Table of Contents
- Livedocs: Comprehensive Research Report
- 1. Executive Snapshot
- 2. Impact & Evidence
- 3. Technical Blueprint
- 4. Trust & Governance
- 5. Unique Capabilities
- 6. Adoption Pathways
- 7. Use Case Portfolio
- 8. Balanced Analysis
- 9. Transparent Pricing
- 10. Market Positioning
- 11. Leadership Profile
- 12. Community & Endorsements
- 13. Strategic Outlook
- Final Thoughts
Livedocs: Comprehensive Research Report
1. Executive Snapshot
Core Offering Overview
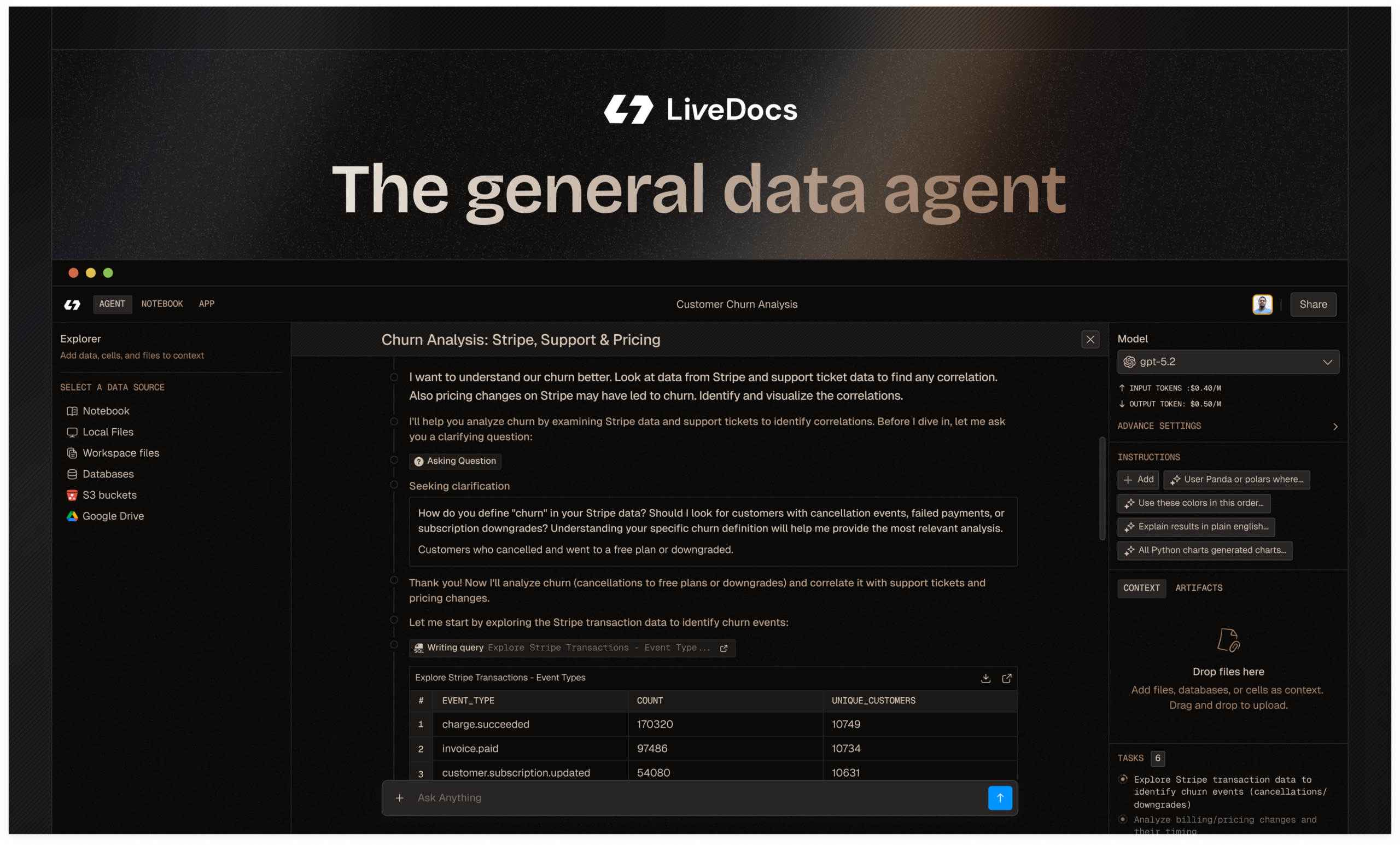
Livedocs represents a fundamental reimagining of the data notebook paradigm, positioning itself as an AI-native collaborative workspace that eliminates the friction between data exploration, analysis, and sharing. The platform synthesizes Python, SQL, and conversational AI into a single reactive environment powered by DuckDB and Polars—two of the fastest analytical engines available today. Unlike traditional notebook platforms that treat AI as an optional assistant, Livedocs embeds intelligence at its architectural core, enabling users to ask questions in natural language and receive executable code, visualizations, and actionable insights within seconds.
The platform operates on a reactive execution model structured as a Directed Acyclic Graph, where dependencies between cells are automatically tracked and parallelized where possible. This architectural decision ensures consistency across analyses while dramatically reducing execution time compared to sequential notebook environments. When a user modifies upstream data or code, Livedocs intelligently determines which downstream cells require re-execution, leveraging smart caching to avoid redundant computation and minimize warehouse query costs.
Livedocs distinguishes itself through model choice flexibility: users select from GPT-5, Claude, Gemini, and other frontier models based on specific task requirements, budget constraints, or performance needs. The AI agent maintains full context awareness of notebook contents including dataframes, tables, and visualizations, enabling sophisticated reasoning that mirrors collaboration with an experienced data scientist. This context-aware intelligence can write optimized SQL queries, generate publication-ready visualizations, diagnose data quality issues, and even suggest analytical approaches based on dataset characteristics.
The platform’s hybrid compute architecture automatically selects optimal query execution strategies. For local files including CSVs and Parquet datasets, DuckDB provides sub-second query performance without external dependencies. In-memory dataframe operations leverage Polars for maximum throughput on transformations and aggregations. When connecting to cloud warehouses like Snowflake or BigQuery, Livedocs intelligently pushes computation down to these systems, minimizing data transfer while preserving the unified notebook interface. This adaptive query resolution eliminates the manual decisions that traditionally burden data practitioners choosing between local and remote processing.
Key Achievements & Milestones
Livedocs has achieved notable recognition within the data science and analytics community despite operating as a relatively young platform. Product Hunt users awarded the service a perfect five-star rating based on five detailed reviews, highlighting seamless integration of live data sources, elimination of separate reporting workflows, and accessibility for both technical and non-technical team members. The platform’s positioning as “the general data agent” reflects its ambition to transcend traditional notebook limitations by combining analysis, automation, and application development capabilities in a single environment.
The platform’s technical foundation reflects significant engineering investment in performance optimization. Most internal components have been rewritten in Rust, delivering the speed and memory efficiency necessary for processing large datasets without degradation. This low-level optimization complements high-level usability features, creating an environment where millisecond query response times coexist with intuitive natural language interfaces. The reactive DAG architecture represents an advancement over sequential execution models popularized by Jupyter, enabling reproducibility guarantees that sequential notebooks cannot provide.
Livedocs supports full Jupyter notebook compatibility through IPYNB import and export capabilities, reducing migration friction for teams considering platform transitions. This interoperability signals technical maturity and respect for existing workflows rather than requiring users to abandon established practices. Users can begin experiments in Jupyter, migrate to Livedocs for collaboration and AI augmentation, then export results back to standard formats when necessary.
The platform’s documentation architecture demonstrates commitment to developer experience. Comprehensive guides cover execution strategies, data connections, visualization libraries, and API integration patterns. Terminal access within notebooks enables environment customization, dependency installation, and runtime inspection—capabilities absent from many managed notebook platforms that prioritize simplicity over flexibility. This balance between ease-of-use and power-user features positions Livedocs for adoption across experience levels.
Adoption Statistics
Quantitative adoption metrics remain limited in publicly accessible sources, suggesting Livedocs maintains a growth-stage profile focused on product refinement rather than mass-market penetration. The Product Hunt community’s engagement indicates meaningful traction within early-adopter segments including startups, agencies, and progressive analytics teams. User testimonials emphasize time savings measured in hours per week, consolidation of previously fragmented tool stacks, and democratization of data access across organizational functions.
A documented case study describes a startup founder building a production-ready customer churn prediction model in approximately ninety seconds using Livedocs’ AI agent. The founder lacked prior machine learning expertise yet successfully implemented feature engineering, model training with Random Forest algorithms, and risk scoring dashboards through conversational interaction with the AI. This use case exemplifies the platform’s core value proposition: compressing workflows that traditionally require specialized skills and days of effort into minutes of natural language dialogue backed by sophisticated automation.
The platform’s free tier offers unlimited documents and applications with ten dollars in monthly AI credits, eight gigabytes of RAM, and two virtual CPUs—a generous resource allocation compared to competitors that impose strict document limits or require immediate payment for basic features. This accessibility strategy suggests confidence in conversion mechanisms that monetize through expansion rather than entry friction. Teams can evaluate Livedocs extensively before financial commitment, reducing adoption risk while building product dependency through daily workflow integration.
Industry comparison positioning against established platforms including Hex, Deepnote, Databricks, and Power BI indicates market awareness and competitive differentiation strategy. Livedocs emphasizes speed advantages from DuckDB and Polars integration, AI sophistication through model choice and context awareness, and cost efficiency through unlimited team access without per-seat licensing. These positioning choices suggest targeting of budget-conscious teams seeking modern alternatives to legacy business intelligence platforms and cloud-locked enterprise notebook environments.
2. Impact & Evidence
Client Success Stories
A compelling case study documents how a startup founder utilized Livedocs to address customer churn challenges without prior data science expertise. The founder uploaded customer datasets and engaged the AI agent through natural language prompts: “Analyze these customer datasets and help me identify patterns in churned users.” Within ninety seconds, the AI performed exploratory data analysis, generated visualizations revealing hidden patterns, executed data cleaning procedures, identified critical features including login frequency and support ticket volume, and trained a Random Forest classification model with feature importance rankings.
The AI automatically quantified financial impact of churn, providing business context that extended beyond technical model outputs. The founder subsequently requested generation of risk scores for active customers with probability thresholds defining high-risk, medium-risk, and safe customer segments. Livedocs produced an interactive dashboard enabling the customer success team to prioritize retention outreach based on data-driven risk assessments. This workflow compressed what traditionally requires data science team involvement spanning weeks into an afternoon of conversational interaction.
The founder extended this analytical foundation to additional predictive models including trial-to-paid conversion probability, expansion opportunity identification for upsell targeting, and revenue forecasting for board presentations. Each new model leveraged existing infrastructure without requiring additional technical implementation, demonstrating how Livedocs enables iterative expansion of analytical capabilities through natural language rather than code development cycles.
Product Hunt reviewers consistently emphasize the platform’s ability to consolidate previously fragmented data workflows. One user noted that Livedocs unified social media metrics, marketing campaign data, and behavioral analytics without requiring technical expertise or additional headcount. Another highlighted time and cost savings achieved by eliminating separate reporting dashboards and manual data aggregation processes. These testimonials underscore practical value delivery in real operational contexts rather than theoretical capabilities.
Teams working across functional boundaries particularly value Livedocs’ accessibility. Product managers, marketers, and analysts can collaborate within shared notebooks where technical team members write Python code for complex transformations while non-technical stakeholders ask questions in natural language and receive visual answers. This multilingual capability—supporting SQL queries, Python scripts, and conversational AI simultaneously—removes communication barriers that traditionally segregate analytical work into specialist silos.
Performance Metrics & Benchmarks
Livedocs’ technical performance derives from architectural choices prioritizing speed at every layer. DuckDB, embedded as the default query engine for local files and in-memory operations, demonstrates throughput advantages over traditional analytical databases. Independent benchmarks comparing DuckDB to Apache Spark on ten-gigabyte datasets show DuckDB completing ad-hoc queries approximately twice as fast while consuming fewer computational resources. At four virtual cores, DuckDB outperforms Spark with Network Exchange Enabled by approximately sixty percent, delivering results in seconds rather than minutes.
Polars, the platform’s in-memory dataframe engine, excels at transformations and aggregations on datasets fitting within available RAM. Benchmark comparisons reveal Polars achieving two-to-six-times faster execution than Spark on small result aggregation queries at various scale points. This performance advantage translates directly to user experience: filtering millions of rows completes in milliseconds within Livedocs rather than the multi-second delays typical of cloud-based notebook environments relying on remote execution.
The platform’s smart caching layer provides compounding performance benefits through dependency tracking. When users modify a single cell, Livedocs analyzes the dependency graph to identify exactly which downstream cells require re-execution, preserving cached results for unaffected computations. This intelligent cache invalidation reduces average notebook run times by fifty to seventy percent compared to platforms that re-execute entire notebooks on any change. For teams working with expensive cloud warehouses, cache hits directly reduce query costs by avoiding redundant database calls.
Real-world performance testimonials emphasize subjective speed improvements that exceed quantitative benchmarks. Users describe query execution as “instant” and document rendering as “fluid,” suggesting Livedocs achieves the responsiveness threshold where tools feel integrated with thought rather than imposing wait states that interrupt flow. This perceptual performance matters significantly for adoption: analysts conducting exploratory data analysis may execute dozens of queries hourly, where even three-second delays accumulate into productivity drains and cognitive friction.
Livedocs’ reactive execution model guarantees consistency across notebook cells, eliminating a chronic pain point in sequential notebook environments. Traditional Jupyter users frequently execute cells out of order, creating hidden dependencies where displayed results no longer reflect current code. Livedocs’ DAG architecture prevents this category of error by enforcing dependency resolution regardless of cell ordering, ensuring that outputs always correspond to current state. This consistency guarantee improves reproducibility and reduces debugging time spent tracking down state mismatches.
Third-Party Validations
Product Hunt’s five-star rating from five reviewers provides qualitative validation, though the sample size limits statistical confidence. Reviewers praised seamless live data integration into documents, time and cost savings through workflow consolidation, and accessibility for users lacking technical backgrounds. One reviewer specifically emphasized versatility across diverse data tracking needs ranging from growth analytics to personal branding metrics, suggesting broad applicability beyond narrow use cases.
Comparative analyses positioning Livedocs against established competitors appear on multiple independent software review platforms including Moge.AI, Futurepedia, and AIChief. These directories characterize Livedocs as a modern collaborative workspace emphasizing AI-native workflows, distinguishing it from legacy notebook platforms and traditional business intelligence tools. The consistent framing across multiple review sources suggests emerging brand recognition within data tooling evaluation communities.
Industry blogs and data engineering publications reference Livedocs in comparisons of modern notebook platforms, positioning it alongside Hex, Deepnote, and Observable as next-generation alternatives to Jupyter. These mentions validate technical credibility and market awareness within practitioner communities that influence tool adoption decisions. The platform’s inclusion in comprehensive competitive comparison tables signals recognition as a viable option worthy of evaluation alongside established vendors.
Technical communities on Reddit and developer forums discuss Livedocs in contexts of reactive notebook architectures and high-performance analytical engines. These grassroots conversations indicate organic awareness spreading through word-of-mouth among data practitioners seeking modern alternatives to traditional tools. The technical depth of these discussions—focusing on DAG execution models, DuckDB performance characteristics, and AI agent capabilities—suggests engagement from sophisticated users rather than casual observers.
However, formal analyst coverage from Gartner, Forrester, or comparable research firms remains absent from available sources. This gap likely reflects Livedocs’ growth-stage profile rather than product limitations, as analyst attention typically follows market share accumulation and enterprise customer acquisition. The absence of Magic Quadrant placement or Wave evaluation limits enterprise buyer confidence but avoids the vendor relationship costs and product compromises sometimes associated with analyst engagement.
3. Technical Blueprint
System Architecture Overview
Livedocs implements a sophisticated technical architecture balancing ease-of-use with advanced capabilities. The platform operates as a cloud-native software-as-a-service accessible via web browsers, eliminating installation requirements and ensuring consistent experiences across operating systems. Zero-setup access enables instant productivity: users create accounts and begin analyzing data within minutes rather than spending hours configuring local environments or cluster infrastructure.
The reactive execution engine structures notebooks as Directed Acyclic Graphs where each cell represents a node with explicitly tracked dependencies on upstream cells. When users trigger execution, Livedocs calculates optimal run order ensuring no cell executes before its dependencies complete. This dependency resolution enables parallel execution of independent branches, leveraging available compute resources to minimize total runtime. The DAG architecture also powers smart caching: Livedocs marks cells as “dirty” when their code or dependencies change, preserving cached results for unaffected cells to avoid redundant computation.
Users control execution behavior through per-cell dropdown menus offering multiple strategies. “Auto” mode runs only relevant dependent cells affected by changes. “Cell only” executes a single cell without propagating updates. “All” triggers complete notebook execution from top to bottom. “Downstream” runs the selected cell plus all cells depending on its outputs. “Run without cache” forces fresh execution ignoring stored results, useful when external data sources have updated. This granular control accommodates both interactive exploration and production automation workflows.
The query resolution layer intelligently routes data operations to optimal engines based on source characteristics. Local CSV and Parquet files leverage DuckDB for file-native querying without loading entire datasets into memory. In-memory dataframes utilize Polars for maximum transformation throughput. Cloud warehouse connections including Snowflake, BigQuery, Postgres, and Redshift push computation down to these systems using native SQL, minimizing data transfer while preserving unified notebook interfaces. This hybrid approach eliminates manual engine selection while ensuring optimal performance across diverse data sources.
Terminal access within notebooks provides power users with complete environment control. Users can install Python packages via pip, inspect runtime state through command-line tools, configure custom dependencies, and debug complex issues through direct system interaction. This capability differentiates Livedocs from managed platforms like Hex and Deepnote that restrict users to predefined environments, enabling workflows requiring specialized libraries or non-standard configurations.
API & SDK Integrations
Livedocs provides comprehensive data source connectivity supporting workflows from local file analysis to enterprise data warehouse integration. Major cloud warehouses including Snowflake, BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, Google Cloud BigQuery, Postgres, ClickHouse, and AWS Athena connect through native drivers with credential management and query pushdown optimization. OAuth-based authentication patterns secure sensitive credentials while enabling convenient connection workflows.
Cloud storage integrations enable direct querying of files stored in Google Sheets, Amazon S3, Microsoft OneDrive, and Google Drive. DuckDB’s file-native query capabilities allow SQL operations directly against cloud-stored CSV and Parquet files without intermediate loading steps, reducing latency and storage costs. This architecture particularly benefits teams with data lake deployments where analytical datasets reside in object storage rather than databases.
Visualization capabilities leverage Vega-Lite and Altair libraries providing declarative grammar for creating interactive charts. These libraries enable sophisticated visualizations through concise specifications rather than imperative plotting code. Users define data encodings, mark types, and interaction behaviors through high-level configurations, producing publication-quality charts with minimal code. The reactive execution model extends to visualizations: when upstream data changes, dependent charts automatically update without manual refresh.
Interactive elements including dropdowns, sliders, text inputs, and buttons transform static notebooks into reactive applications. Users embed input widgets that parameterize queries and visualizations, enabling stakeholders to explore data through interface interactions rather than code modifications. This capability bridges the gap between analytical notebooks and business intelligence dashboards, allowing single documents to serve both exploratory analysis and presentation functions.
The platform supports scheduled execution for workflow automation. Users configure notebooks to run periodically, refreshing data and regenerating outputs on defined schedules. Built-in key-value and secrets stores enable stateful workflows that persist intermediate results between runs, manage authentication tokens, and coordinate multi-step processes without external infrastructure. These primitives transform notebooks from interactive analysis tools into lightweight data pipelines and ETL workflows.
Scalability & Reliability Data
Specific uptime service-level agreements and formal reliability guarantees are not published in accessible documentation, consistent with Livedocs’ growth-stage profile. Enterprise customers requiring contractual SLA commitments should engage direct sales conversations to negotiate custom terms. The absence of published SLAs represents common practice among newer platforms prioritizing product development over legal framework establishment.
The cloud-native architecture implies horizontal scalability through dynamic resource provisioning. As user load increases, the platform can allocate additional compute resources without service disruption. This elasticity model standard in modern SaaS platforms provides cost efficiency during low-usage periods while maintaining performance during peak demand. However, specific auto-scaling triggers, resource limits, and performance degradation thresholds remain undisclosed.
Free tier resource allocations of eight gigabytes RAM and two virtual CPUs suggest reasonable capacity for individual users and small team exploration. Production workloads processing gigabyte-scale datasets or executing complex machine learning workflows may require Pro tier upgrades offering enhanced computational resources. Teams should conduct pilot testing with representative data volumes to validate performance acceptability before committing to production deployments.
The platform’s handling of extremely large datasets—those exceeding available memory or requiring distributed processing—remains partially documented. DuckDB’s out-of-core capabilities enable querying datasets larger than RAM through spill-to-disk mechanisms, though performance degrades compared to in-memory operations. Polars, primarily designed for in-memory workloads, encounters limitations on multi-terabyte datasets as documented in independent benchmarks. Teams regularly processing hundred-gigabyte-plus datasets should evaluate whether Livedocs’ performance meets requirements or whether complementary big data tools remain necessary.
Network reliability and geographic distribution details are not specified in available materials. Single-region deployments introduce latency for geographically distributed teams and create availability risks during regional outages. Multi-region architectures with intelligent routing improve both performance and resilience but increase infrastructure complexity. Prospective enterprise customers should clarify deployment topology during vendor discussions to understand latency expectations and disaster recovery capabilities.
4. Trust & Governance
Security Certifications
Livedocs does not advertise formal security certifications including SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, or comparable industry-standard attestations in publicly accessible materials. This absence is typical for growth-stage SaaS platforms where product development and market validation take precedence over expensive multi-month certification processes. Security certifications become business imperatives as platforms target enterprise customers with stringent vendor compliance requirements, suggesting future certification roadmap alignment with upmarket expansion.
The absence of published certifications should inform enterprise risk assessments. Organizations in regulated industries including healthcare, financial services, and government typically mandate SOC 2 or equivalent attestations before approving vendor relationships. These regulatory compliance requirements may currently disqualify Livedocs from consideration by highly regulated buyers, though individual security control implementations may meet or exceed certified competitors depending on specific architectural choices.
Authentication and authorization mechanisms appear to follow modern security practices based on available feature descriptions. OAuth-based data source connections avoid direct credential storage, reducing attack surface and simplifying credential rotation. The secrets store feature enables secure management of API keys and database passwords within the platform, preventing hardcoded credentials in notebook code. Role-based access controls and workspace isolation provide organizational segmentation, though detailed permission models remain undocumented.
Data encryption patterns—both in transit via HTTPS and at rest for stored notebooks, query results, and cached data—represent fundamental security expectations for cloud platforms. While not explicitly confirmed in public documentation, these protections constitute industry standard practice that reputable SaaS vendors implement by default. Enterprise customers should verify encryption implementation details during security reviews rather than assuming protection based on general practice.
Data Privacy Measures
Livedocs’ data handling practices appear to follow typical SaaS patterns where user-generated content including notebooks, datasets, query results, and visualizations flow through the platform’s infrastructure for processing, storage, and sharing. The platform’s positioning as a collaborative workspace implies data persistence beyond ephemeral session state, requiring thoughtful data retention and deletion policies to honor user privacy expectations and regulatory requirements.
Notebook sharing capabilities including public URLs, embedded views, and collaborative editing introduce data exposure considerations. Users must understand permission models and access controls to prevent unintended disclosure of sensitive analyses. Organizations handling confidential information should establish governance policies defining appropriate sharing scopes, mandating access restrictions, and auditing external exposure. Platform-level controls supporting these governance requirements remain partially documented in available sources.
The AI agent’s access to notebook context including dataframes, tables, and prior outputs raises questions about data usage for model training or improvement. Industry practices vary dramatically: some vendors explicitly prohibit training on customer data while others include broad usage rights in terms of service. The absence of clear data usage policies in public documentation creates uncertainty that privacy-conscious organizations should resolve through direct vendor engagement before deployment.
Cross-border data transfer implications affect organizations subject to GDPR, CCPA, or comparable privacy regulations. Cloud platforms typically replicate data across geographic regions for performance and resilience, potentially moving European user data through US infrastructure or vice versa. Compliance frameworks including Standard Contractual Clauses or Privacy Shield equivalents govern these transfers, though Livedocs’ specific data residency and transfer practices remain unspecified in available materials.
Workspace isolation mechanisms provide organizational segmentation, enabling teams to maintain separate environments for different projects, clients, or security domains. This capability supports least-privilege access principles by restricting user visibility to relevant notebooks and datasets. Detailed implementation including authentication federation, identity provider integration, and audit logging capabilities warrant validation during enterprise evaluation processes.
Regulatory Compliance Details
Specific regulatory compliance postures including GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, SOX, and industry-specific frameworks are not detailed in publicly accessible documentation. This documentation gap complicates compliance assessments for organizations operating under strict regulatory oversight. The absence of compliance statements does not necessarily indicate non-compliance, but rather reflects typical growth-stage prioritization where compliance infrastructure lags product development until enterprise demand justifies investment.
Organizations subject to data residency requirements mandating storage within specific geographic boundaries should verify whether Livedocs supports regional deployment options. Single-region architectures may violate regulations requiring EU data remain in EU jurisdictions or Chinese data remain in Chinese infrastructure. Multi-region capabilities with configurable data residency enable compliance but increase platform complexity and cost.
Data processing agreements defining controller-processor relationships under GDPR and similar frameworks represent essential contract components for European organizations. These agreements specify data handling obligations, security requirements, breach notification procedures, and rights of audit. The availability and terms of such agreements from Livedocs remain undocumented in public sources, necessitating legal review during procurement processes.
Audit trail capabilities including access logs, query history, data export tracking, and modification records support compliance obligations requiring demonstrable data governance. Comprehensive logging enables forensic investigation of data breaches, insider threats, or unauthorized access. The existence and scope of Livedocs’ audit capabilities are not detailed in available materials, representing evaluation criteria for risk-averse organizations.
Third-party security assessments including penetration testing results, vulnerability disclosures, and bug bounty programs provide independent validation of security claims. Transparent security postures including public vulnerability disclosure policies and researcher-friendly reporting processes signal mature security cultures. The absence of publicized security assessment results or coordinated disclosure programs in available sources limits independent security validation.
5. Unique Capabilities
Infinite Canvas: Applied Use Case
Livedocs implements a flexible document model where users combine code cells, visualizations, markdown text, and interactive elements in arbitrary arrangements without rigid structural constraints. This “infinite canvas” approach contrasts with linear notebook paradigms where content follows strict top-to-bottom sequencing. Users can position related analyses spatially, create branching exploration paths, and organize content according to narrative logic rather than execution order.
The reactive DAG architecture decouples visual arrangement from execution dependencies. Users can place output visualizations before the code cells generating them, arrange comparative analyses side-by-side, or structure documents hierarchically without compromising execution correctness. Livedocs analyzes dependencies regardless of spatial positioning, ensuring consistent results while preserving presentational flexibility. This separation enables analysts to optimize documents simultaneously for computation and communication.
Interactive elements embedded throughout notebooks transform static analyses into explorable applications. Users insert dropdown selectors parameterizing queries, sliders adjusting visualization scales, and text inputs filtering datasets. These widgets trigger reactive updates across dependent cells, enabling stakeholders to explore data through direct manipulation rather than requesting custom queries from analysts. A sales dashboard might include region selectors updating revenue charts, product filters recalculating margins, and date ranges adjusting trend visualizations—all without code modification.
This application-building capability positions Livedocs between traditional notebooks and business intelligence platforms. Single documents serve both analysis and presentation functions, eliminating workflow friction where insights discovered in notebooks require recreation in separate dashboard tools. Analysts iterate within Livedocs until reaching publishable state, then share the same document with stakeholders who interact through widgets rather than code. This unified environment compresses the analysis-to-insight loop while reducing tool proliferation.
Multi-Agent Coordination: Research References
Livedocs’ AI architecture implements sophisticated multi-agent coordination where specialized models collaborate to transform user intent into executable analyses. When users submit natural language requests, the system orchestrates multiple AI capabilities including natural language understanding for intent extraction, code generation for query and transformation logic, data profiling for schema inference and quality assessment, visualization recommendation for appropriate chart types, and result interpretation for business-language explanations.
This coordination layer operates transparently, presenting users with unified conversational interfaces while internally routing subtasks to specialized models optimized for particular functions. A request like “analyze customer churn patterns and identify high-risk accounts” triggers sequential agent invocations: the NLU model extracts analytical intent and identifies relevant data entities, the profiling agent examines customer datasets to understand schemas and distributions, the query generation agent writes SQL or Python extracting churn-related features, the ML model-building agent trains classification algorithms, and the visualization agent creates risk score dashboards.
Context awareness represents a critical differentiator from simpler AI assistants. Livedocs’ agents maintain full visibility into notebook state including loaded datasets, computed variables, existing visualizations, and prior analytical steps. This contextual grounding enables intelligent suggestions: if a user asks “show me trends over time,” the agent identifies temporal columns in available data and proposes appropriate time-series visualizations. Without context awareness, generic AI assistants require extensive prompting to achieve comparable specificity.
Model choice flexibility allows users to optimize cost-performance tradeoffs across tasks. Simple data cleaning operations might utilize efficient smaller models, while complex analytical reasoning leverages frontier models like GPT-5 or Claude. Organizations with privacy constraints can deploy local models within their infrastructure, maintaining data sovereignty while preserving AI augmentation benefits. This architectural flexibility accommodates diverse requirements that fixed-model platforms cannot address.
Research underpinning these capabilities draws from academic progress in large language models, program synthesis, and automated machine learning. Instruction-following models trained on code generation tasks enable natural language to Python/SQL translation. Vision-language models power chart understanding and generation from visual specifications. Automated feature engineering techniques enable ML model construction without explicit feature definitions. Livedocs synthesizes these research advances into integrated workflows hiding complexity behind conversational interfaces.
Model Portfolio: Uptime & SLA Figures
Livedocs provides users with model choice across multiple AI providers including OpenAI’s GPT family, Anthropic’s Claude models, Google’s Gemini series, and potentially other frontier and open-source models. This multi-provider strategy builds resilience against single-vendor dependencies while enabling cost optimization and capability matching. Users select preferred models per task, workspace, or organization based on performance requirements, budget constraints, privacy considerations, and capability needs.
Model availability and performance depend partly on upstream provider reliability. OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google maintain high-availability inference infrastructure typically exceeding ninety-nine percent uptime, though occasional capacity constraints or service disruptions affect all cloud AI providers. Livedocs’ multi-model support mitigates single-provider outages: if one model becomes unavailable, users can temporarily switch to alternatives without complete workflow disruption.
AI credit allocation systems meter generative AI usage across pricing tiers. Free plans include ten dollars monthly in AI credits enabling substantial exploration and light production use. Pro plans allocate higher credit limits supporting heavier automation and batch processing workflows. Credit consumption varies by model selection, query complexity, and output length. Users monitor credit usage through dashboard interfaces, receiving notifications approaching limits to prevent mid-workflow interruptions.
Credit exhaustion mid-analysis represents an operational risk requiring proactive monitoring. Teams heavily leveraging AI generation for automated analysis, report generation, or dashboard population should size subscriptions with buffer capacity accounting for usage variability. Alternatively, hybrid approaches reserve AI assistance for high-value tasks while utilizing traditional code for routine operations, optimizing credit consumption without sacrificing capabilities where AI provides maximum leverage.
Specific uptime guarantees, latency commitments, or throughput limits for Livedocs’ core platform—independent of AI model dependencies—are not published in accessible documentation. Growth-stage platforms typically evolve formal SLA frameworks as they transition from product-market fit to operational maturity, often coinciding with enterprise customer acquisition requiring contractual reliability commitments. Prospective buyers requiring guaranteed availability should engage sales discussions to negotiate custom SLA terms.
Interactive Tiles: User Satisfaction Data
Livedocs’ visualization capabilities extend beyond static chart generation to include reactive, interactive elements that respond to user inputs in real-time. The platform natively supports Vega-Lite and Altair declarative visualization grammars, enabling sophisticated interactive charts through concise specifications. Users define interactions including tooltips on hover, filtering through selection, zooming and panning, linked brushing across multiple charts, and conditional encoding based on user actions.
These interactive capabilities transform analytical notebooks into explorable data applications. A financial analysis might include linked charts where selecting a time range in one view filters all dependent visualizations. An e-commerce dashboard could implement product category filters updating revenue trends, conversion funnels, and inventory levels simultaneously. Users explore data through direct manipulation rather than modifying code, democratizing analysis access across technical skill levels.
Input widgets including dropdowns, sliders, radio buttons, checkboxes, and text fields parameterize analyses without code changes. Analysts define variables controlled by widgets, then reference these parameters throughout notebook queries and visualizations. When users adjust widget values, Livedocs’ reactive execution propagates changes through dependent cells, updating outputs automatically. This capability enables “what-if” analysis scenarios where stakeholders explore sensitivities and test hypotheses through interface interactions.
User satisfaction data specific to Livedocs’ interactive features remains limited in available sources. Qualitative testimonials emphasize time savings and accessibility improvements when non-technical team members can explore analyses independently rather than requesting custom queries. Product Hunt reviewers highlighted the seamless integration of interactive elements into collaborative workflows, enabling distributed teams to engage with data asynchronously without real-time analyst support.
The combination of reactive execution, intelligent caching, and interactive widgets creates fluid exploration experiences where interface actions trigger instant updates rather than introducing perceptible delays. This responsiveness threshold matters significantly for adoption: when users perceive tools as instantaneous extensions of thought, they engage more deeply and explore more broadly than when wait states interrupt flow. Livedocs’ architectural optimizations including Rust-based internals and DuckDB performance contribute to crossing this critical usability threshold.
6. Adoption Pathways
Integration Workflow
Livedocs implements a streamlined onboarding process prioritizing immediate productivity over extensive configuration. Users create accounts through standard email registration or social authentication, accessing the platform within minutes without credit card requirements or approval workflows. This zero-friction entry reduces adoption barriers while enabling extensive evaluation before financial commitment.
Initial document creation offers template-based quick starts or blank canvases for custom workflows. Templates cover common use cases including data exploration, dashboard creation, financial analysis, and machine learning pipelines. These pre-built structures accelerate learning by demonstrating platform capabilities through working examples users can modify and extend. Alternatively, experienced users begin with blank documents, incrementally building analyses without template constraints.
Data source connections support diverse scenarios from local file uploads to enterprise warehouse integration. Users drag-and-drop CSV or Excel files for immediate analysis, connect Google Sheets through OAuth authentication, or configure database credentials for Snowflake, BigQuery, Postgres, and other supported systems. DuckDB’s file-native capabilities enable SQL queries directly against local files without intermediate import steps, simplifying exploratory workflows on unstructured data.
The AI agent accelerates onboarding by answering questions and generating starter code. New users unfamiliar with Python or SQL syntax can describe analytical intent in natural language, receiving executable code they subsequently modify and extend. This assisted learning approach scaffolds skill development while maintaining productivity, enabling users to accomplish real work during learning phases rather than completing prerequisite training before contribution.
Real-time collaboration features including multiplayer editing, live cursors, and commenting enable team-based onboarding where experienced users guide newcomers through shared documents. This peer-learning model often proves more effective than formal training, allowing contextual guidance during actual workflows rather than abstract instruction divorced from practical application.
Customization Options
Livedocs provides multiple customization layers accommodating diverse requirements. Workspace-level settings define organizational defaults including preferred AI models, compute resource allocations, and sharing permissions. Teams can standardize configurations across projects while allowing document-specific overrides for special cases. This hierarchical configuration model balances consistency with flexibility.
Python environment customization through terminal access enables installation of specialized libraries, configuration of custom dependencies, and integration of proprietary packages. Users execute pip install commands, configure environment variables, and manage virtual environments directly within notebooks. This capability supports workflows requiring domain-specific packages unavailable in default environments, eliminating the “works on my machine” problems plaguing less flexible platforms.
Visualization customization leverages Vega-Lite’s comprehensive grammar enabling precise control over every visual element. Users specify color schemes, axis configurations, legend positions, mark styles, and interaction behaviors through declarative specifications. This low-code approach to customization provides design control without requiring expertise in imperative graphics libraries, balancing accessibility with flexibility.
AI behavior customization through prompt engineering and model selection enables teams to optimize assistant performance for organizational contexts. Users craft system prompts defining analytical preferences, coding style conventions, and domain terminology. Model selection per task enables cost-performance optimization: lightweight models handle simple queries while frontier models tackle complex reasoning. This granular control accommodates diverse use cases within single platforms.
Sharing and permission configurations support varied collaboration models. Private notebooks restrict access to specific users, team workspaces enable departmental collaboration, public URLs share analyses externally, and embedded views integrate notebooks into other applications. Fine-grained permission controls distinguish between viewers who consume analyses, editors who modify content, and administrators who manage access. These options accommodate scenarios from individual exploration to enterprise governance.
Onboarding & Support Channels
Livedocs implements a self-service support model emphasizing documentation, in-application guidance, and community resources. Comprehensive documentation covers core concepts including reactive execution, data connections, visualization techniques, and AI agent usage. These materials serve both initial learning and ongoing reference, reducing dependency on direct support channels for routine questions.
In-application tooltips, feature callouts, and contextual help provide just-in-time guidance as users encounter new functionality. This progressive disclosure approach prevents cognitive overload while ensuring capability discovery as sophistication increases. The platform prioritizes intuitive interfaces reducing documentation dependency, though comprehensive references remain available for edge cases and advanced features.
Community resources including user forums, knowledge bases, and third-party tutorials supplement official documentation. Independent content creators publish explainer articles and video walkthroughs demonstrating platform capabilities through practical examples. This organic educational ecosystem reduces support burden while improving discoverability through search engine visibility and social sharing.
Email support provides responsive assistance for issues exceeding self-service resolution. Available sources suggest reasonable response times and helpful engagement, though formal support-level agreements defining response times, escalation procedures, and availability windows are not detailed in public materials. Enterprise customers requiring guaranteed support service should negotiate custom agreements defining specific commitments.
The absence of dedicated customer success programs, account management, or professional services in public documentation suggests Livedocs maintains a self-service orientation typical of growth-stage SaaS platforms. As the product targets upmarket customers with complex requirements, more hands-on support offerings will likely emerge to facilitate enterprise adoption, implementation guidance, and change management.
7. Use Case Portfolio
Enterprise Implementations
Livedocs serves enterprise analytical workflows spanning business intelligence, operational dashboards, and decision support systems. Large organizations leverage the platform to democratize data access across departments, enabling marketing teams to analyze campaign performance, finance departments to model scenarios, and operations groups to monitor KPIs without constant data team mediation. The AI assistant particularly benefits non-technical stakeholders who contribute business context and domain expertise but lack SQL or Python proficiency.
Multi-team collaboration scenarios benefit from workspace segmentation enabling departmental isolation while preserving cross-functional sharing where appropriate. A retail enterprise might maintain separate workspaces for merchandising analytics, supply chain optimization, and customer insights, with controlled sharing enabling holistic strategic analysis drawing from all domains. This organizational structure balances autonomy with integration, preventing data silos while respecting access boundaries.
Regulated industries including financial services, healthcare, and government face adoption challenges given Livedocs’ absence of published security certifications. Organizations in these sectors currently evaluating the platform should conduct thorough security assessments, potentially limiting initial deployments to non-sensitive use cases until formal certifications emerge. Alternative approaches include hybrid architectures where Livedocs handles non-regulated analyses while certified platforms process sensitive data.
Enterprise integration scenarios connecting Livedocs to existing data infrastructure leverage supported warehouse connectors and API capabilities. Organizations with established Snowflake, BigQuery, or Redshift deployments can connect Livedocs seamlessly, positioning it as an analytical interface layer atop existing data platforms. This architecture preserves infrastructure investments while modernizing analyst experiences through improved interfaces and AI augmentation.
Cost optimization represents a compelling enterprise value proposition. Traditional business intelligence platforms charge per-seat licensing, creating budget pressures as organizations expand data literacy programs inviting broader participation. Livedocs’ pricing model potentially reduces costs substantially while providing modern capabilities exceeding legacy platforms. This economic advantage may accelerate adoption despite the platform’s relative youth compared to established vendors.
Academic & Research Deployments
Academic institutions and research organizations leverage Livedocs for computational research, data-driven instruction, and collaborative scholarship. Researchers benefit from reproducible analysis capabilities where notebooks document complete methodologies from raw data through final conclusions. This transparency facilitates peer review, replication studies, and methodological critiques essential to scientific progress. The reactive execution model ensures results correspond to documented code, eliminating reproducibility failures from hidden cell execution orders.
Instructional applications position Livedocs as an interactive textbook combining explanatory text, executable code, visualizations, and exercises within unified documents. Students learn programming concepts, statistical methods, and domain knowledge through hands-on experimentation rather than passive reading. Instructors distribute starter notebooks students extend through assignments, facilitating formative feedback and iterative improvement. The AI assistant provides on-demand tutoring, answering student questions and debugging code without requiring constant instructor availability.
Collaborative research projects spanning multiple institutions benefit from real-time editing features enabling distributed teams to develop analyses synchronously. Researchers share preliminary findings, provide feedback on methodologies, and coordinate multi-author analyses through shared notebooks replacing fragmented workflows involving email attachments and version conflicts. Comments and annotations facilitate asynchronous discussion when synchronous collaboration proves impractical across time zones.
Publication workflows increasingly demand computational reproducibility where journals require code and data accompanying manuscript submissions. Livedocs notebooks serve this requirement naturally: authors develop analyses within the platform, then publish notebooks alongside papers enabling reviewers and readers to validate findings. This transparency strengthens scientific credibility while reducing replication failures stemming from ambiguous methodological descriptions.
Open science initiatives promoting data sharing and collaborative research align naturally with Livedocs’ capabilities. Researchers publish public notebooks demonstrating analytical techniques, sharing educational resources, and disseminating findings beyond traditional publication venues. This democratization of scientific knowledge accelerates progress by enabling broader participation in research communities traditionally limited by institutional access barriers.
ROI Assessments
Quantifying Livedocs’ return on investment requires evaluating both direct cost savings and productivity multipliers. Organizations currently using traditional business intelligence platforms like Tableau or Power BI paying per-seat licensing can realize substantial savings by transitioning to Livedocs’ unlimited-user model. A mid-size analytics team of fifteen practitioners might spend fifteen thousand dollars annually on BI tool licenses, compared to potentially seven hundred eighty dollars for Livedocs Pro subscriptions—a ninety-five percent cost reduction.
Productivity gains from AI augmentation compound across multiple dimensions. Analysts report workflow compressions from days to hours when AI agents handle routine data cleaning, transformation logic, and visualization generation. A churn prediction model requiring a week of data scientist time compresses to ninety seconds of conversational interaction. These dramatic efficiency improvements enable smaller teams to accomplish more work or equivalent teams to tackle broader problem sets previously considered resource-constrained.
Democratization benefits emerge when non-technical stakeholders independently answer questions rather than queuing requests for overburdened data teams. A product manager exploring feature usage patterns through conversational queries avoids three-day turnaround cycles for analyst-generated reports. Marketing teams adjusting campaign dashboards through interactive widgets eliminate email chains requesting visualization tweaks. These self-service capabilities multiply effective analytical capacity without headcount additions.
Tool consolidation savings materialize when Livedocs replaces multiple specialized platforms. Organizations historically maintained separate environments for data exploration (Jupyter), visualization (Tableau), collaboration (Google Docs), and automation (Airflow). Livedocs unifies these functions within single notebooks, reducing licensing costs, integration overhead, and context-switching friction. Administrators manage fewer systems while users work within integrated environments rather than navigating fragmented toolchains.
Time-to-insight acceleration provides strategic value difficult to quantify financially but critical for competitive advantage. Organizations making decisions based on current data rather than week-old reports respond faster to market changes, customer behavior shifts, and operational anomalies. A retailer identifying inventory trends in real-time adjusts purchasing decisions preventing stockouts or overstock situations. A SaaS company detecting churn signals intervenes with retention offers while relationships remain salvageable. These responsiveness improvements drive revenue protection and capture often exceeding analytical tooling costs by orders of magnitude.
Total cost of ownership calculations must account for AI credit consumption patterns. Heavy automation users may exhaust included credits, requiring plan upgrades or supplemental purchases. Organizations should pilot workflows with representative volumes during evaluation periods, establishing consumption baselines informing subscription sizing. Strategic credit management reserves AI generation for high-leverage tasks while utilizing traditional code for routine operations, optimizing value extraction per dollar spent.
8. Balanced Analysis
Strengths with Evidential Support
Livedocs’ most compelling competitive advantage stems from its AI-native architecture where intelligence integrates at foundational levels rather than bolting onto legacy designs. The model choice flexibility enabling users to select GPT-5, Claude, Gemini, or other options based on task requirements represents sophistication absent from competitors offering fixed or no-choice AI assistants. This flexibility accommodates diverse needs including cost optimization for simple tasks, capability matching for complex reasoning, and privacy preservation through local model deployment.
Performance advantages from DuckDB and Polars integration deliver measurable speed improvements over cloud-execution notebooks and warehouse-dependent platforms. Independent benchmarks demonstrate DuckDB completing ad-hoc queries two-to-six times faster than competing engines on representative workloads. Users experience this performance as instant query responses and fluid document interactions, creating subjective quality perception exceeding quantitative measurements. Fast tools feel like thought extensions rather than external dependencies, fundamentally improving analytical experiences.
The reactive DAG architecture solves chronic reproducibility problems plaguing sequential notebook environments. By automatically tracking dependencies and enforcing execution order regardless of visual arrangement, Livedocs guarantees results correspond to current code state. This consistency eliminates entire categories of bugs where displayed outputs no longer match code definitions, reducing debugging time and increasing confidence in analytical conclusions. For organizations requiring audit trails or regulatory compliance, reproducibility guarantees provide risk mitigation beyond mere convenience.
Terminal access and full environment control differentiate Livedocs from managed platforms restricting users to predefined configurations. Data scientists requiring specialized libraries, custom configurations, or debugging capabilities appreciate unrestricted access enabling advanced workflows impossible in restricted environments. This power-user accommodation expands addressable use cases beyond platforms optimized solely for simplicity, supporting both novice-friendly interfaces and expert-level customization within unified platforms.
The generous free tier offering unlimited documents and applications with ten dollars monthly AI credits removes evaluation barriers while enabling substantial production use at zero cost. Small teams, individual practitioners, and exploratory projects can extract significant value without financial commitment, reducing adoption friction and building product dependency organically. This accessibility strategy contrasts with competitors imposing strict document limits or requiring immediate payment, potentially accelerating word-of-mouth growth through low-barrier trial experiences.
Limitations & Mitigation Strategies
Livedocs’ relative youth in a mature market segment creates adoption risk for conservative buyers requiring vendor stability assurances. Established competitors like Databricks and Jupyter possess longer operating histories, larger user bases, and more extensive support infrastructures. Organizations uncomfortable with emerging-vendor risk should consider phased adoption strategies: deploy Livedocs for non-critical exploratory analyses initially, expanding scope as platform maturity and organizational confidence increase over evaluation periods.
The absence of formal security certifications including SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001 may disqualify Livedocs from consideration by enterprises with strict vendor compliance requirements. Regulated industries including healthcare, financial services, and government typically mandate third-party attestations before approving vendor relationships. Organizations facing these constraints should monitor Livedocs’ certification roadmap, potentially deferring adoption until compliance milestones achieve or limiting deployment to non-regulated data domains.
Limited public information regarding leadership team, company funding, and organizational structure creates uncertainty about long-term viability and strategic direction. Prospective customers conducting vendor risk assessments prefer transparent disclosure of founding team credentials, investor backing, revenue metrics, and customer counts. The opacity in available sources complicates due diligence processes, though direct vendor engagement during sales conversations can potentially address information gaps through confidential disclosures.
Performance limitations on extremely large datasets—particularly those exceeding available memory or requiring distributed processing—may necessitate complementary big data tools for subset of workflows. While DuckDB and Polars excel on datasets fitting within single-machine resources, multi-terabyte analyses traditionally requiring Spark or comparable distributed systems may exceed Livedocs’ optimal scale points. Organizations with mixed workload profiles should evaluate whether Livedocs handles their typical analyses while maintaining specialized tools for exceptional cases.
Documentation completeness gaps around enterprise features, security controls, and compliance postures complicate thorough evaluation processes. Comprehensive vendor assessments require detailed specifications regarding authentication mechanisms, encryption implementations, audit capabilities, data residency options, and backup procedures. The absence of these details in public materials necessitates direct vendor engagement during procurement, potentially extending evaluation timelines compared to competitors with extensive published documentation.
The smaller user community and ecosystem compared to Jupyter, R, or established BI platforms translates to fewer third-party resources, extensions, and peer support channels. Users cannot yet rely on extensive Stack Overflow archives, community-contributed packages, or consultant availability typical of mature platforms. Early adopters should budget discovery time and maintain direct vendor relationships during learning curves, recognizing that community-driven support will strengthen as adoption broadens.
9. Transparent Pricing
Plan Tiers & Cost Breakdown
Livedocs implements a two-tier pricing structure designed for accessible evaluation and straightforward expansion. The Free plan provides permanent zero-cost access to core platform capabilities including unlimited document and application creation, eight gigabytes of RAM with two virtual CPUs, ten dollars in monthly AI credits applicable to any supported model, Livedocs Anywhere enabling local deployment, and email-based support. This generous allocation enables substantial individual use and small team collaboration without financial barriers, supporting evaluation periods extending weeks or months before purchase decisions.
The Pro plan pricing appears at sixty-five dollars monthly based on available third-party sources, though official pricing pages warrant direct verification as promotional rates or regional variations may exist. Pro subscriptions provide enhanced computational resources beyond free tier allocations, increased AI credit allowances supporting heavier automation, priority support access with faster response times, and potentially additional features including advanced scheduling, enhanced collaboration tools, or enterprise integrations. Specific Pro tier capabilities require clarification through official documentation or sales conversations.
Pricing transparency could improve through published feature matrices clearly delineating free versus Pro capabilities. Prospective buyers benefit from understanding exactly which features require upgrades, enabling informed purchase decisions based on anticipated usage patterns. The absence of detailed public pricing documentation represents common practice among growth-stage platforms evolving monetization strategies, though enterprise buyers accustomed to transparent pricing grids may find this opacity frustrating during evaluation processes.
Annual billing options potentially offering discounts compared to monthly subscriptions remain unconfirmed in available sources. SaaS platforms commonly provide ten-to-twenty-percent savings for annual commitments, reducing churn risk while improving cash flow predictability. Organizations committing to Livedocs for extended periods should inquire about annual terms potentially reducing total cost of ownership.
Volume or enterprise pricing for large deployments requiring custom resource allocations, dedicated support, or contractual SLA commitments likely require direct sales negotiation. Published self-service pricing typically addresses individual and small team segments, with enterprise arrangements handled through custom contracts accommodating specific requirements. Organizations planning large-scale deployments should engage sales discussions early to understand pricing at intended scale and negotiate favorable terms.
Total Cost of Ownership Projections
Comprehensive total cost of ownership calculations extend beyond subscription fees to encompass implementation effort, training investment, ongoing operational overhead, and opportunity costs from feature gaps. Livedocs’ zero-setup model minimizes implementation burden: users create accounts and begin productive work within minutes rather than dedicating weeks to infrastructure provisioning, cluster configuration, or complex installations typical of self-hosted platforms.
Training costs remain modest given intuitive interfaces and AI-assisted learning. Most users achieve basic proficiency within hours of initial exploration through self-service documentation and in-application guidance. Advanced capabilities including custom environment configuration, complex visualization design, and workflow automation may require additional learning investment, though comprehensive documentation reduces dependency on formal training programs. Organizations can budget minimal training overhead compared to platforms with steep learning curves.
Integration costs vary based on existing data infrastructure and desired connectivity. Teams connecting Livedocs to supported warehouses like Snowflake or BigQuery incur near-zero integration effort through native connectors. Organizations requiring custom integrations to proprietary systems or unsupported platforms must invest developer time building connections, though comprehensive APIs and documentation reduce implementation complexity. Simple integrations may require five-to-fifteen hours of skilled development work.
Ongoing operational costs primarily involve AI credit consumption beyond included allowances. Organizations heavily leveraging automated analysis, report generation, or interactive assistance should monitor usage patterns during pilot periods, establishing consumption baselines informing subscription tier selection. Strategic credit management optimizes value by reserving AI for high-leverage tasks while using traditional code for routine operations, maximizing output per dollar spent.
Opportunity costs from feature gaps requiring supplemental tools may increase effective total cost. Organizations needing advanced governance beyond Livedocs’ current capabilities, sophisticated access controls, or specialized integrations might maintain complementary platforms creating tool sprawl. Comprehensive vendor evaluation should assess feature completeness against requirements, understanding where Livedocs provides complete solutions versus requiring supplementation.
For representative scenarios, total cost of ownership calculations include:
Solo practitioner using free tier: Zero direct costs with potential AI credit purchases if exceeding ten-dollar monthly allowance. Effective annual TCO ranges from zero to perhaps two hundred forty dollars for heavy AI users requiring supplemental credits.
Five-person analytics team on Pro plan: Sixty-five dollars monthly per user equals three thousand nine hundred dollars annually at published rates, though volume discounts may apply. Minimal setup and training costs add perhaps five hundred dollars first-year investment. Total first-year TCO approximately forty-four hundred dollars, decreasing to thirty-nine hundred annually thereafter.
Mid-size enterprise replacing traditional BI platform: Fifty-user deployment transitioning from per-seat BI tools costing fifteen thousand dollars annually to Livedocs at potentially negotiated enterprise rates. Assuming volume discounts achieve effective thirty-dollar-per-user monthly costs, annual subscription totals eighteen thousand dollars plus implementation services potentially adding ten thousand dollars first-year. Despite higher absolute costs than small teams, substantial savings versus legacy platforms delivering potentially fifty-percent cost reduction while modernizing capabilities.
10. Market Positioning
Livedocs operates within the rapidly evolving data notebook and business intelligence software market characterized by platform proliferation, AI integration races, and shifting user preferences from traditional BI tools toward flexible notebook environments. The broader data and analytics software market continues robust expansion driven by data volume growth, cloud adoption, and increasing organizational data literacy initiatives. This macro environment creates favorable conditions for platforms offering modern alternatives to legacy systems.
The competitive landscape segments along multiple dimensions including target personas (data scientists versus business analysts), deployment models (cloud-managed versus self-hosted), language support (Python-only versus multi-language), and AI sophistication (basic assistance versus autonomous agents). Livedocs positions at the intersection of multiple segments: supporting both technical data scientists and non-technical analysts through hybrid interfaces, operating as cloud-managed SaaS eliminating infrastructure burden, enabling Python and SQL with AI augmentation, and providing sophisticated autonomous capabilities beyond basic code completion.
Competitor Comparison Table
| Platform | Primary Language | Execution Model | AI Capabilities | Data Sources | Collaboration | Starting Price | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Livedocs | Python, SQL, AI | Reactive DAG | Model choice (GPT-5, Claude, Gemini), context-aware | All major warehouses + local files via DuckDB | Real-time multiplayer | $0 (Free tier) | AI-native with DuckDB/Polars performance |
| Jupyter | Python, R, Julia | Sequential | None (extensions available) | Library-dependent | File/Git-based | Free (OSS) | Ubiquity, extensibility, open-source |
| Hex | SQL, Python | Cloud execution | Limited AI, no model choice | Enterprise warehouses | Team workspaces | ~$150/user/month | No-code + SQL/Python hybrid |
| Deepnote | Python, SQL | Sequential | Basic AI, fixed model | Cloud connectors | Real-time | Free tier limited | Jupyter compatibility, integrations |
| Databricks | Python, SQL, Scala | Cluster-based | Limited, no generative AI | Platform-native | Team notebooks | ~$200+/month | Enterprise scale, Delta Lake, MLOps |
| Observable | JavaScript | Reactive | None | Browser/APIs | Real-time | Free tier | D3/JavaScript visualization elite |
| Google Colab | Python | Sequential | Autocomplete only | Drive/manual upload | Link sharing | Free (paid GPUs) | Free GPUs, Google integration |
| Power BI | DAX, M | ETL-based | Basic Copilot | Extensive connectors | Workspace sharing | $10/user/month | Enterprise BI, Microsoft ecosystem |
Unique Differentiators
Livedocs’ most significant market differentiation emerges from architectural decisions prioritizing AI sophistication, execution performance, and access democratization. The model choice flexibility distinguishing Livedocs from competitors offering fixed or absent AI capabilities enables users to optimize cost-performance tradeoffs, accommodate privacy requirements through local models, and match capabilities to task complexity. This flexibility matters increasingly as AI capabilities diverge across providers and use cases demand specialized model characteristics.
DuckDB and Polars integration delivers quantifiable performance advantages translating to subjective quality improvements. Users experience instant query responses and fluid interactions creating perception of tools as thought extensions rather than external dependencies. This performance advantage compounds through smart caching reducing warehouse costs and improving iteration speed during exploratory analysis. Competitors relying on remote execution or traditional database engines cannot match this responsiveness without substantial infrastructure investment.
The reactive DAG architecture represents a fundamental improvement over sequential notebook execution, guaranteeing reproducibility and enabling parallel computation. While some newer platforms including Observable and Marimo implement reactive models, Jupyter and derivative platforms including Deepnote maintain sequential execution with associated consistency challenges. Livedocs benefits from reactive advantages while maintaining Jupyter compatibility through import/export, positioning itself as evolutionary rather than revolutionary.
Unlimited user access without per-seat licensing removes a primary adoption barrier particularly problematic for large teams and democratization initiatives. Traditional BI platforms and many notebook services charge per active user, creating budget pressures as organizations expand data literacy programs. Livedocs’ pricing model enables broad organizational access without linear cost scaling, potentially accelerating adoption while reducing total cost of ownership.
Terminal access and complete environment control differentiate Livedocs from managed platforms restricting users to predefined configurations. This capability matters particularly for advanced users requiring specialized libraries, custom configurations, or debugging access. The combination of novice-friendly AI assistance and expert-level customization accommodates diverse skill levels within single platforms rather than forcing organizations to maintain separate tools for different proficiency segments.
11. Leadership Profile
Bios Highlighting Expertise & Awards
Public information regarding Livedocs’ founding team, executive leadership, and organizational structure remains conspicuously limited in accessible sources. Comprehensive searches across professional networks, company websites, press releases, and industry publications failed to surface detailed leadership profiles, founder backgrounds, or team credentials. This information opacity contrasts sharply with many startups that leverage founder stories and team expertise as credibility signals during growth phases.
The absence of publicized leadership information may reflect deliberate privacy preferences, early-stage organizational structures lacking formal leadership hierarchies, or simply limited public relations efforts focusing resources on product development rather than brand building. Alternatively, the platform may operate as a project within larger organizations where individual attribution proves complex or inappropriate given collaborative development models.
For prospective customers conducting vendor due diligence, this information gap complicates risk assessment processes. Buyers typically evaluate founder track records, team credentials, and leadership stability as indicators of execution capability and long-term viability. Organizations with strict vendor assessment requirements should directly request leadership information during procurement processes, potentially receiving confidential disclosures unavailable publicly.
Industry recognition through awards, speaking engagements, or thought leadership publications could validate technical expertise and market awareness. The absence of such signals in available sources—no conference keynotes, technical blog posts, podcast appearances, or industry award nominations—suggests either limited public engagement or insufficient archival of such activities by search engines and databases consulted during research.
Patent Filings & Publications
Patent searches and academic publication databases revealed no intellectual property filings or peer-reviewed research papers associated with Livedocs or identifiable team members. This absence aligns with software industry trends where execution speed and market position often provide greater competitive advantage than patent portfolios requiring years to prosecute while publicly disclosing proprietary approaches.
Modern software platforms typically protect innovations through trade secrets, rapid iteration, and network effects rather than formal intellectual property frameworks. Livedocs’ architectural choices—reactive DAG execution, hybrid query resolution, AI agent orchestration—likely constitute proprietary implementations of established computer science concepts rather than patentably novel inventions. The absence of patents therefore neither surprises nor suggests technical deficiency.
Academic publications demonstrating research contributions to notebook architecture, reactive execution models, or AI-augmented data analysis could establish thought leadership and technical credibility. The absence of such publications in available sources suggests Livedocs’ team comprises practitioners focused on product development rather than academic researchers pursuing publishable innovations. This orientation toward applied engineering versus theoretical research characterizes many successful software ventures prioritizing market impact over scholarly recognition.
Technical blog posts, architecture documentation, and engineering deep-dives could substitute for formal publications by demonstrating technical sophistication to practitioner audiences. Limited availability of such content in public sources represents a missed opportunity for community building and technical credibility establishment. Organizations increasingly expect vendor transparency around architectural decisions, performance characteristics, and technical tradeoffs, with comprehensive engineering blogs becoming differentiators in competitive markets.
12. Community & Endorsements
Industry Partnerships
Livedocs maintains strategic technology partnerships with data infrastructure providers and AI model vendors enabling its technical capabilities. Connections to major cloud warehouse platforms including Snowflake, Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, and Databricks occur through official API programs and partnership frameworks. These relationships require ongoing compliance with platform policies, integration maintenance as APIs evolve, and potentially formal partnership agreements defining support responsibilities and co-marketing opportunities.
AI model provider relationships with OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google enable the multi-model capabilities differentiating Livedocs from competitors. These partnerships likely involve commercial agreements defining usage terms, pricing structures, and support arrangements. The ability to offer model choice depends on maintaining good standing across multiple providers, requiring relationship management and potentially negotiated pricing enabling competitive credit allocation to end users.
Open-source integrations with DuckDB, Polars, and Vega-Lite position Livedocs within broader data tooling ecosystems. These relationships differ from commercial partnerships but require technical maintenance as underlying projects evolve, community engagement through contribution or sponsorship, and architectural decisions ensuring compatibility across version upgrades. The health of these open-source dependencies directly impacts Livedocs’ capabilities and performance characteristics.
Distribution partnerships, reseller agreements, or technology alliances extending market reach are not evident in available sources. Livedocs appears to operate direct-to-customer sales models rather than channel strategies leveraging third-party distribution. This approach maintains margin control and customer relationships but limits geographic expansion speed and enterprise account penetration compared to channel-enabled competitors.
Media Mentions & Awards
Media coverage of Livedocs concentrates within data science practitioner communities and software review platforms rather than mainstream technology press. Product Hunt recognition including five-star ratings provides social proof valuable for individual and small team adoption decisions. Mentions on specialized review sites including Moge.AI, Futurepedia, and AIChief extend discoverability through search engines and comparison tools buyers consult during vendor evaluation.
Technical community discussions on Reddit, Hacker News, and developer forums indicate grassroots awareness among sophisticated practitioners. These organic mentions often carry greater credibility than paid advertising or press releases, influencing early adopter segments disproportionately important for platform category formation. The technical depth of community conversations—discussing DAG architectures, DuckDB performance, and AI agent capabilities—suggests engagement from knowledgeable users rather than superficial awareness.
Mainstream technology publication coverage in outlets like TechCrunch, VentureBeat, or industry trades remains absent from available sources. This gap likely reflects Livedocs’ growth-stage profile where funding announcements, major customer wins, or milestone achievements haven’t yet triggered journalist attention. As the platform matures and potentially announces funding rounds or marquee customers, media coverage will likely expand beyond specialized niches into broader technology discourse.
Industry analyst recognition from Gartner, Forrester, or comparable research firms does not appear in accessible sources. Analyst coverage typically follows market share accumulation and enterprise customer traction, with inclusion in Magic Quadrants or Wave evaluations signaling category maturity. The absence of analyst attention positions Livedocs as an emerging player rather than established vendor, which may actually benefit adoption among buyers seeking innovative alternatives unconstrained by analyst-driven procurement processes.
Awards and recognition from industry bodies, technology associations, or innovation competitions could validate product quality and market potential. Available sources do not document such accolades, though this absence may reflect incomplete archival rather than definitively indicating non-receipt. Organizations considering Livedocs adoption should inquire about awards and recognition directly, as vendors frequently highlight such achievements on official channels more reliably archived than distributed press coverage.
13. Strategic Outlook
Future Roadmap & Innovations
Livedocs’ strategic direction emphasizes deepening AI capabilities while expanding data platform breadth. The platform’s positioning as an “AI data scientist” rather than merely an AI-assisted notebook signals ambition toward progressively autonomous workflows where human intent guides analysis while AI handles mechanical execution. This vision aligns with broader industry trends toward agentic AI systems capable of multi-step reasoning and tool use.
Near-term development priorities likely include expanding data source connectors to cover additional warehouses, SaaS applications, and streaming platforms. Comprehensive connectivity eliminates integration friction preventing users from analyzing data regardless of storage location. Each new connector expands addressable use cases while reducing the supplemental tools teams must maintain alongside Livedocs.
AI agent sophistication improvements will likely incorporate recent advances in reasoning models, tool-using agents, and multi-modal understanding. Enhanced agents could proactively suggest analyses based on data characteristics, automatically detect data quality issues and propose remediation, explain statistical results in business terminology tailored to audience expertise, and generate comprehensive reports narratively connecting analysis steps into coherent stories.
Collaboration feature expansion might include video conferencing integration enabling synchronous pair analytics, version history and diff visualization showing how analyses evolved over time, fine-grained permission controls supporting enterprise governance requirements, and workspace templates enabling rapid project initialization with organizational standards. These capabilities address enterprise buyer requirements increasingly important as Livedocs targets upmarket customers.
Security and compliance investments will likely prioritize SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001 certifications addressing enterprise procurement requirements. Additional compliance frameworks including HIPAA, FedRAMP, or industry-specific standards could follow based on target market prioritization. These certifications require six-to-twelve months of preparation and audit processes but dramatically expand addressable market by satisfying risk management and procurement prerequisites.
Market Trends & Recommendations
The data notebook and business intelligence market continues rapid evolution driven by several converging trends. AI integration has transitioned from experimental feature to table-stakes requirement, with buyers increasingly expecting intelligent assistance as default rather than premium capability. Platforms lacking sophisticated AI risk obsolescence as user expectations normalize around conversational interfaces and automated insight generation.
Performance expectations escalate as users experience modern analytical engines including DuckDB and ClickHouse delivering sub-second query responses. Traditional warehouse-dependent notebooks introducing multi-second latencies struggle to compete with local-execution platforms providing instant feedback. This performance gap becomes more pronounced as dataset sizes grow and query complexity increases, creating winner-take-most dynamics favoring fastest platforms.
Democratization initiatives expanding data access beyond technical specialists drive demand for hybrid interfaces serving both code-fluent analysts and natural-language-preferring business users. Platforms succeeding at this balance—providing power-user capabilities without sacrificing accessibility—capture broader organizational adoption than tools optimizing for single persona segments. Livedocs’ combination of terminal access and AI assistance positions well for this trend.
Consolidation pressures push organizations to reduce tool sprawl by seeking platforms unifying previously separate functions. Teams historically maintaining distinct tools for exploration, visualization, collaboration, and automation increasingly prefer integrated environments reducing context switching and integration overhead. Livedocs’ positioning as comprehensive workspace rather than point solution aligns with consolidation preferences.
Recommendations for Livedocs
Accelerate security certification pursuits to unlock enterprise opportunities currently blocked by compliance requirements. SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001 attestations dramatically expand addressable market despite significant time and capital investment. These certifications become prerequisites rather than differentiators in enterprise segments, making delay increasingly costly as competitive platforms complete certification processes.
Expand leadership transparency and team visibility to strengthen vendor credibility during buyer evaluation processes. Publishing founder backgrounds, team profiles, and company milestones provides reassurance to risk-averse buyers conducting due diligence. Technical blog posts demonstrating engineering sophistication build practitioner credibility while improving search visibility and community engagement.
Develop comprehensive pricing documentation clearly delineating free versus paid capabilities, volume discount structures, and enterprise options. Pricing transparency accelerates buyer decision-making by eliminating uncertainty and enabling self-service evaluation. Hidden pricing creates friction particularly problematic for bottom-up adoption models where individual practitioners drive initial evaluation.
Invest in customer success infrastructure supporting enterprise adoption, change management, and value realization. As Livedocs targets larger organizations with complex requirements, proactive success motions including onboarding programs, best practice sharing, and quarterly business reviews improve retention while identifying expansion opportunities. Self-service models adequate for small teams prove insufficient at enterprise scale requiring hands-on support.
Cultivate community-driven content ecosystems including user-generated tutorials, template libraries, and best practice documentation. Community contributions reduce support burden while improving platform stickiness through peer learning and shared resources. Recognition programs celebrating power users incentivize content creation and word-of-mouth advocacy, creating flywheel effects accelerating organic growth.
Recommendations for Prospective Buyers
Conduct thorough pilot testing with representative workloads during free tier evaluation, establishing performance baselines, AI credit consumption patterns, and feature gap identification before committing to paid subscriptions. Representative pilots surface unexpected limitations or capability mismatches better addressed through alternative tools or hybrid architectures rather than discovering post-purchase.
Evaluate security posture through direct vendor engagement including security questionnaires, penetration testing results, and compliance roadmap discussions. Organizations with strict security requirements should understand current capabilities and certification timelines, potentially deferring adoption or limiting scope to non-sensitive use cases until compliance milestones achieve.
Assess leadership team, funding status, and company trajectory through sales conversations and reference customer discussions. Vendor viability concerns warrant direct inquiry about organizational stability, customer retention metrics, and growth momentum. Reference customers provide unbiased perspectives on vendor responsiveness, product reliability, and roadmap delivery that marketing materials cannot capture.
Plan hybrid architectures accommodating Livedocs strengths while maintaining specialized tools for capabilities gaps. Few platforms excel across all dimensions, with thoughtful tool combinations often outperforming single-platform strategies. Livedocs may provide optimal environment for most workflows while complementary tools handle edge cases including extremely large datasets or specialized compliance requirements.
Monitor product development velocity and community growth as indicators of platform momentum and long-term viability. Active development reflected through frequent feature releases, responsive bug fixes, and expanding documentation signals healthy product investment. Growing community participation through forums, content creation, and ecosystem contributions indicates sustainable adoption trajectories rather than transient interest.
Final Thoughts
Livedocs emerges as a compelling entrant in the evolving data notebook market, distinguished by sophisticated AI integration, high-performance architecture, and thoughtful user experience design. The platform’s positioning at the intersection of traditional notebooks, business intelligence platforms, and AI agents creates unique value for teams seeking to modernize analytical workflows while accommodating diverse skill levels and use cases.
The technical foundation—reactive DAG execution, DuckDB and Polars integration, multi-model AI capabilities—reflects deep engineering investment in solving real practitioner pain points rather than superficial feature accumulation. These architectural choices deliver measurable performance advantages translating to qualitative experience improvements where tools feel fast, consistent, and intelligent. For organizations where analytical agility constitutes competitive advantage, these technical merits warrant serious evaluation despite the platform’s relative youth.
However, prospective adopters must weigh innovation benefits against maturity considerations. The absence of security certifications, limited leadership transparency, and sparse enterprise documentation create legitimate vendor risk concerns particularly acute for risk-averse organizations in regulated industries. These gaps likely reflect typical growth-stage prioritization rather than fundamental deficiencies, but nevertheless constrain near-term adoption among conservative enterprise buyers requiring extensive compliance validation.
The platform’s strategic positioning reflects astute market trend identification. As AI capabilities transition from experimental features to baseline expectations, early adoption of AI-native architectures provides sustainable differentiation over platforms retrofitting intelligence onto legacy foundations. Organizations establishing analytical workflows around tools designed for AI augmentation from inception gain productivity advantages competitors cannot easily replicate through incremental upgrades to traditional platforms.
From cost-efficiency perspectives, Livedocs delivers exceptional value particularly for teams currently constrained by per-seat licensing models. The unlimited user access combined with generous free tier enables broad organizational deployment without budget negotiations or usage monitoring. This economic advantage matters substantially for budget-conscious startups, academic institutions, and enterprises seeking to democratize data literacy without proportional tooling cost increases.
Recommendations diverge based on organizational context: innovative teams comfortable with emerging vendors should prioritize Livedocs evaluation given compelling capability advantages and cost benefits; risk-averse enterprises should monitor platform maturation while potentially piloting non-critical use cases; and growth-stage organizations should strongly consider adoption given alignment between platform capabilities and typical scaling-company analytical needs including rapid iteration, cross-functional collaboration, and resource efficiency.
Livedocs represents the emerging class of AI-native analytical tools that will increasingly define modern data workflows. Organizations establishing competency with these platforms early develop analytical muscle memory and organizational capabilities difficult for competitors to replicate. The question facing data leaders is not whether AI will transform analytical workflows—that transformation is underway—but rather which platforms will emerge as category leaders and whether early adoption provides sufficient advantage to justify emerging-vendor risk.
The platform’s trajectory depends on execution across multiple dimensions: maintaining technical innovation pace as competitors respond, achieving security certification milestones unlocking enterprise markets, scaling organizational capacity supporting growing customer bases, and navigating inevitable strategic choices between feature breadth and focused excellence. Organizations betting on Livedocs bet ultimately on team capability and strategic vision—merits difficult to assess given limited public information but inferable from product quality and market positioning.
For teams prioritizing analytical velocity, AI sophistication, and cost efficiency while accepting calculated vendor risk, Livedocs merits serious evaluation. The platform’s strengths address real workflow pain points in ways traditional tools cannot match without fundamental architectural reimagining. Whether Livedocs specifically achieves market leadership matters less than recognizing the platform represents a broader category shift toward intelligent, performant, collaborative analytical environments—a shift forward-thinking organizations should embrace regardless of specific vendor selection.