Table of Contents
Overview
As AI coding capabilities become increasingly sophisticated, the challenge shifts from individual agent performance to orchestrating multiple agents working in concert on complex projects. agor, an open-source platform by Preset, addresses this emerging need by providing the first truly multiplayer orchestration environment for AI coding agents. Rather than treating AI assistants as isolated tools or simple extensions to traditional IDEs, agor reimagines agent coordination as a spatial, real-time activity where human developers and multiple AI agents collaborate simultaneously on a shared canvas. Think of it as Figma for AI coding—developers can deploy multiple Claude Code, OpenAI GPT-4, and Google Gemini agents working in parallel on different aspects of a project, all coordinated through Git-linked worktrees, visual workflow automation, and real-time team presence indicators. Launched in November 2025, agor represents a fundamental rethinking of how development teams can leverage multiple AI agents effectively.
Key Features
agor delivers comprehensive agent orchestration capabilities designed for team-based AI coding workflows:
- Agent swarm control: Deploy and coordinate multiple Claude Code, OpenAI GPT-4 (formerly Codex), and Gemini sessions simultaneously, with each agent working independently or collaboratively on parallel tasks through the built-in MCP server coordination layer.
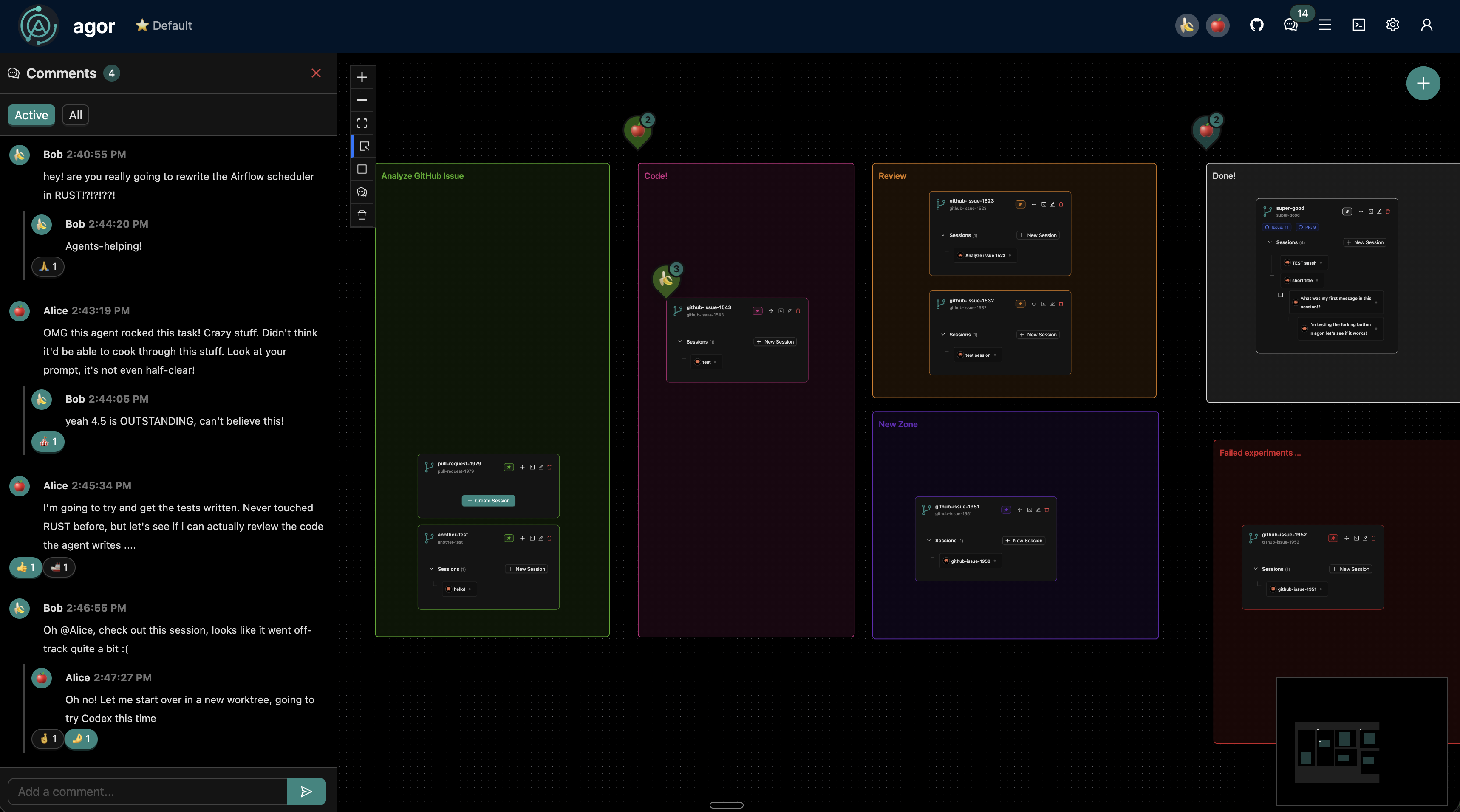
- Multiplayer spatial canvas: Organize AI coding sessions across a Figma-style 2D board where teams can visualize agent progress, share context, and coordinate through spatial comments, emoji reactions, and persistent annotations pinned to specific zones.
- Git-linked worktrees: Each agent session maintains an isolated Git worktree with automatic port management and environment configuration, enabling reproducible, isolated development environments that prevent conflicts and resource collisions.
- Zone-triggered automation: Define spatial workflow zones that automatically trigger templated prompts when agents enter them, enabling sophisticated multi-step automation sequences like “review when complete” or “test before deployment.”
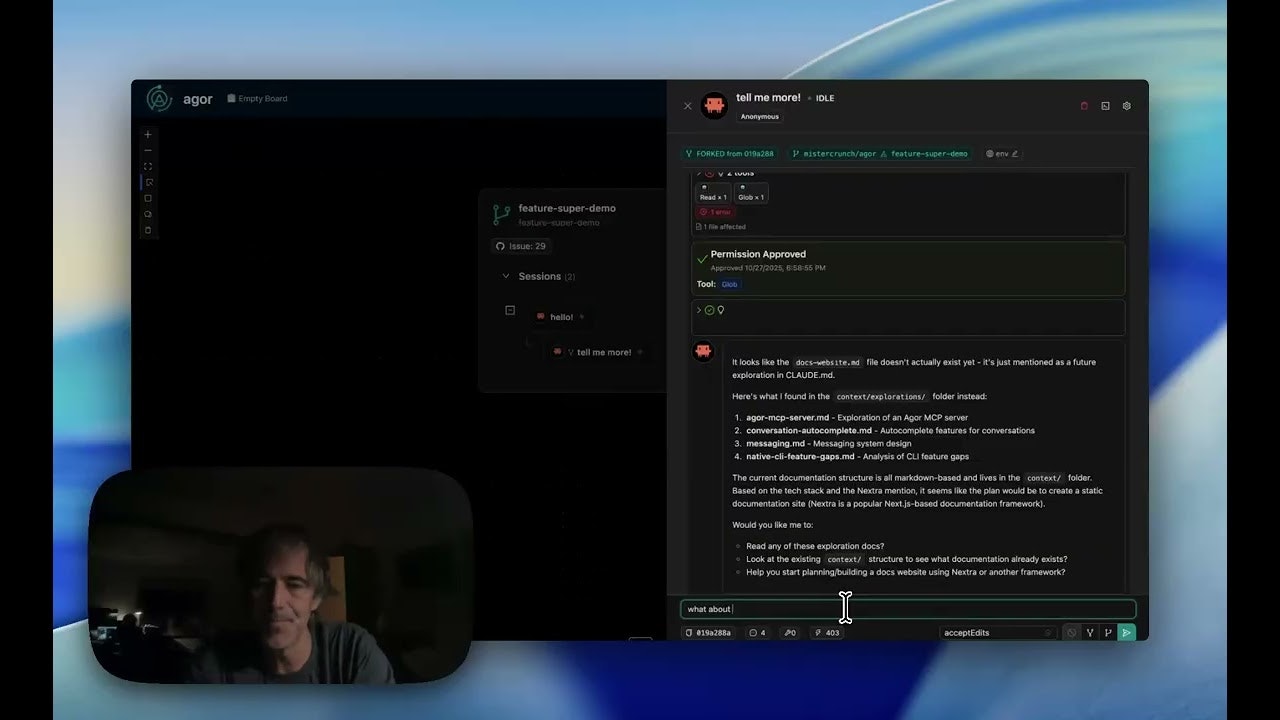
- Session trees and forking: Create hierarchical agent workflows—fork sessions to explore alternative approaches without losing the original path, spawn subsessions for focused subtasks that report back to parent sessions, and visualize the complete session genealogy.
- Real-time multiplayer presence: WebSocket-powered multi-cursor indicators, live presence awareness, and collaborative cursor broadcasting let teams and agents see who’s working where in real-time.
- Integrated MCP server: Model Context Protocol implementation enables agent-to-agent communication, supervision, and coordination without external tools, allowing agents to ask other agents for help or escalate decisions.
- Built-in scheduler: Trigger templated prompts on custom cadences, enabling background agent work, periodic reviews, and scheduled automation sequences that run according to team-defined timelines.
- Pluggable agent providers: Extensible architecture supports additional agent providers beyond the three primary platforms, with modular design for custom integrations.
- Mobile-optimized interface: Access agent sessions, send prompts, and monitor progress from mobile devices with a responsive UI designed for on-the-go management.
How It Works
agor’s architecture emphasizes spatial organization and team coordination. Teams begin by initializing agor on their local development environment using the npm-based CLI tool. The setup creates a daemon that manages agent orchestration, Git worktree isolation, and MCP server coordination. Teams then access the web UI to visualize the spatial canvas—a 2D board representing the current project’s orchestration topology.
From there, teams define zones by drawing regions on the canvas. Within each zone, teams configure zone triggers—templated prompts that execute whenever an agent enters that region. For example, a “Review” zone might trigger a prompt like “Review this code and suggest improvements.” An agent placed in that zone automatically receives the prompt and begins its review task.
Multiple agents (Claude Code, GPT-4, Gemini) can be deployed simultaneously to different zones or tasks. Each agent runs in an isolated Git worktree with its own port allocation and environment, preventing resource conflicts. The MCP server layer enables agents to communicate—one agent can ask another for information, escalate decisions, or request assistance on specific subtasks.
All activity appears on the spatial canvas with real-time cursor indicators showing where each team member and agent is focused. Comments pinned to specific zones create persistent context. The built-in scheduler enables automated workflows—agents can be triggered on intervals or based on conditions, enabling background work that requires no human intervention.
Every change pushes to the linked Git repository automatically when teams approve. The entire orchestration state (agent positions, zone triggers, session trees) remains version-controlled and reproducible, enabling teams to run identical orchestration sequences across multiple projects or time periods.
Use Cases
agor’s agent orchestration capabilities serve diverse development scenarios where parallel processing, team coordination, and workflow automation prove valuable:
- Parallel pull request workflows: Deploy multiple agents to review different aspects of a large PR simultaneously—one reviews logic, another checks security, a third validates performance implications—then aggregate findings in the spatial canvas.
- Multi-model code generation strategies: Explore different implementation approaches by deploying Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini to the same problem concurrently, then compare results and select the strongest approach.
- Continuous automated code review: Station agents in “review zones” that automatically analyze all commits to a branch, providing immediate feedback without waiting for human reviewers.
- Large-scale refactoring projects: Coordinate multiple agents across different modules of a large codebase, with spatial zones organizing work by feature/component and preventing cross-cutting concerns.
- Isolated regression testing: Spin up temporary test environments with agents assigned to run test suites in isolation, with automatic cleanup and port management preventing conflicts.
- Context-switching reduction: Teams using agor report dramatically reduced context switching compared to juggling multiple tools—all orchestration happens in one spatial canvas.
- Reproducible development workflows: Version-controlled orchestration state enables teams to record successful workflows and replay them identically for similar projects.
- Learning and experimentation: Students, researchers, and developers exploring multi-agent architectures benefit from agor’s visual orchestration and real-time feedback.
Pros \& Cons
Advantages
- Open-source with self-hosting: Full source code available on GitHub; deploy on your infrastructure without vendor lock-in or recurring licensing costs.
- True multiplayer orchestration: Genuinely novel approach to agent coordination—no other tool provides spatial canvas orchestration for multiple AI agents.
- Git-native design: Deep integration with Git worktrees and automatic repo management means developers work in familiar version control contexts.
- MCP implementation: Built-in Model Context Protocol enables agent-to-agent communication without external orchestration layers.
- Reproducible environments: Isolated worktrees, automatic port management, and version-controlled orchestration state enable identical automation across teams and time.
- Extensible architecture: Pluggable agent providers and customizable zone triggers enable integration with emerging AI platforms.
- No vendor lock-in: Unlike commercial alternatives, agor’s open-source nature prevents dependency on proprietary platforms or APIs.
- Rich feature set for collaborative teams: Multi-cursor presence, spatial comments, session trees, and automated workflows exceed most developer tools’ collaboration features.
Disadvantages
- Steeper learning curve: Spatial canvas metaphor and zone-trigger architecture require conceptual investment compared to simpler agent tools.
- Multiplayer-first design: While solo users can use agor effectively, the platform clearly optimizes for team coordination; solo workflows may feel over-engineered.
- Local infrastructure requirements: Self-hosting requires infrastructure management, daemon configuration, and operational overhead; no managed SaaS option currently available.
- Agent provider dependency: Quality depends on Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini’s capabilities; improvements to underlying models automatically improve agor, but limitations are inherited.
- Emerging ecosystem: As a recently launched platform, the integration ecosystem remains limited; advanced extensions or third-party zone templates are still developing.
- Mobile UI trade-offs: While mobile-responsive, the spatial canvas loses nuance on small screens; full orchestration management remains desktop-optimal.
- Initial setup complexity: Worktree isolation, daemon configuration, and environment setup require technical expertise; non-technical team members may struggle with initial configuration.
How Does It Compare?
The agent orchestration landscape encompasses multiple distinct categories, each serving different developer needs:
GitHub Copilot Teams (\$30/user/month) provides AI-assisted coding with chat, code generation, and team context management built into GitHub. It emphasizes seamless IDE integration and GitHub’s native ecosystem. However, Copilot Teams focuses on single-agent assistance; it doesn’t orchestrate multiple agents or provide workflow automation. Teams receiving Copilot suggestions don’t coordinate agent efforts or manage parallel AI activities. agor’s strength lies precisely where Copilot Teams has minimal capability: orchestrating multiple independent agents on complex, parallelizable tasks. For teams prioritizing GitHub integration and single-agent assistance, Copilot Teams remains simpler; for teams wanting multi-agent orchestration, agor is essential.
AutoGPT (open-source) provides agent autonomy—a single agent that can recursively break down tasks and execute them with access to tools. AutoGPT emphasizes autonomous task execution; agor emphasizes coordinated multi-agent work. AutoGPT excels at single-agent problem-solving; agor excels at teams directing multiple agents toward shared goals. They serve complementary but different philosophies: AutoGPT = single agent autonomy; agor = multi-agent choreography.
MetaGPT (open-source) simulates role-based multi-agent teams (product manager, architect, developer, tester roles working together). MetaGPT provides a framework for agents to play specific roles and communicate. However, MetaGPT focuses on role-based simulation; agor focuses on spatial orchestration and workflow automation. MetaGPT agents execute sequentially within predetermined roles; agor agents can work in parallel across arbitrary tasks defined by teams. For simulated team-based workflows, MetaGPT’s role-based approach is elegant; for teams wanting flexible, visual agent coordination, agor’s spatial canvas is more intuitive.
Dify (open-source) provides a low-code platform for building AI workflows with visual flow editors and multi-step automation. Dify supports multiple agent types and workflow coordination. However, Dify targets business process automation broadly; agor specifically targets development teams and Git workflows. Dify’s strength is business process flexibility; agor’s strength is developer-centric integration with Git, worktrees, and code-specific orchestration patterns.
Microsoft Agent Framework (via Azure/Copilot Studio) provides orchestration for agents across Microsoft 365, Azure Services, and custom applications. It emphasizes enterprise integration and compliance. However, Microsoft Agent Framework targets enterprise customers with existing Microsoft investments; agor targets individual developers and small teams. Microsoft’s approach is platform-first; agor’s approach is developer-first and self-hostable.
LangChain Agent Frameworks (open-source) provide Python/TypeScript libraries for building agents with tool access and reasoning loops. LangChain is infrastructure for building agents; agor is infrastructure for coordinating multiple agents. Developers use LangChain to construct agent logic; developers use agor to deploy and orchestrate LangChain agents (or other agents) across teams.
agor’s distinctive positioning centers on its unique combination of spatial orchestration, Git integration, and multiplayer coordination. While other platforms orchestrate agents through sequential task flows or role definitions, agor visualizes coordination spatially—allowing teams to literally see where each agent is working, dragging agents between zones, and defining automated workflows through spatial zones rather than traditional DAGs or flow diagrams. This visual approach, combined with Git-native design and true multiplayer presence indicators, creates a genuinely novel development experience. For teams managing multiple agents on complex projects, agor offers orchestration capabilities that existing tools don’t provide.
Final Thoughts
agor represents a fundamental rethinking of how development teams engage with multiple AI agents. Rather than viewing agents as individual assistants or tools to be called sequentially, agor treats agent orchestration as a team sport—something requiring coordination, real-time awareness, spatial organization, and workflow automation. The spatial canvas metaphor proves intuitive for developers accustomed to collaborative tools like Figma or Miro. For teams deploying multiple Claude Code, GPT-4, and Gemini agents, agor’s ability to coordinate parallel agent work, visualize progress, and automate workflows addresses genuine pain points in current development practices. The open-source model with self-hosting options eliminates vendor lock-in concerns that often plague commercial agent platforms. While the steeper learning curve and local infrastructure requirements represent trade-offs, the capability to orchestrate truly parallel, coordinated, multi-agent workflows makes agor compelling for development teams at the frontier of AI-driven development. As AI agents become increasingly capable and teams expand their use of multiple specialized agents, agor positions itself as essential infrastructure for managing that complexity.