Table of Contents
Overview
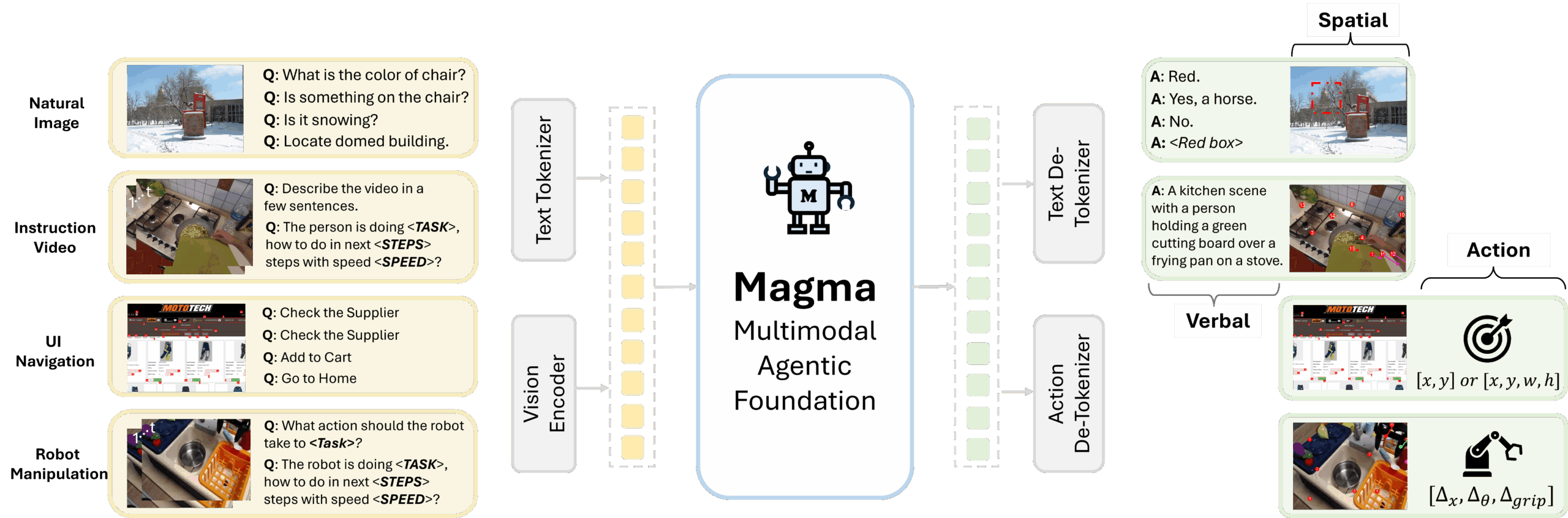
The world of AI is constantly evolving, and Microsoft Research is pushing boundaries with its latest creation: Magma. This innovative foundation model is designed to power multimodal AI agents capable of navigating both digital interfaces and the physical world. Imagine AI that can understand what it sees, reads, and is told, then act accordingly. That’s the promise of Magma, a powerful tool poised to reshape how we interact with technology. Let’s dive into the details of this exciting development.
Key Features
Magma boasts a range of impressive features that set it apart in the AI landscape:
- Multimodal Input Processing: Magma can simultaneously process images, text, and contextual data, allowing for a richer understanding of its environment.
- Integration of Vision, Language, and Actions: By combining these three core capabilities, Magma can perform complex tasks that require understanding and responding to the world around it.
- Cross-Platform Adaptability: This model is designed to operate across various platforms, making it versatile for different applications.
- Capable of Real and Virtual Environment Interaction: Magma can interact with both physical environments through robots and virtual environments through software interfaces.
- Foundation Model Architecture: Built upon a foundation model, Magma can be fine-tuned for specific tasks, making it highly adaptable.
How It Works
Magma’s functionality hinges on its ability to process diverse inputs and translate them into actionable steps. The model ingests multimodal data – images, text, and contextual information – to build a comprehensive understanding of its surroundings. This understanding then informs its actions, whether it’s navigating a user interface, controlling a robot, or interacting with a smart environment. Magma is trained on a vast dataset, enabling it to perform tasks that involve visual reasoning, UI navigation, and physical interactions. This comprehensive training allows it to adapt to various scenarios and execute tasks effectively.
Use Cases
Magma’s unique capabilities open doors to a wide array of applications:
- Human-Computer Interaction Research: Magma can be used to explore new ways for humans and computers to interact, leading to more intuitive and efficient interfaces.
- Robotic Control: By providing robots with the ability to understand their environment, Magma can enable more sophisticated and autonomous robotic systems.
- Multimodal Assistant Development: Magma can power AI assistants that can understand and respond to both visual and textual cues, creating a more natural and helpful user experience.
- Smart Environment Navigation: Magma can be used to create AI agents that can navigate and interact with smart environments, such as smart homes and offices.
- Interface Automation Testing: Magma can automate the testing of user interfaces, ensuring that they are user-friendly and functional.
Pros & Cons
Like any cutting-edge technology, Magma has its strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages
- Unified Model for Multiple Modalities: Magma offers a single model capable of handling various types of data, simplifying development and deployment.
- Capable of Real-World Deployment: Its design allows for integration into real-world applications, making it more than just a theoretical concept.
- State-of-the-Art Research Foundation: Built upon the latest research, Magma represents a significant advancement in AI technology.
Disadvantages
- Still Experimental: As a relatively new technology, Magma is still in the experimental phase, and its capabilities may evolve over time.
- High Compute Requirements: Running Magma requires significant computational resources, which may limit its accessibility.
- Limited Public Accessibility: Currently, access to Magma is limited, primarily for research purposes.
How Does It Compare?
When comparing Magma to other multimodal AI models, several key differences emerge. OpenAI’s GPT-4V is another powerful multimodal model, but it is more general-purpose. Magma, on the other hand, is specifically tailored for interaction tasks. Google DeepMind’s RT-2 is focused on robotics, while Magma offers more flexibility in terms of interface interaction. This specialization makes Magma a strong contender for applications requiring precise control and understanding of both digital and physical environments.
Final Thoughts
Magma represents a significant step forward in the development of multimodal AI agents. Its ability to integrate vision, language, and action capabilities opens up exciting possibilities for human-computer interaction, robotics, and smart environments. While it’s still in its early stages and faces challenges in terms of accessibility and computational requirements, Magma’s potential to transform how we interact with technology is undeniable. Keep an eye on this space, as Magma and similar technologies are poised to shape the future of AI.