Table of Contents
Overview
The field of vision-language AI continues its rapid advancement, with models increasingly capable of understanding and reasoning about visual content. Molmo 2 represents the Allen Institute for AI’s latest contribution to this space, delivering a suite of open-source multimodal models that excel at video and multi-image understanding. Released in December 2025, Molmo 2 distinguishes itself through its focus on precise grounding capabilities—providing pixel coordinates and timestamps to justify its answers rather than simply generating text responses. Built on foundations including Qwen 3 and AI2’s own OLMo language models, these models are released under Apache 2.0 licensing with open weights, training data, and code, enabling researchers and developers to study, modify, and deploy them for diverse applications.
Key Features
Molmo 2 delivers several advanced capabilities designed for sophisticated visual understanding:
- Video Grounding and Temporal Localization: Molmo 2 analyzes video content to identify specific objects, actions, and events, returning both pixel coordinates and timestamps that precisely locate where and when things occur within video sequences. This enables the model to provide verifiable evidence for its answers rather than relying solely on text generation.
- Multi-Image and Multi-Frame Analysis: The system processes multiple images simultaneously or analyzes video as sequences of frames, maintaining coherence across visual inputs. This supports tasks like comparing multiple images, tracking objects across video frames, and understanding temporal relationships between visual events.
- Open Weights and Training Transparency: All model weights, newly introduced training datasets including video pointing and tracking data, and comprehensive data recipes are publicly released. This transparency enables end-to-end research, customization, and community-driven improvements under the permissive Apache 2.0 license.
- Multiple Model Variants: Molmo 2 offers three distinct versions optimized for different use cases—an 8B parameter model built on Qwen 3 for maximum performance, a 4B parameter efficiency-focused variant also using Qwen 3, and a 7B parameter Molmo 2-O version based entirely on OLMo providing full stack transparency from vision encoder through language model.
- Counting-by-Pointing Capability: Rather than simply stating numbers, Molmo 2 identifies and marks each instance it counts within images or videos, providing spatial evidence for quantitative answers and maintaining persistent object IDs across frames even through occlusions.
How It Works
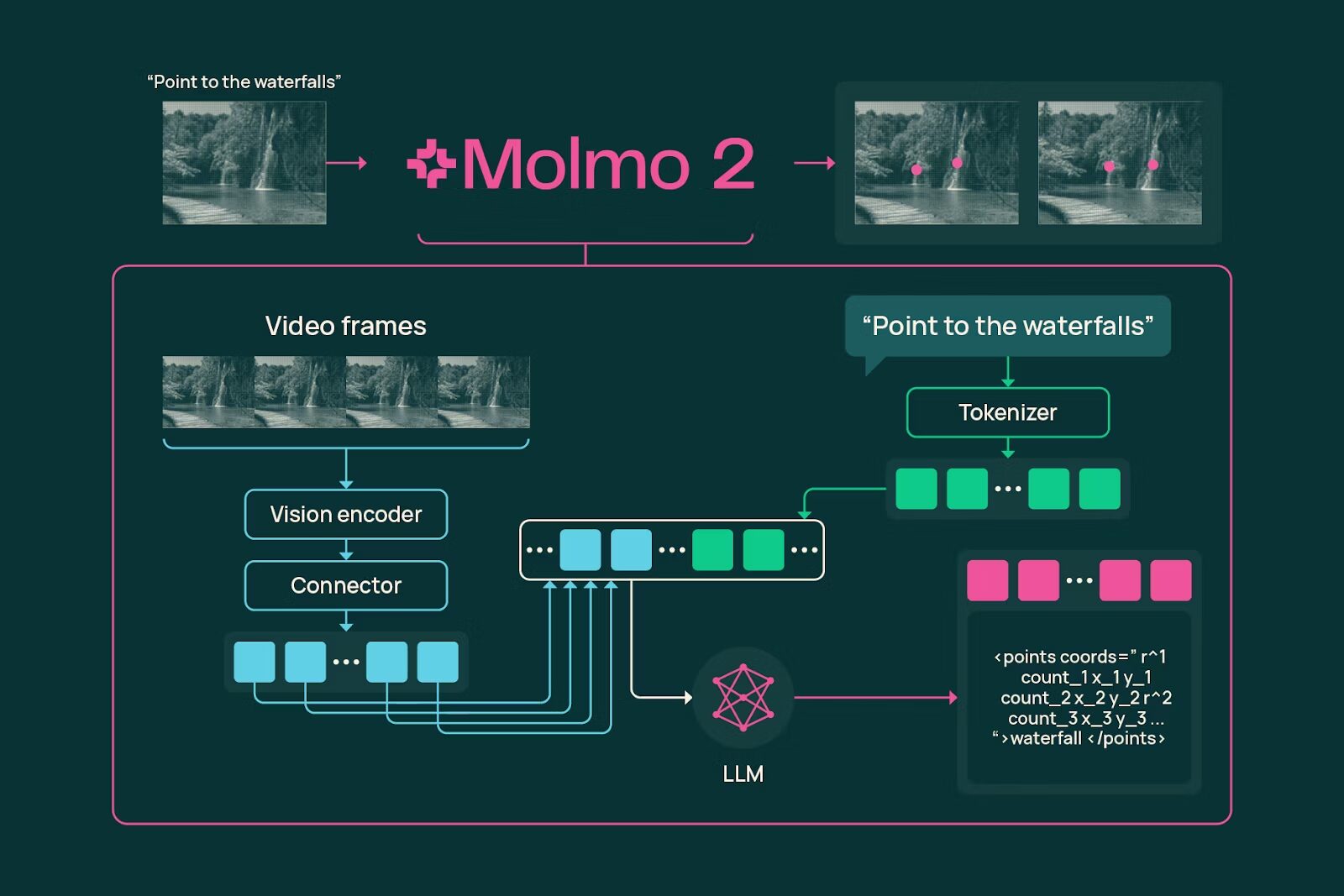
Molmo 2 employs a three-component architecture optimized for multimodal understanding. The system begins with a SigLIP-2 vision encoder that processes images or video frames into visual token representations. These vision tokens are enriched with temporal information through a lightweight connector module that interleaves visual features with timestamps, frame indices, and positional encodings, enabling the model to reason jointly across space, time, and language.
The enriched visual tokens feed into either Qwen 3 or OLMo language model backbones depending on the variant. Unlike traditional vision-language models that treat frames as independent images, Molmo 2 uses bidirectional attention between visual tokens, allowing information to flow across frames and images. This cross-frame connectivity improves the model’s ability to track objects through occlusions, understand temporal dynamics, and maintain coherent reasoning across extended sequences.
During training, Molmo 2 employs novel token-weighting approaches to learn tasks more evenly, sequence packing and message-tree scheduling to accelerate training efficiency, and grounding supervision that teaches the model to associate textual descriptions with precise spatial and temporal coordinates. This training strategy enables Molmo 2 to not only describe what it sees but pinpoint exactly where and when events occur.
Use Cases
Molmo 2’s grounding capabilities enable applications requiring precise visual localization:
- Video Content Analysis and Search: Enable semantic search within video libraries by having Molmo 2 identify and timestamp specific events, objects, or actions, creating searchable metadata for video archives without manual annotation.
- Multi-Object Tracking with Persistent IDs: Track multiple entities across video sequences while maintaining stable identities even through occlusions and re-entries, supporting applications in surveillance, sports analytics, and autonomous vehicle perception.
- Robotics Perception and Spatial Awareness: Provide robots with grounded visual understanding for navigation, manipulation, and environment interaction. Molmo 2 will soon integrate into AI2’s MolmoAct model for enhanced robotic spatial reasoning.
- Dense Video Captioning: Generate highly descriptive narratives for long video clips with temporal markers, enabling accessibility applications and automated documentation of visual content with verifiable grounding.
- Anomaly and Artifact Detection: Identify unusual events in video sequences or detect flaws in generated video content such as inconsistent lighting or broken object geometry, pointing to specific frames and regions where anomalies occur.
- Subtitle-Aware Video Question Answering: Combine visual evidence with in-video text like subtitles or on-screen text to answer questions that require integrating both visual and textual information sources.
Pros \& Cons
Advantages
- Superior Video Grounding Performance: Molmo 2 achieves state-of-the-art results among open multimodal models on video tracking and grounding benchmarks, outperforming both open-weight alternatives and competing with closed proprietary systems like Gemini 2.0 Flash.
- Verifiable Visual Evidence: Unlike models that only generate text answers, Molmo 2 provides pixel coordinates and timestamps as evidence, enabling users to verify where the model is looking and what visual information supports its conclusions.
- Fully Open Research Platform: Complete transparency with Apache 2.0 licensing, open weights, training data, and code enables researchers to study every component, customize the architecture, and build upon the foundation without restrictive licenses.
- Efficient Parameter Scaling: The 8B parameter Molmo 2 variant outperforms the original 72B parameter Molmo on image grounding benchmarks, demonstrating architectural improvements deliver stronger performance in more efficient packages.
Disadvantages
- Limited General Knowledge: Compared to massive general-purpose models with hundreds of billions of parameters trained on broader datasets, Molmo 2’s knowledge base remains more focused on visual understanding tasks rather than encyclopedic world knowledge.
- Video Grounding Accuracy Challenges: While leading among open models, no model including Molmo 2 yet reaches 40% accuracy on the most challenging video counting benchmarks, indicating substantial room for improvement in complex temporal reasoning.
- Specialization Trade-offs: Molmo 2 optimizes specifically for vision and video tasks with grounding capabilities. It is not designed as a general-purpose conversational AI for non-visual tasks where other models may perform better.
- Research Use Restrictions: While model weights are Apache 2.0 licensed, Molmo 2 is trained on third-party datasets subject to academic and non-commercial research use restrictions. Users must review source dataset licenses when evaluating commercial deployment suitability.
How Does It Compare?
The multimodal AI landscape in early 2026 features strong competition across proprietary and open-source models. Here’s how Molmo 2 positions itself:
GPT-4o (OpenAI)
GPT-4o delivers powerful multimodal capabilities processing text, images, audio, and video with real-time voice interaction and unified architecture. For video understanding, GPT-4o requires converting videos to 2-4 frames per second for processing through its vision capabilities. GPT-4o excels at broad multimodal reasoning, conversational AI, and general-purpose understanding across modalities. However, it operates as a closed proprietary system without transparency into training data, architecture details, or weights. Molmo 2 differentiates itself through complete open-source transparency, specialized video grounding with temporal localization returning precise coordinates and timestamps, and focus on verifiable visual evidence rather than text-only responses. For applications requiring proprietary model performance with minimal setup, GPT-4o offers superior convenience and broader capabilities. For research transparency, customization, and tasks emphasizing precise visual grounding with evidence, Molmo 2 provides capabilities GPT-4o’s closed nature cannot match.
Gemini 2.0 Flash (Google DeepMind)
Gemini 2.0 Flash offers twice the speed of Gemini 1.5 Pro while delivering enhanced multimodal understanding, supporting text, image, and video inputs with up to 1 million token context windows. Available generally since February 2025, Gemini 2.0 Flash features improved spatial understanding for accurate bounding box generation, native tool use, bidirectional streaming through the Multimodal Live API, and multimodal output generation including text, images, and speech. The model handles approximately 45-60 minutes of video content and excels at real-time applications. Gemini 2.0 Flash represents a proprietary offering with superior integration into Google’s ecosystem and broader modality support. Molmo 2 counters with complete open-source access enabling modification and research, specialized video tracking maintaining persistent object IDs across occlusions, and grounding outputs providing verifiable pixel-level evidence. Gemini 2.0 Flash suits production applications within Google Cloud requiring enterprise support and multimodal generation. Molmo 2 serves researchers, developers seeking full transparency, and applications prioritizing precise temporal and spatial grounding over breadth.
Qwen2.5-VL and Qwen3-VL (Alibaba)
Qwen-VL represents a series of open vision-language models built on Alibaba’s Qwen language model foundation. Qwen2.5-VL features large-scale pretraining up to 18T tokens, extended context windows reaching 128K tokens, improved instruction following, robust multilingual support, and capabilities including image captioning, visual question answering, and visual grounding. Qwen3-VL introduces further enhancements with dense and MoE architectures, precise object grounding using relative position coordinates supporting boxes and points, general OCR and key information extraction across languages, and improved video understanding including video OCR and long-form video analysis. Both Qwen-VL variants offer comprehensive multimodal capabilities with strong performance across standard benchmarks. Molmo 2 differentiates through deeper specialization in video temporal grounding with timestamp precision, superior multi-object tracking maintaining persistent IDs, and training transparency including open datasets specifically for video pointing and tracking. Qwen-VL models provide broader general-purpose multimodal understanding with excellent multilingual support. Molmo 2 focuses narrowly on video grounding excellence with full research transparency. Choose Qwen-VL for general multimodal applications requiring strong baseline performance. Choose Molmo 2 for tasks demanding precise video grounding with verifiable evidence.
Claude 3.7 Sonnet (Anthropic)
Claude 3.7 Sonnet delivers advanced vision capabilities alongside Anthropic’s signature strong reasoning and instruction following. The model processes images with improved speed compared to predecessor versions, supports compositional and causal reasoning on visual inputs, and now offers fine-tuning capabilities for domain-specific computer vision applications. Claude 3.7 Sonnet excels at visual question answering, image analysis for content moderation, and structured output generation from visual inputs. As a proprietary model, it provides convenient API access with strong safety features but no transparency into training or architecture. Molmo 2 offers complementary strengths through open-source availability enabling full customization, native video understanding with frame-by-frame analysis rather than single-image processing, and precise grounding with coordinates and timestamps that Claude does not natively provide. Claude 3.7 Sonnet suits production deployments requiring reliable image understanding with strong reasoning and safety features. Molmo 2 serves video-centric applications, research requiring transparency, and use cases where temporal grounding evidence is essential.
LLaVA Family (Microsoft / University of Wisconsin-Madison)
LLaVA represents a pioneering open-source multimodal model combining CLIP vision encoders with language model backbones, originally achieving GPT-4-level capabilities on visual understanding benchmarks. LLaVA-1.5 introduced enhanced two-layer MLP projection for better vision-language alignment and improved performance across image captioning, visual question answering, and conversation about visual content. The LLaVA family emphasizes cost-efficient training approaches, end-to-end multimodal training strategies, and open-source datasets advancing community research. However, LLaVA primarily focuses on single-image understanding and conversational capabilities rather than video analysis or temporal reasoning. Molmo 2 extends beyond LLaVA’s image-centric design with native video support, temporal grounding capabilities LLaVA lacks, multi-frame tracking with persistent object IDs, and specialized training for pointing and grounding tasks. LLaVA remains excellent for image-based multimodal conversations and research on vision-language alignment. Molmo 2 advances into video understanding territory with temporal localization that LLaVA’s architecture does not address.
Llama 4 Scout and Maverick (Meta AI)
Llama 4 Scout (17B active parameters, 16 experts) and Llama 4 Maverick (17B active parameters, 128 experts) represent Meta’s multimodal MoE models supporting text, vision, and reasoning across modalities. Maverick achieves performance comparable to GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash on benchmarks while using fewer active parameters through expert routing. The models feature 10-million-token context windows, operate efficiently on single H100 GPUs, and demonstrate strong combinatorial reasoning. Both provide robust general-purpose multimodal understanding though primarily oriented toward text and static image analysis. Molmo 2 specializes in video temporal understanding, offering frame-by-frame grounding and tracking that Llama 4’s architecture does not emphasize. Llama 4 models suit general multimodal applications requiring strong reasoning with efficiency. Molmo 2 targets video-specific tasks demanding temporal precision and spatial grounding evidence.
Pixtral 12B (Mistral AI)
Pixtral 12B represents Mistral’s multimodal offering combining vision understanding with language capabilities, demonstrating strong instruction following that outperforms other open-source models like Qwen2-VL 7B and LLaVa-OneVision 7B on specialized benchmarks. Mistral emphasizes conversational multimodal interaction and instruction adherence. However, Pixtral focuses primarily on image understanding rather than video analysis. Molmo 2 provides video-native capabilities with temporal grounding, multi-frame tracking, and timestamp localization that extend beyond Pixtral’s image-centric design. Pixtral suits applications requiring excellent instruction following for image tasks. Molmo 2 addresses video analysis use cases Pixtral does not target.
GLM-4.5V and GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking (Zhipu AI)
GLM-4.5V delivers flagship-level multimodal performance using MoE architecture for efficiency, while GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking provides cost-effective multimodal reasoning with visible reasoning processes. These models excel at general multimodal tasks including document understanding and visual reasoning. Molmo 2 differentiates through specialized video grounding capabilities, open training transparency, and temporal localization features the GLM models do not emphasize. GLM models serve general multimodal applications well. Molmo 2 addresses niche video grounding requirements with evidence-based outputs.
Final Thoughts
Molmo 2 represents a significant advancement in open-source video understanding, introducing capabilities that bridge the gap between descriptive vision-language models and precise computer vision systems. By combining natural language reasoning with pixel-level grounding and temporal localization, Molmo 2 enables a new class of applications requiring verifiable visual evidence rather than text-only responses.
The model’s strongest contribution lies in democratizing advanced video analysis capabilities previously limited to proprietary systems or specialized computer vision pipelines. Researchers gain complete transparency into training data, architecture, and weights under permissive Apache 2.0 licensing, enabling modifications and improvements that closed systems prohibit. The release of open video pointing and tracking datasets further accelerates community research in grounded multimodal understanding.
Performance results demonstrate Molmo 2’s leadership among open models on video tracking and grounding benchmarks, with the 8B variant outperforming its 72B predecessor through architectural improvements. The ability to maintain persistent object IDs across occlusions, provide temporal timestamps for events, and generate verifiable spatial coordinates addresses pain points in video analysis workflows where traditional models provide descriptions without evidence.
However, users should carefully evaluate Molmo 2’s specialization against their requirements. The model optimizes specifically for vision and video tasks with grounding capabilities but does not compete with general-purpose LLMs on broad knowledge tasks or extended text generation. Training data restrictions limit some commercial deployments despite Apache 2.0 model licensing. Video grounding accuracy, while leading among open models, still shows substantial improvement headroom with no model yet reaching 40% on the most challenging counting benchmarks.
The competitive landscape includes powerful alternatives serving different needs. Proprietary systems like GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash offer broader multimodal capabilities with convenient API access and enterprise support. Open alternatives like Qwen3-VL provide excellent general-purpose multimodal understanding with strong multilingual support. LLaVA excels at conversational image understanding. Each serves specific use cases effectively.
Molmo 2’s value proposition centers on transparent, customizable video understanding with verifiable grounding—a combination unavailable elsewhere at this quality level in open-source form. For robotics perception requiring spatial awareness, video content analysis demanding temporal precision, research exploring vision-language architectures, or applications where explaining visual reasoning through evidence matters, Molmo 2 delivers capabilities worth serious consideration.
Looking forward, the integration with MolmoAct for robotic navigation and the continued development of grounding capabilities suggest Molmo 2’s architecture may influence how future multimodal models balance language fluency with spatial precision. For organizations committed to open-source AI, requiring full model transparency, or building video-centric applications where traditional vision-language models fall short, Molmo 2 represents a significant step forward in making advanced video understanding accessible, transparent, and customizable.