhanced metadata API and Model Context Protocol server enabling backend building outside Xano using preferred IDEs or AI tools, supporting extensibility and integration into diverse development ecosystems.
- Frontend Static Hosting: Deploy and host static frontend applications directly within Xano, with VS Code Extension integration enabling synchronized frontend code deployment, creating a truly unified full-stack development platform.
- Enterprise Compliance and Security: SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR, HDS, and HIPAA compliance certifications ensuring enterprise-grade security. Role-based governance, branch-based development with merge workflows, and deployment controls support team collaboration at scale. Options for both cloud-hosted and self-hosted deployment preserve flexibility for varying data residency and security requirements.
- Expanded Onboarding Resources: Upgraded starter templates including core database tables, authentication API endpoints with password reset flows, email notification statements, event logging APIs, and example Agent chatbot implementations accelerating time-to-productivity for new users.
How It Works
Xano 2.0’s operational model accommodates radically different developer preferences and workflows through its tri-modal development approach, ensuring each paradigm receives first-class support.
Visual builders begin by designing database schemas through an intuitive interface resembling spreadsheet editing but delivering enterprise PostgreSQL capabilities underneath. Tables, relationships, indexes, and constraints are defined graphically. With data structures established, developers create API endpoints using either the node-based Canvas view or structured Function Stack interface. The Canvas view presents logic as connected workflow nodes representing data transformations, conditional branches, database queries, external API calls, and responses. The Function Stack shows the same logic as ordered execution steps. Both views provide identical capabilities—the choice reflects cognitive preference rather than functional limitation.
Code-first developers can bypass visual interfaces entirely, connecting Visual Studio Code or compatible IDEs directly to their Xano workspace through the native extension. XanoScript can be written directly with full IDE features including syntax highlighting, intelligent autocomplete based on workspace context, inline error detection, and debugging capabilities. Changes save directly to Xano’s backend, deploying instantly without manual publishing steps. This workflow mirrors traditional backend development but eliminates infrastructure management, deployment pipelines, and DevOps complexity.
AI-assisted developers describe desired functionality in natural language through the Logic Assistant. “Create an endpoint that accepts a user email, searches the users table, sends a password reset email if found, and returns appropriate status codes” becomes executable XanoScript through AI generation. The assistant explains generated code, suggests optimizations, and iteratively refines based on clarifications. This approach dramatically reduces the expertise barrier for backend development while maintaining production-quality output.
Regardless of entry point, all three paradigms interoperate seamlessly. Logic created visually can be viewed and edited as XanoScript. Code written in an IDE appears in visual builders with appropriate node representations. AI-generated implementations can be refined through any interface. Git sync exports the entire workspace as code, enabling external version control and review regardless of how logic was originally created. This flexibility ensures teams can adopt Xano without imposing a single development philosophy, accommodating diverse skill sets and preferences.
Throughout development, Xano handles infrastructure automatically. Database optimization, API scaling, authentication security, function execution environments, and monitoring all operate without manual configuration. Changes deploy instantly to development environments, with structured workflows supporting staging and production promotion through branching and merging capabilities. The platform eliminates the traditional gap between development and operations, enabling developers to focus entirely on business logic and application functionality.
Use Cases
Xano 2.0’s comprehensive capabilities and flexible development paradigms enable adoption across diverse project contexts and team compositions.
- Rapid Startup MVP Development: Founders and lean teams can launch production-ready backends in days rather than months, using visual builders to iterate quickly based on user feedback without hiring specialized backend engineers. As product-market fit solidifies and complexity grows, the same platform scales to millions of users while offering code-level control when needed.
- Enterprise Backend Modernization: Large organizations can rebuild legacy backend systems using visual development for speed while maintaining enterprise compliance requirements. Role-based access control, audit logging, branch-based development, and self-hosting options address governance needs, while Git integration enables existing code review and deployment workflows.
- SaaS Application Backends: Product teams building multi-tenant SaaS applications benefit from Xano’s authentication, database multi-tenancy support, and API generation capabilities. The platform handles complex requirements like row-level security, rate limiting, and usage tracking while enabling rapid feature development through visual or code-based approaches.
- Mobile and Web Application Backends: Cross-platform mobile apps and progressive web applications leverage Xano’s automatically generated, documented REST APIs. Real-time capabilities through webhooks and Agents support collaborative features, while file storage and transformation handle media-rich applications.
- Internal Tool and Automation Development: IT and operations teams build internal dashboards, workflow automation, and system integrations using visual builders without extensive coding expertise. The Agents system enables sophisticated automation orchestrating multiple systems and services.
- API-First Product Development: Teams building API products or microservices architectures use Xano to rapidly develop, document, and deploy production-grade APIs. Automatic Swagger documentation, versioning support, and flexible deployment options align with API-first development practices.
- Agency and Freelancer Client Projects: Development agencies leverage Xano’s speed for client deliverables while maintaining quality and scalability. The platform’s flexibility accommodates diverse client requirements, and Git integration enables white-label delivery of codebases when clients require backend portability.
- Technical Prototyping and Validation: Product managers and designers prototype backend functionality to validate concepts without engineering resources. AI-assisted logic generation enables rapid experimentation, with the ability to hand off functional backends to engineers for refinement and scaling.
Pros \& Cons
Advantages
- Unprecedented Development Paradigm Flexibility: The ability to seamlessly switch between visual building, direct code editing, and AI-assisted generation means teams never face tool-imposed methodology constraints. Use the approach that fits each task and team member’s strengths.
- True Production-Grade Without Trade-Offs: Unlike platforms requiring eventual migration or reconstruction for scale, Xano 2.0 delivers enterprise compliance, security certifications, unlimited scalability, and sophisticated features from day one. What you prototype is what scales.
- Code Portability Through Git Integration: The XanoScript export and Git sync capabilities provide confidence against vendor lock-in concerns. Your backend logic exists as code in version control, enabling external backup, review, and potential migration if organizational needs change.
- Comprehensive Backend Consolidation: Replaces 6-8 separate tools typically required for APIs, databases, serverless functions, authentication, CI/CD, monitoring, and observability. This consolidation dramatically reduces complexity, integration overhead, and operational costs.
- AI-Accelerated Development Without Sacrificing Control: The Logic Assistant accelerates initial development and reduces expertise barriers, but generated code remains fully transparent, editable, and portable. This avoids the “black box” problems of some AI-driven development platforms.
- Visual Interface for Complex Logic Understanding: Even when working primarily in code, the Canvas and Function Stack views provide invaluable visualization for understanding complex logic flows, debugging, and onboarding team members—capabilities pure code environments lack.
- Developer Experience Parity Across Paradigms: Whether building visually, coding in VS Code, or using AI assistance, the experience feels optimized for that approach rather than one paradigm being a compromised afterthought.
Disadvantages
- Platform Learning Curve for Maximum Leverage: While individual paradigms (visual, code, AI) are accessible independently, fully leveraging Xano’s capabilities across all three approaches and understanding when to use each requires investment in learning the platform’s philosophy and patterns.
- XanoScript Language Ecosystem Maturity: As a purpose-built language launched with Xano 2.0, XanoScript lacks the mature ecosystem, extensive libraries, community resources, and third-party tooling available for established languages like JavaScript, Python, or Go. This may create friction for complex custom logic.
- Pricing at Scale for High-Volume Applications: While accessible for startups through the \$29/month Starter tier, applications with millions of API requests, large database sizes, or extensive Lambda function execution can encounter significant costs compared to self-managed infrastructure, particularly for price-sensitive or non-venture-backed businesses.
- Managed Platform Constraints: Despite self-hosting options, the cloud-hosted version imposes some infrastructure-level constraints on database tuning, server configuration, and deployment architectures that teams with specialized infrastructure requirements or extreme optimization needs might find limiting.
- Visual Builder Limitations for Certain Logic Patterns: Extremely complex algorithmic logic, intensive data processing, or specialized computational tasks may prove cumbersome to represent visually or within XanoScript’s backend-optimized scope, potentially requiring external services or custom Lambda functions.
How Does It Compare?
Understanding Xano 2.0’s position requires examining the backend platform landscape as it exists in late 2025, where competitors span pure visual no-code tools, developer-focused open-source solutions, managed cloud platforms, and traditional Backend-as-a-Service offerings.
Bubble represents the most prominent full-stack no-code platform, enabling complete application development—frontend and backend—without code. Bubble excels for non-technical founders building entire web applications through visual interfaces, with its strength in unified full-stack development. However, Bubble’s backend capabilities are tightly coupled to its frontend builder, limiting usage with custom frontends, mobile apps, or as a standalone API layer. Bubble’s database and logic remain proprietary to the platform with limited export capabilities. For teams needing a general-purpose, API-first backend that powers diverse frontend technologies, Xano provides more flexibility. For founders building web applications who prefer a unified, fully visual environment handling both UI and backend, Bubble’s integrated approach may better serve their needs.
Supabase has emerged as the leading open-source Firebase alternative, built on PostgreSQL and emphasizing developer-friendly, database-first architecture. Supabase excels for developers comfortable with SQL and relational database design, offering powerful real-time capabilities, row-level security implemented directly in PostgreSQL, Edge Functions for serverless logic, and a generous free tier. Supabase’s open-source nature and self-hosting capabilities provide maximum transparency and vendor lock-in protection. However, Supabase targets technical developers proficient in SQL, database design, and code-first development. It lacks visual building interfaces and requires significantly more coding compared to Xano. Where Supabase demands database and backend development expertise, Xano’s visual builders enable non-technical team members to contribute. For developer-centric teams prioritizing open-source, PostgreSQL power, and accepting hands-on technical work, Supabase represents an excellent choice. For teams mixing technical and non-technical contributors or prioritizing visual development speed, Xano’s no-code-first approach with code escape hatches provides better accessibility.
Firebase remains Google’s dominant mobile and web backend platform, offering real-time NoSQL database (Firestore), authentication, cloud functions, hosting, and deep integration with Google Cloud ecosystem. Firebase 2025 introduces Firebase Studio, an AI-powered development environment enabling rapid full-stack prototyping, and Data Connect offering relational PostgreSQL alongside traditional Firestore. Firebase’s strength lies in its comprehensive Google ecosystem integration, generous free tier, and battle-tested scalability for millions of users. Firebase Studio’s AI-driven prototyping now competes directly with Xano’s AI-assisted development. However, Firebase fundamentally remains a code-first platform requiring JavaScript/TypeScript proficiency, lacks visual logic builders for backend workflows, and its NoSQL-first architecture (despite recent PostgreSQL additions) differs from Xano’s relational approach. Firebase suits technical teams deeply invested in Google Cloud, mobile-first applications leveraging Firebase’s SDKs, or projects benefiting from tight Google service integration. Xano better serves teams wanting visual development options, relational database flexibility from the start, and platform-agnostic deployment.
Backendless provides a comprehensive Backend-as-a-Service with visual UI builders (for frontend), no-code logic, real-time database, messaging, and flexible deployment including self-hosted and fully managed options. Backendless shares Xano’s no-code backend vision but extends further into frontend UI building. However, Backendless faces adoption challenges including steeper learning curves despite no-code promises, higher pricing, and smaller community compared to alternatives. Reviews indicate performance and scaling concerns for larger applications. Backendless appeals to teams wanting both backend and basic frontend UI building in one platform without caring about code access or portability. Xano focuses exclusively on backend excellence while integrating seamlessly with any frontend technology, offering clearer code export and Git integration, and benefiting from stronger recent momentum and community growth.
AWS SageMaker, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform backend services (Lambda, API Gateway, RDS, etc.) provide maximum flexibility, power, and control for teams with DevOps expertise. These platforms enable arbitrary architecture, language choice, fine-grained optimization, and integration with broader cloud services. However, they require significant infrastructure expertise, involve substantial manual configuration, create operational overhead for teams, and lack visual development or AI-assisted building tools. Traditional cloud platforms serve large enterprises with specialized DevOps teams, applications with highly specific infrastructure requirements, or teams already deeply committed to a specific cloud ecosystem. Xano eliminates this complexity while delivering production-grade capabilities, making it ideal for teams that want cloud-scale backends without cloud-scale operations burden.
Appwrite represents another open-source Backend-as-a-Service alternative, offering self-hosted Docker-based deployment with authentication, document-based database, storage, and serverless functions. Appwrite emphasizes self-hosting control and privacy, appealing to organizations with strict data sovereignty requirements. However, Appwrite uses a document-based NoSQL approach rather than relational PostgreSQL, lacks Xano’s mature visual logic builders and AI assistance, and requires more infrastructure management even when self-hosted. Appwrite suits teams requiring self-hosted, privacy-first backends with document-oriented data, accepting more hands-on technical work. Xano provides richer development paradigms including visual and AI-assisted workflows, relational database power, and managed cloud hosting reducing operational burden.
Parse Server, the open-source legacy of the original Parse platform, continues serving applications through Node.js/Express-based deployment. Parse offers familiarity for teams migrating from the original Parse, self-hosting flexibility, and active community support through hosting services like Back4App. However, Parse represents older Backend-as-a-Service architecture predating modern no-code and AI-assisted development paradigms. It lacks visual builders, AI assistance, and the comprehensive integrated tooling modern platforms provide. Parse serves teams maintaining existing Parse-based applications or preferring mature, stable, traditional BaaS patterns. Xano represents a modern evolution beyond Parse’s generation of backend platforms.
Xano 2.0’s distinctive positioning emerges at the intersection of accessibility, power, and flexibility. Where Bubble provides full-stack visual development but constrains backend portability, Supabase offers developer-centric open-source power but requires significant technical expertise, Firebase delivers Google ecosystem integration but remains code-first, and traditional cloud platforms provide maximum control but demand DevOps specialization, Xano threads a unique path: visual building accessible to non-developers, full code-level control through XanoScript and IDE integration for engineers, AI-assisted development accelerating both novices and experts, and production-grade infrastructure without operations burden. This tri-modal approach makes Xano particularly compelling for diverse teams with mixed technical backgrounds, startups needing to move fast without compromising future scalability, agencies serving varied client needs, and enterprises modernizing backends without displacing existing team skill sets. The platform succeeds in genuinely serving multiple personas—citizen developers, professional engineers, and AI-augmented builders—within a unified, interoperable environment rather than forcing a single development philosophy.
Final Thoughts
Xano 2.0 represents a significant milestone in backend development platforms, successfully delivering on the promise of “build your way” without compromising on production quality or scale. The platform’s October 2025 release marks a genuine evolution beyond the binary choice between no-code simplicity and code-level control that has constrained previous backend solutions.
The tri-modal development paradigm—visual building, direct code editing, and AI-assisted generation—stands as Xano 2.0’s most important innovation. Rather than treating these as separate tools poorly integrated together, Xano architected them as first-class citizens of a unified platform where switching between paradigms feels natural and productive. This design choice reflects a mature understanding that different developers, different tasks, and different project phases benefit from different approaches. The platform respects cognitive diversity rather than enforcing methodological orthodoxy.
The XanoScript language and VS Code integration demonstrate Xano’s commitment to serving professional developers alongside no-code builders. Developers no longer face the frustrating constraint of hitting a “no-code ceiling” that forces platform abandonment or painful workarounds when requirements exceed visual building capabilities. The presence of real code, version control, and IDE integration provides confidence that what you build on Xano remains yours—understandable, portable, and maintainable according to software engineering best practices.
The Logic Assistant’s AI capabilities represent thoughtful AI integration rather than superficial chatbot additions. By generating actual XanoScript code that developers can inspect, modify, and learn from, Xano avoids the “magic black box” problem plaguing some AI-driven development tools. This transparency makes AI a genuine productivity multiplier rather than a abstraction layer obscuring understanding.
The comprehensive backend consolidation Xano provides—replacing typically 6-8 separate tools for APIs, databases, functions, auth, CI/CD, and monitoring—addresses real team pain. The cognitive overhead and integration brittleness of stitching together disparate services creates substantial hidden costs in modern development. Xano’s unified approach eliminates these friction points while preserving the quality typically associated with specialized tools.
However, prospective adopters should carefully evaluate fit against their specific context. Teams with deep infrastructure expertise and highly specialized requirements may find Xano’s managed platform model constraining compared to bare-metal cloud infrastructure. Organizations requiring maximum vendor independence might hesitate despite Git export capabilities. Price-sensitive projects with extremely high API volumes should model costs carefully. And teams must invest time learning Xano’s paradigms to fully leverage its capabilities—the platform’s power demands engagement rather than offering surface-level simplicity.
The platform’s security certifications (SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR) and enterprise features (RBAC, branching, compliance controls) demonstrate Xano’s ambitions beyond startup experimentation toward enterprise backend infrastructure. The availability of self-hosted deployment alongside managed cloud service addresses the full spectrum from privacy-first to operations-light requirements.
As backend development continues evolving from manual infrastructure wrangling toward higher-level productivity platforms, tools that successfully balance accessibility and power while avoiding artificial constraints will increasingly define how teams build. Xano 2.0’s achievement lies in delivering genuine flexibility across development paradigms without compromising on production quality, security, or scale. For startups racing to validate products, enterprises modernizing legacy systems, agencies serving diverse clients, and teams mixing technical backgrounds, Xano offers a compelling answer to the persistent question: how do we build production backends faster without sacrificing quality or future flexibility? The answer, Xano demonstrates, involves meeting developers where they are—whether that’s visual building, code editing, or AI collaboration—and ensuring those paths interoperate rather than conflict.