Table of Contents
Overview
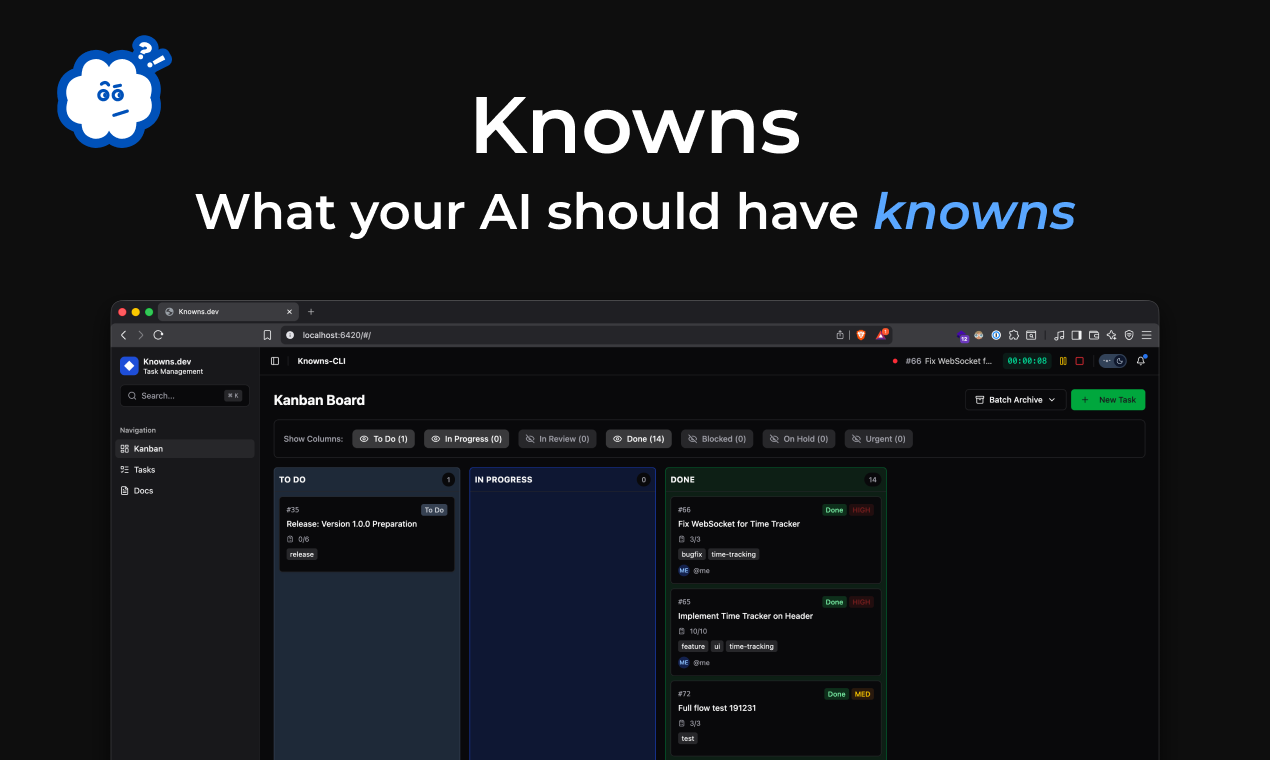
Knowns CLI is a modern, terminal-based workspace designed to solve the “context fragmentation” problem in AI-assisted development. By providing a dedicated knowledge layer that sits on top of your existing files, it allows AI agents to understand project-specific conventions and historical decisions without repetitive prompting. The platform acts as a persistent memory for your repository, using standardized protocols to feed documentation directly into the reasoning loop of your favorite AI coding assistants.
Key Features
- Context-Aware Task Linking: Allows developers to associate specific architectural patterns or documentation files with active tasks, enabling AI agents to pull necessary guidelines automatically.
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) Integration: Features automated setup to register local project memory with AI clients, ensuring a seamless flow of data between your terminal and agents like Claude Code or Cursor.
- Automated Knowledge Extraction: Bridges the gap between execution and documentation by allowing AI to “write back” implemented logic and refined patterns into the project wiki.
- Modular AI Guidelines: Generates stage-specific instructions (e.g.,
knowns agents guideline --stage execution) that synchronize with CLAUDE.md or AGENTS.md files for multi-agent compatibility. - Git-Native Data Storage: Stores all tasks, documentation, and time logs as Markdown files within a local
.knowns/directory, preventing vendor lock-in and allowing for easy version control. - Built-in Productivity Tracking: Includes native time tracking and reporting functionality, allowing developers to manage billing and performance metrics directly from the command line.
How It Works
Knowns CLI functions as a local context server that organizes your project’s intellectual property into a structure readable by AI. When a developer starts a new feature, they create a task in the CLI and link relevant “patterns” or documentation blocks. During the coding session, AI agents use the MCP server provided by Knowns to resolve these references in real-time. Once the task is finished, the AI analyzes the changes and updates the relevant documentation to reflect the new state of the codebase. This cycle ensures that documentation is a living asset that evolves alongside the code, rather than becoming a “stale” artifact.
Use Cases
- AI-Driven Feature Implementation: Guiding coding agents through complex refactors by providing them with the exact architectural patterns they must follow via linked docs.
- Solo Developer Velocity: Optimizing indie hacker workflows by centralizing time tracking, project documentation, and task management in a single, high-speed terminal interface.
- Reducing AI Hallucinations: Preventing coding assistants from making incorrect assumptions about a codebase by providing a “ground truth” through persistent project memory.
- Automated Client Reporting: Leveraging the built-in time tracker to generate accurate work logs and implementation summaries for external stakeholders.
Pros & Cons
Advantages
- Eliminates Manual Context Sharing: Saves significant time by removing the need to copy-paste documentation or project rules into every new AI chat session.
- High Developer Ergonomics: Designed for a CLI-first workflow, keeping developers in their flow state without the distraction of a separate web-based UI.
- Privacy and Control: Since all data is stored as local Markdown files, teams maintain full ownership and privacy over their project’s most sensitive documentation.
- Standardized Protocol Support: By adopting MCP, Knowns ensures long-term compatibility with the rapidly growing ecosystem of AI tools and models.
Disadvantages
- Limited Non-Technical Appeal: The command-line-only interface is specifically built for developers and may be less accessible to project managers or non-technical contributors.
- Dependency on AI Quality: The “write-back” feature’s effectiveness is tied to the underlying reasoning capabilities of the AI model being used for the task.
How Does It Compare?
- Linear
- Best for: Large-scale team project management with heavy administrative requirements.
- Key Distinction: Linear is a high-level tracking tool. Knowns CLI is an execution-level “knowledge bridge” that feeds task context directly into AI reasoning loops.
- Obsidian
- Best for: Personal knowledge management and “second brain” note-taking.
- Key Distinction: Obsidian is a passive note-taking tool. Knowns CLI is an “active” documentation layer that links project notes to specific task execution and automated AI workflows.
- Claude Code / Cursor Agent
- Best for: Real-time code editing and AI-assisted programming.
- Key Distinction: These are the “users” of the context. Knowns CLI provides the “source” of that context, acting as the structured memory that these coding agents query to avoid mistakes.
- Aider
- Best for: Terminal-based pair programming and automated file editing.
- Key Distinction: Aider focuses on the “act” of coding. Knowns focuses on the “organization” of the knowledge and tasks surrounding that code, often used alongside tools like Aider to provide a richer context.
- Taskwarrior
- Best for: Minimalist, terminal-only task management for power users.
- Key Distinction: Taskwarrior is a traditional task manager. Knowns CLI is an AI-native workspace that integrates the “reasoning” behind a task into its management flow.
Final Thoughts
Knowns CLI represents a fundamental shift in how developers maintain “mental state” during AI-assisted programming. By moving documentation from a secondary reference into a primary input for AI reasoning, it significantly reduces the friction of modern software development. While it remains a niche tool for terminal enthusiasts and solo makers, its adoption of the Model Context Protocol suggests it will become an essential component of the professional AI-native developer stack. For those tired of “re-explaining” their projects to AI every morning, Knowns CLI offers a high-performance, local-first solution that truly enables “zero-context” prompting.