Table of Contents
Overview
Building complex software with AI coding assistants often hits what developers call the “linearity barrier”—as context windows fill and projects grow, even advanced AI models begin to degrade, producing hallucinations and losing coherence. Dropstone introduces a fundamentally different approach to AI-assisted development through its proprietary D3 Engine and Recursive Swarm Architecture. Rather than relying on sequential token prediction like traditional coding assistants, Dropstone deploys thousands of autonomous agents that explore divergent solution paths simultaneously, pruning error-prone branches before committing code. Built as a fully compatible Visual Studio Code fork, this agentic IDE maintains the familiar developer experience while introducing capabilities designed for long-horizon reasoning and architectural planning.
Key Features
- Recursive Swarm Architecture: Dropstone instantiates up to 10,000 ephemeral Scout agents utilizing optimized Small Language Models to explore divergent solution trees in parallel, testing low-probability strategies and identifying high-confidence solutions through distributed computation.
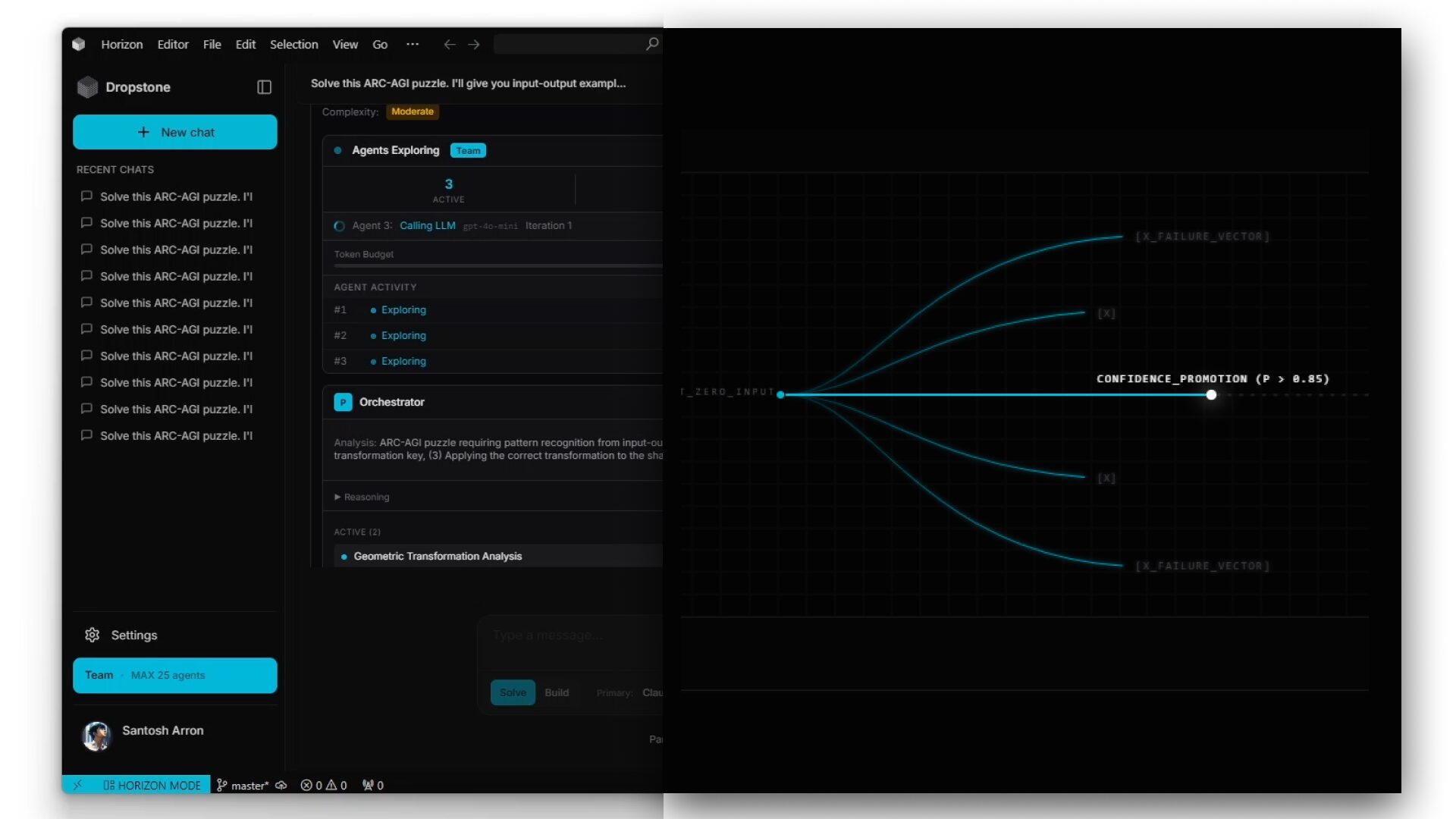
- Horizon Mode: This advanced feature enables extended inference horizons exceeding 24 hours by decoupling active workspace from latent history, maintaining causal logic across millions of tokens without the degradation typical of sliding-window models used in conventional assistants.
- D3 Engine (Dynamic Distillation \& Deployment): The proprietary runtime separates reasoning time from token generation, intelligently routing tasks between Scout Swarms for exploration and Frontier Models for high-fidelity synthesis, with deterministic state management.
- Hallucination Defense: Through Silent Flash protocol and peer agent verification, Dropstone achieved a 1.4% hallucination rate on the Deep-Sec benchmark compared to 14.2% for zero-shot approaches, actively pruning failed branches in real-time to prevent hallucination cascades.
- Local and Cloud Model Support: Unlimited access to Ollama models for local processing with complete privacy control, plus integration with Claude, GPT-4o, GPT-5, and O3-mini for cloud-based reasoning tasks.
How It Works
Dropstone operates on a paradigm fundamentally different from linear token prediction. When you assign a coding task, the D3 Runtime spawns thousands of autonomous Scout agents that explore multiple solution paths concurrently rather than committing to a single trajectory. These agents utilize a shared vector-space layer to propagate “Negative Knowledge”—information about failed approaches—allowing the entire swarm to prune invalid logic branches in real-time. Solutions that achieve high confidence thresholds are promoted to Frontier Models for refinement before being presented to you.
The system maintains separation between active workspace and latent history, enabling context retention across extended development sessions without degradation. As you work, Dropstone serializes your corrections into a local vector layer, creating a persistent learning system that prevents recurring logic errors. This recursive approach allows the IDE to handle increasing architectural complexity while maintaining 60fps UI responsiveness by running intensive computation on detached worker threads.
Use Cases
- Large-Scale Codebase Refactoring: Deploy autonomous agents to analyze architectural debt at depths exceeding traditional language models, executing complex refactoring operations across multiple files while maintaining structural integrity.
- Autonomous Feature Development: Assign complete programming objectives to agents for independent execution, supporting extended workflow automation through MCP Server integration and Computer Use API.
- Architectural Planning and System Design: Leverage Horizon Mode for long-term planning that maintains coherent logic across extended inference chains, visualizing complex structures before implementation.
- Complex Debugging: Identify and resolve race conditions, concurrency issues, and subtle logical flaws through parallel simulation of execution paths.
- Cross-Team Collaboration: Synchronize immutable reasoning states across team members using Merkle-DAG architecture, propagating decision history and failure patterns to prevent redundant problem-solving.
Pros \& Cons
Advantages
- Significantly Reduced Hallucination Rate: Achieves 1.4% hallucination rate through consensus-based validation, dramatically lower than single-path generation approaches.
- Extended Context Retention: Virtual context window spanning millions of tokens through recursive definition search and associative memory, surpassing traditional context window limitations.
- Handles Complex Architectural Logic: Simulation-based approach excels at multi-step reasoning and architectural planning where predictive models struggle with context degradation.
- VS Code Compatibility: Zero learning curve for developers familiar with VS Code, eliminating adoption friction while providing advanced autonomous capabilities.
Disadvantages
- Higher Computational Requirements: Swarm simulation demands more processing power than simple autocomplete, potentially introducing latency for trivial single-line edits.
- Complexity Learning Curve: Understanding and effectively utilizing features like Horizon Mode, Agent Mode, and swarm mechanics requires investment compared to straightforward code completion tools.
- Subscription Cost: Professional features require paid plans starting at \$15 monthly, which may be prohibitive for hobbyists or those needing only basic assistance.
How Does It Compare?
The AI coding assistant landscape in 2026 offers diverse approaches, from simple autocomplete to full autonomous agents. Here’s how Dropstone positions itself:
GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot remains the industry standard for AI code completion, powered by OpenAI’s Codex and GPT-4 models. Copilot excels at inline suggestions, learning coding style, and providing natural autocomplete as you type. It integrates natively into VS Code, JetBrains IDEs, Vim, and Neovim with Copilot Chat for explanations. At \$10 per month for individuals and \$4 per user monthly for teams, it offers the most affordable entry point. However, Copilot operates on predictive token generation—guessing the next sequence based on context. Dropstone differs fundamentally by using agentic simulation to plan, validate, and prune solutions before generation, offering deeper architectural awareness at higher computational cost. For developers needing basic autocomplete and occasional explanations, Copilot provides better value. For complex refactoring and architectural planning, Dropstone’s swarm approach offers capabilities Copilot cannot match.
Cursor
Cursor has redefined AI-first editing with its conversational interface, codebase-wide context, and natural language prompts for writing, editing, and refactoring. At \$20 monthly, Cursor provides an excellent balance of power and usability with emphasis on developer control over what AI touches. Both Cursor and Dropstone offer sophisticated multi-file editing, but their philosophies differ. Cursor focuses on conversational AI assistance within an intuitive editor interface, making it accessible for rapid iteration. Dropstone emphasizes background swarm simulation and autonomous agent execution for long-horizon tasks. Cursor works better for developers who want responsive, chat-driven assistance. Dropstone targets those tackling complex architectural challenges requiring extended reasoning beyond typical context windows.
Windsurf
Windsurf is an AI-native code editor built by Codeium featuring Cascade, an agentic system that understands entire projects before making suggestions. At \$15 monthly (same as Dropstone Pro), Windsurf offers Supercomplete for intent prediction, real-time lint fixing, MCP support for tool integration, and terminal command execution. Windsurf and Dropstone share similar pricing and autonomous capabilities. Windsurf’s Cascade applies AI-generated changes in real-time to local files for immediate preview, emphasizing seamless flow. Dropstone’s recursive swarm architecture prioritizes error prevention through parallel simulation before code commitment. Windsurf may feel more immediate and responsive for iterative development, while Dropstone’s approach suits projects where correctness and architectural integrity outweigh speed.
Cline (VS Code Extension)
Cline is an autonomous coding agent extension for VS Code supporting Claude 3.7 Sonnet, DeepSeek, and other models through OpenRouter, Anthropic, OpenAI, and local providers. It creates and edits files, executes terminal commands, uses browser capabilities via Computer Use, and integrates Model Context Protocol for custom tools. Cline is free and open-source with API costs only. For budget-conscious developers comfortable with pay-per-use API pricing, Cline offers remarkable flexibility. Dropstone provides a more integrated experience with proprietary swarm architecture and learning systems, but requires subscription commitment. Cline suits developers who want granular control over model selection and API costs, while Dropstone appeals to those seeking a complete autonomous development environment with advanced error prevention.
Bolt
Bolt is a browser-based prompt-to-app generator that creates full-stack applications from natural language descriptions. It generates React with Tailwind CSS frontends, Node.js with Express backends, and PostgreSQL databases with Prisma, offering visual editing and one-click Vercel deployment. Bolt targets rapid prototyping and non-technical builders creating complete applications quickly. Dropstone focuses on professional development workflows within existing codebases. Bolt excels at scaffolding new projects from scratch for immediate deployment, while Dropstone provides deep codebase analysis, refactoring, and architectural planning for complex existing projects. These tools serve different markets—Bolt for rapid prototyping and MVPs, Dropstone for serious software engineering.
Aider
Aider is a terminal-based AI pair programming tool with exceptional Git integration, automatically committing changes with meaningful messages. Supporting Claude 3.7 Sonnet, DeepSeek, GPT-4o, and local models via Ollama, Aider offers architect mode for planning, ask mode for consultation, and multi-file editing. It works with popular languages and costs only API fees with no subscription. Aider appeals to terminal-native developers who prefer command-line workflows and want explicit control over every change. Dropstone provides a graphical IDE experience with autonomous agents working in background. Aider’s transparency and Git-centric approach suits developers who want to review every modification, while Dropstone’s swarm simulation targets those willing to delegate more autonomy for complex problem-solving.
Void
Void is an open-source, privacy-focused AI code editor forked from VS Code, backed by Y Combinator. It supports local models via Ollama and LM Studio or direct API connections to Claude, GPT, and Gemini, ensuring AI processing happens locally or through direct calls without third-party middlemen. Void offers inline editing, contextual chat, file system awareness, and the ability to view and edit underlying prompts. As an open-source alternative, Void provides complete control and transparency at no subscription cost beyond API usage. Dropstone offers proprietary swarm architecture and learning systems not available in open-source alternatives. Void suits privacy-conscious developers and those who want to customize their tools extensively, while Dropstone provides turnkey advanced capabilities with professional support.
Amazon Q Developer
Amazon Q Developer evolved from CodeWhisperer, integrating with JetBrains IDEs and VS Code with unique CLI agent capabilities. It handles large projects with multi-file changes through dev agents, generates documentation and diagrams with doc agents, and provides automated code review. Optimized for AWS development with security scanning built-in, Q Developer offers a free tier for individuals and \$19 monthly for Pro features. For teams heavily invested in AWS ecosystems, Q Developer provides native integration advantages. Dropstone offers broader architectural reasoning and swarm-based error prevention across any technology stack. Q Developer excels within AWS workflows, while Dropstone provides platform-agnostic advanced reasoning.
Tabnine
Tabnine prioritizes privacy and speed with context-aware completions, refactoring support, real-time linting, and automatic documentation. It integrates with all major IDEs and offers team learning from organizational codebases while maintaining code privacy. Starting at \$12 monthly for Pro plans with free tier available, Tabnine balances privacy, performance, and cost. Compared to Dropstone’s swarm simulation, Tabnine focuses on fast, privacy-preserving autocomplete. Tabnine suits organizations with strict privacy requirements needing reliable code completion, while Dropstone targets complex architectural challenges requiring extended reasoning.
Replit Ghostwriter
Replit Ghostwriter operates within Replit’s browser-based collaborative IDE, offering real-time code completion, transformation, and intelligent open-source code search. At \$20 monthly for Core plans with free tier available, Ghostwriter emphasizes accessibility and collaborative coding in cloud environments. Ghostwriter excels for educational settings, pair programming, and browser-based development. Dropstone provides deeper local codebase integration and autonomous agent capabilities for professional development. Choose Ghostwriter for collaborative, browser-based workflows and Replit for learning environments; choose Dropstone for complex local development projects.
Final Thoughts
Dropstone represents a significant architectural departure from mainstream AI coding assistants. By replacing linear token prediction with recursive swarm simulation, it addresses fundamental limitations that plague conventional approaches as context windows saturate and projects grow complex. The 1.4% hallucination rate achieved through consensus-based validation demonstrates the potential of this multi-agent approach for mission-critical code generation.
The tool’s strength lies in scenarios where correctness and architectural integrity matter more than immediate responsiveness. Large-scale refactoring, complex system design, and long-horizon planning benefit from Dropstone’s ability to simulate and validate thousands of potential solutions before committing. The learning system that serializes corrections into persistent memory offers genuine evolution beyond session-based context.
However, this power comes with tradeoffs. The computational overhead of swarm simulation may feel excessive for simple autocomplete tasks where tools like GitHub Copilot or Tabnine excel. The \$15 monthly Pro subscription positions Dropstone at the premium end of individual developer tools, matching Windsurf but exceeding Copilot. The interface complexity and conceptual framework require investment to master compared to straightforward predictive assistants.
Dropstone’s VS Code compatibility provides crucial adoption advantages, eliminating the friction of learning entirely new interfaces while introducing advanced capabilities beneath familiar surfaces. The support for both unlimited local Ollama models and premium cloud models offers flexibility between privacy and performance.
For senior engineers, technical leads, and architects working on complex codebases where subtle logical errors carry significant consequences, Dropstone merits serious consideration. The recursive swarm approach delivers capabilities unavailable in simpler tools. For developers primarily needing autocomplete, basic refactoring, or working on straightforward projects, the computational overhead and subscription cost may outweigh benefits.
The competitive landscape includes strong alternatives across different priorities. Cursor provides more intuitive conversational interaction. Windsurf offers comparable autonomous capabilities with different architectural trade-offs. Cline and Aider deliver powerful functionality at lower cost for developers comfortable with their respective interfaces. Void provides open-source transparency and privacy control.
Dropstone positions itself for developers pushing boundaries of AI-assisted development who value architectural correctness and are willing to invest in learning a more sophisticated tool. As the technology matures and computational efficiency improves, the swarm-based approach may represent the future direction of AI coding assistance—one where tools genuinely reason about code rather than merely predicting tokens. For forward-thinking engineering teams building complex systems, Dropstone offers a compelling glimpse into that future, available today for those ready to explore beyond conventional coding assistants.