Table of Contents
Overview
Qoder offers both a standalone AI-powered IDE developed by Alibaba Cloud and a plugin for JetBrains IDEs, providing AI-assisted coding capabilities designed to enhance developer productivity through intelligent code completion, project understanding, and automated task execution. The JetBrains plugin integration brings agentic coding features directly into IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, Android Studio, and other JetBrains environments, enabling developers to leverage advanced AI models without leaving their familiar development environment.
As AI coding assistants proliferate across the development landscape, Qoder positions itself as a solution emphasizing deep project context understanding and agentic workflows—capabilities designed to move beyond simple autocomplete suggestions toward comprehensive multi-step task automation. The platform supports multiple advanced AI models and aims to understand not just code syntax but architectural relationships, framework-specific patterns, and project structure.
Key Features
Qoder provides several core capabilities through its JetBrains plugin:
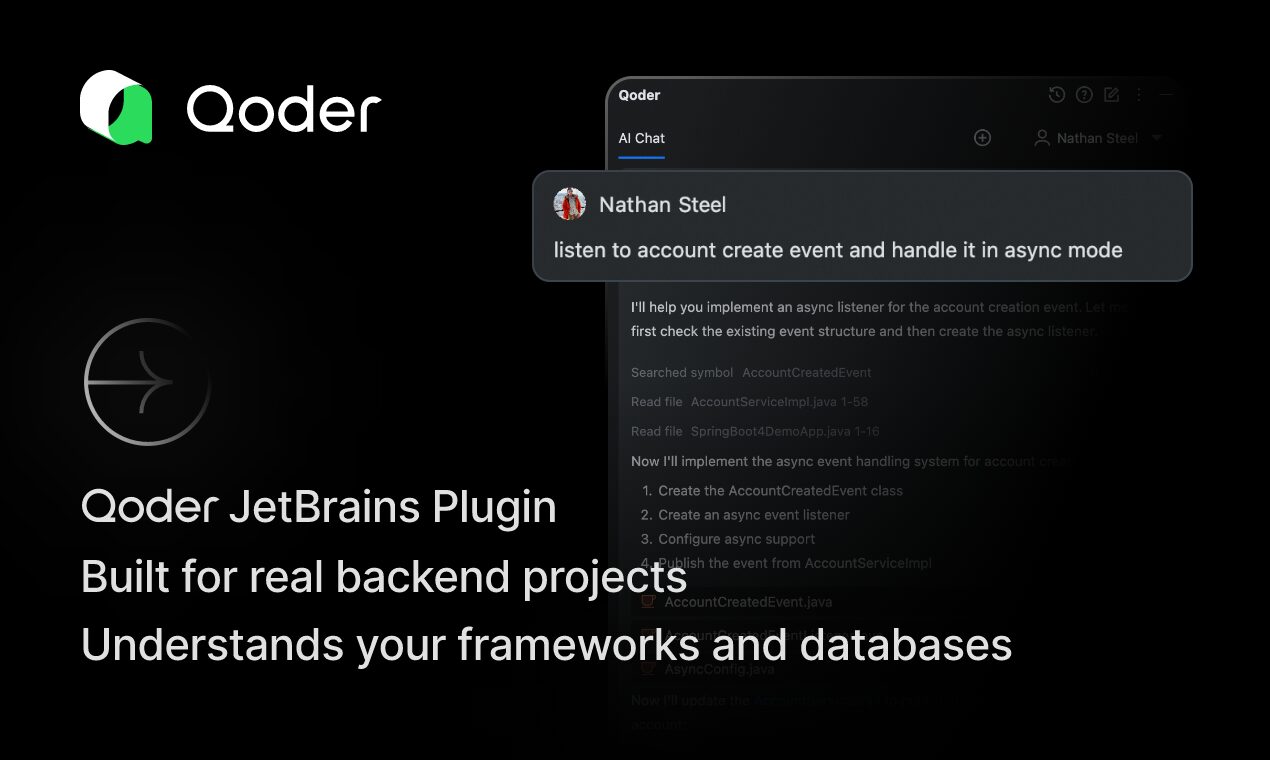
AI Chat Interface: The central hub for interacting with Qoder features two distinct operational modes. Ask mode functions as a conversational assistant where developers pose questions about code, request explanations, or seek guidance on implementation approaches. Agent mode enables delegating complete tasks to autonomous AI execution, where the system plans, executes, and verifies multi-step changes across the codebase.
Intelligent Code Completion: Context-aware code suggestions draw on project-wide understanding rather than limiting analysis to currently open files. The system provides completion for single lines, complete functions, and multi-line code blocks, adapting suggestions based on coding patterns, framework conventions, and existing project structure.
Project Indexing and Context: Qoder builds comprehensive models of project architecture by indexing code files, analyzing dependencies, and mapping relationships between components. This indexing enables the AI to understand how changes in one module affect others, supporting more intelligent suggestions and reducing the risk of breaking modifications.
Real-Time Error Detection: The system identifies potential bugs, syntax errors, and code quality issues during development, providing immediate feedback before compilation or runtime testing. Error explanations help developers understand root causes rather than merely flagging problems.
Code Optimization Suggestions: Beyond identifying errors, Qoder proactively recommends performance improvements, refactoring opportunities, adherence to best practices, and more maintainable code patterns based on industry standards and project-specific conventions.
Multi-Language Support: The platform accommodates multiple programming languages, enabling polyglot development teams to benefit from consistent AI assistance across different technology stacks within the same project.
Multi-Step Task Automation: Agentic workflows allow developers to describe high-level objectives in natural language, with Qoder planning and executing the necessary code changes, file modifications, and configuration updates to accomplish the goal. This automation extends beyond simple code generation to coordinated modifications across multiple files and project layers.
How It Works
Qoder’s operation follows an architecture designed to balance comprehensive context with responsive performance:
Upon installing the Qoder plugin in a JetBrains IDE, developers activate the service which begins initial project indexing. This indexing process analyzes source code files, parses syntax trees, examines project structure and dependencies, identifies framework-specific patterns (such as Spring configuration in Java projects), and builds a searchable knowledge base of the codebase.
The indexing depth depends on project size and complexity, with large codebases requiring more initial processing time. Once complete, the index enables contextual AI features throughout the development workflow.
Developers interact with Qoder primarily through the integrated chat panel accessible within the IDE sidebar or via keyboard shortcuts. In Ask mode, users pose questions like “How does the authentication flow work in this application?” or “What’s the best way to implement caching for this service?” Qoder analyzes the question, searches relevant code sections using semantic understanding, and generates responses grounded in actual project implementation rather than generic programming advice.
Agent mode enables more ambitious delegation. A developer might request “Add a new REST endpoint to the User service that returns active accounts with pagination support.” Qoder’s agentic system then plans the required steps, potentially including creating new method signatures in service classes, implementing business logic with appropriate error handling, adding corresponding controller endpoints with proper annotations, updating data access layers to support pagination queries, and generating unit tests for the new functionality.
Before applying changes, Qoder presents a preview allowing developers to review proposed modifications file-by-file. After approval, the plugin applies changes, runs code inspections, and may execute tests to verify functionality.
Throughout active coding, inline completions suggest next steps based on current context. The completion engine considers surrounding code, project patterns, imported dependencies, and developer coding style to generate relevant suggestions.
Use Cases
Qoder serves multiple development scenarios and team configurations:
Large-Scale Enterprise Applications: Development teams maintaining monolithic codebases with hundreds of thousands of lines across numerous modules benefit from Qoder’s architectural understanding. When implementing new features that touch multiple layers—database schema, data access objects, business logic services, API controllers, and frontend integration—Qoder’s ability to understand cross-layer dependencies helps ensure consistent implementation without inadvertently breaking existing functionality.
Framework-Specific Development: Java developers building Spring-based microservices can leverage Qoder’s understanding of Spring conventions including dependency injection patterns, bean lifecycle management, annotation semantics, and configuration hierarchies. This framework awareness enables more intelligent suggestions that align with established Spring best practices rather than generic Java patterns.
Onboarding and Knowledge Transfer: New team members joining projects with complex or poorly documented architectures use Qoder to accelerate learning. Rather than manually tracing execution flows through dozens of files, developers ask Qoder to explain how specific features work, generating narrative descriptions with code references that clarify implementation approaches.
Refactoring and Technical Debt Reduction: When modernizing legacy code, migrating frameworks, or implementing architectural improvements, Qoder’s multi-file awareness helps identify all locations requiring updates. A request like “Refactor all DAO classes to use the new connection pool” can trigger coordinated changes across the data access layer with consistency checks.
Test Generation and Quality Assurance: Developers request automated test creation for specific methods, classes, or features. Qoder generates unit tests with appropriate mocking, edge case coverage, and assertion patterns based on the code under test and existing test conventions in the project.
Boilerplate Elimination: Repetitive coding tasks including CRUD operation implementation, DTO creation, API endpoint scaffolding, and configuration file generation can be delegated to Qoder’s automation, freeing developers to focus on complex business logic requiring human creativity and domain expertise.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
Qoder offers several potential benefits for JetBrains users:
The deep IDE integration provides a native-feeling experience compared to external AI tools requiring context switching between applications. Working entirely within IntelliJ, PyCharm, or other JetBrains environments maintains development flow and leverages the IDE’s existing project knowledge, version control integration, and debugging capabilities.
Project-wide context awareness differentiates Qoder from code completion tools limited to currently open files or narrow context windows. Understanding how components interact across the entire codebase enables more intelligent suggestions that account for architectural constraints and existing patterns.
Agentic task execution represents an evolution beyond traditional autocomplete, enabling developers to delegate complete feature implementation or refactoring tasks rather than generating code snippet-by-snippet. This higher-level automation can significantly accelerate development velocity for well-defined tasks.
Multi-language and framework support accommodates polyglot development teams and microservice architectures where different services employ different technology stacks. A single AI assistant understanding Java, Python, JavaScript, and other languages simplifies tooling compared to language-specific alternatives.
Disadvantages
Qoder also faces several limitations and considerations:
Initial indexing overhead for large projects may require significant time and computing resources. Codebases with hundreds of thousands of lines or extensive dependency chains demand thorough analysis before optimal AI assistance becomes available. This setup cost affects first-time users and projects with frequent structural changes.
The quality and accuracy of AI suggestions depend heavily on project structure and code quality. Poorly organized codebases with inconsistent patterns, minimal documentation, or antipattern prevalence may receive less reliable recommendations. Well-architected projects with clear conventions benefit more from context-aware assistance.
As a relatively new entrant, Qoder lacks the extensive user community, third-party integrations, and proven track record of established alternatives like GitHub Copilot or JetBrains’ native AI Assistant. Early adopters may encounter bugs, incomplete features, or gaps in documentation that mature platforms have addressed.
Dependency on cloud-based AI models raises considerations about latency, internet connectivity requirements, code privacy, and data transmission to external servers. Organizations with strict data sovereignty requirements or air-gapped development environments may face constraints.
The effectiveness of agentic features depends on clear task specification and well-bounded problems. Ambiguous requests or tasks requiring deep domain knowledge may produce suboptimal results requiring significant developer correction, potentially negating time savings.
How Does It Compare?
Qoder competes in the increasingly crowded AI coding assistant market, differentiated primarily by its agentic capabilities and project-wide context emphasis:
Native JetBrains Solutions
JetBrains AI Assistant: The official AI assistant built directly into JetBrains IDEs with comprehensive integration across IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, WebStorm, Rider, and all major JetBrains products. Provides AI chat with project context, advanced code completion powered by Mellum (JetBrains’ proprietary LLM), intelligent refactoring suggestions, test and documentation generation, and error explanation. Supports multiple AI model providers including GPT-4.5, GPT-o1, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.5 models.
JetBrains AI Assistant excels in native IDE integration, leveraging JetBrains’ deep understanding of code structure through Abstract Syntax Trees and Program Structure Interface analysis. The hybrid model approach combines cloud-based and local processing options. Pricing starts at \$10/month individual or \$100/year as an add-on to JetBrains subscriptions.
Compared to Qoder, JetBrains AI Assistant offers proven reliability backed by JetBrains’ established reputation, seamless integration without third-party plugin concerns, and comprehensive language support across JetBrains’ entire IDE portfolio. Qoder may differentiate through specialized agentic workflows, specific framework understanding (particularly for Spring), or alternative AI model options, though direct feature-for-feature comparisons require hands-on evaluation.
Junie Agent: JetBrains’ groundbreaking autonomous coding agent introduced in 2025, representing the company’s vision for agentic AI development. Junie brings autonomous task delegation and execution natively into JetBrains IDEs with multi-step planning, code quality verification, test generation, and style guideline adaptation. Achieves 53.6% success rate on SWEBench Verified benchmark.
Available in IntelliJ Ultimate and PyCharm Pro, Junie represents JetBrains’ direct entry into autonomous agent territory. Compared to Qoder’s agentic features, Junie benefits from native implementation by the IDE vendor with potential deeper integration and optimization. Users choosing between Qoder and Junie should evaluate specific task success rates, workflow preferences, and ecosystem commitment.
Established Third-Party Assistants
GitHub Copilot: The market-leading AI coding assistant with massive adoption, extensive language support, and proven reliability since launching the category. Provides code completion, chat interface, pull request assistance, test generation, and documentation creation. Supports multiple models including GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini through multi-model selection.
Copilot offers unmatched ecosystem integration with GitHub workflows, enterprise security controls, and cross-editor compatibility beyond JetBrains (VS Code, Visual Studio, Neovim). Individual pricing at \$10/month, team at \$19/user/month, enterprise with custom pricing.
Compared to Qoder, Copilot provides broader market validation and extensive user community but operates primarily on token-window basis rather than deep architectural understanding. Copilot excels at local code completion and function generation; Qoder aims for project-wide context and multi-file agentic workflows. Organizations already invested in GitHub ecosystems may find Copilot’s integration advantages compelling.
Codeium: Fast-growing AI assistant offering exceptional performance with sub-150ms response times, 70+ language support, repository-wide context understanding, and Cascade agent for automated workflows. Provides generous free tier alongside paid subscriptions.
Codeium emphasizes speed, privacy-focused development options, and enterprise deployment capabilities including self-hosting. Individual pricing free with optional Pro upgrades; enterprise with custom deployment.
Compared to Qoder, Codeium offers proven performance benchmarks and established free tier attracting individual developers and small teams. Both emphasize context-aware suggestions and agent capabilities. Users should evaluate based on specific model preferences, IDE integration quality, and framework-specific understanding needs.
AI-Native Development Environments
Cursor IDE: A complete VS Code fork built from the ground up for AI-first development. Offers multi-model support with flexible bring-your-own-key options, “Max Mode” with 1 million token context windows, and deeply integrated AI throughout the editing experience. Pricing at \$20/month provides full access.
Cursor requires adopting a new IDE entirely, representing significant workflow investment but potentially maximum AI integration. Compared to Qoder’s plugin approach within existing JetBrains environments, Cursor demands greater commitment but may offer more seamless AI-native experiences for developers willing to migrate.
Windsurf: Modern AI coding environment with “Cascade” collaborative editing where developers and AI work simultaneously on code. Emphasizes real-time collaboration between human and AI rather than sequential suggestion-and-acceptance workflows.
Windsurf targets developers seeking fundamentally different interaction patterns compared to traditional coding augmented by AI suggestions. Qoder maintains familiar JetBrains workflows with AI enhancement; Windsurf reimagines the development experience.
Specialist Alternatives
Onuro: Revolutionary AI coding platform emphasizing voice-controlled development with multimodal AI processing (video, audio, design mockups, screenshots), autonomous actions, and dynamic model switching based on task complexity. Represents cutting-edge interaction paradigms beyond text-based prompting.
Onuro appeals to developers seeking next-generation interfaces and maximum interaction flexibility. Compared to Qoder’s text-based chat and agent modes, Onuro explores multimodal futures. Early adopters and accessibility-focused users may prefer Onuro’s voice control; traditional developers may find Qoder’s conventional interfaces more immediately productive.
Tabnine: Privacy-focused AI assistant emphasizing on-premises deployment, local model options, and enterprise security controls. Provides code completion and chat across multiple IDEs with particular emphasis on data sovereignty.
Organizations with strict data protection requirements may prefer Tabnine’s local deployment over cloud-dependent alternatives. Qoder’s cloud-based approach provides potentially stronger models and faster updates at the cost of external data transmission.
Key Differentiators
Qoder distinguishes itself through several positioning choices:
The JetBrains plugin approach provides AI capabilities within established developer workflows rather than requiring IDE migration. This lowers adoption friction compared to standalone AI-native IDEs while potentially offering deeper integration than generic browser-based coding assistants.
Emphasis on agentic multi-step automation targets developers seeking higher-level delegation rather than line-by-line suggestions. While many assistants now offer agent modes, Qoder’s architecture design prioritizes autonomous task execution.
Project-wide architectural understanding through comprehensive indexing aims to address limitations of token-window-based assistants that struggle with large codebases. The effectiveness of this approach compared to alternatives’ context management strategies requires hands-on evaluation.
However, Qoder enters a mature, competitive market where established players have significant advantages in user base, ecosystem integration, proven reliability, and community resources. Success depends on demonstrating meaningful superiority in specific use cases, frameworks, or workflows rather than merely matching feature checklists.
Pricing and Availability
Qoder operates on a freemium model with tiered access:
The platform offers an introductory preview period providing 2,000 requests, where each AI interaction (reading, editing, creating) counts as one request. Typical agent-driven tasks consume 300-400 requests, translating to approximately several hours of active usage during evaluation.
Paid subscription tiers provide expanded request allocations, though specific pricing details for ongoing use have not been widely published. Prospective users should consult Qoder’s official website or contact the team for current pricing structures.
The Qoder JetBrains plugin is available through the JetBrains Plugin Marketplace for installation in IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, Android Studio, WebStorm, and other JetBrains IDEs. The plugin requires internet connectivity for AI model access and cloud-based processing.
Qoder also offers a standalone IDE product separate from the JetBrains plugin, providing an alternative for developers not committed to the JetBrains ecosystem.
Final Thoughts
Qoder represents an emerging entrant in the highly competitive AI coding assistant market, offering agentic capabilities and project-wide context understanding tailored to JetBrains IDE users. For developers working within IntelliJ, PyCharm, or other JetBrains environments who seek AI assistance beyond simple autocomplete, Qoder provides an alternative worth evaluating—particularly for large-scale backend applications, framework-specific development (especially Java/Spring ecosystems), and teams interested in experimenting with autonomous agent workflows.
However, prospective users should approach Qoder with realistic expectations informed by the competitive landscape. Established alternatives like JetBrains’ own AI Assistant and Junie Agent offer native integration backed by the IDE vendor with proven reliability. GitHub Copilot provides market-leading adoption and ecosystem integration. Cursor and Windsurf represent AI-native environments for developers willing to migrate entirely.
Qoder’s success depends on demonstrating clear advantages in specific domains—whether through superior Spring framework understanding, more effective agentic task execution, better architectural comprehension for massive codebases, or other differentiated capabilities that justify adoption over established alternatives.
The platform’s relatively recent emergence means early adopters should anticipate ongoing development, potential rough edges, and evolving feature sets as the product matures. Organizations with enterprise requirements should carefully evaluate data privacy implications, support availability, long-term viability, and integration with existing development toolchains before committing to Qoder for critical workflows.
For individual developers and small teams comfortable experimenting with emerging tools, Qoder’s free preview period provides a risk-free evaluation opportunity. Testing the platform on representative projects with realistic workflows will reveal whether its architectural understanding and agentic capabilities deliver meaningful productivity improvements over existing AI assistants already in use.
Ultimately, the proliferation of capable AI coding assistants means developers enjoy increasing choice. Rather than declaring universal winners, the optimal selection depends on specific contexts: IDE preferences, programming languages, framework ecosystems, team workflows, budget constraints, and data governance requirements. Qoder occupies a niche serving JetBrains users seeking agentic automation with project-wide context, competing against both native JetBrains solutions and third-party alternatives. Hands-on evaluation remains the most reliable method for determining fit.