Table of Contents
Overview
The AI development landscape transformed dramatically on October 15, 2025, when Anthropic introduced Agent Skills, a revolutionary feature enabling Claude to dynamically load specialized expertise through modular instruction packages. Within days, the community responded with Claude Skills Hub, an independent directory built to help users navigate this emerging ecosystem.
Claude Skills Hub serves as a centralized discovery platform for Claude Skills, the new capability pattern that allows users to teach Claude specialized, repeatable tasks through structured folders containing instructions, scripts, and resources. Rather than re-explaining processes or brand guidelines in every conversation, Skills enable persistent knowledge that Claude automatically activates when relevant to the task at hand.
Built by independent developer EconomistThis5542 using a fully serverless architecture on Cloudflare Pages with D1 database and R2 storage, Claude Skills Hub aggregates both official Anthropic skills and community-created skills from prominent collections like BehiSecc’s awesome-claude-skills and travisvn’s repositories. Launched on Product Hunt on October 22, 2025, where it garnered 121 upvotes and 66 comments, the platform addresses a critical need that emerged immediately following Anthropic’s Skills announcement: how to discover, evaluate, and integrate skills when they’re scattered across GitHub and other repositories.
The platform provides intuitive search powered by MiniSearch, category-based filtering, instant ZIP downloads for quick integration, and a roadmap toward sandbox testing directly connected to Claude’s API. While GitHub submission and embedded testing remain in development as of late October 2025, the core discovery and distribution functionality already serves the growing Claude community seeking to enhance their AI workflows.
Understanding Claude Skills Hub requires grasping what Claude Skills fundamentally are. Skills represent a paradigm shift from one-off prompts to reusable, composable capability packages. Each skill is a directory containing a SKILL.md file with YAML frontmatter metadata, natural language instructions, and optional executable scripts or reference documents. Claude preloads lightweight metadata from all available skills at session start, consuming only a few dozen tokens per skill. When a user request matches a skill’s domain, Claude loads the full instructions and resources on-demand, maintaining speed while accessing specialized expertise.
This three-level progressive disclosure architecture enables teams to install dozens of skills without performance degradation. Skills work uniformly across Claude.ai, Claude Code, and the Anthropic API, providing genuine portability. They can stack together with Claude automatically coordinating multiple skills for complex workflows. Perhaps most importantly, skills can include executable code for tasks where programmatic reliability exceeds language model generation, such as mathematical calculations, data processing, API calls, or file operations.
Key Features
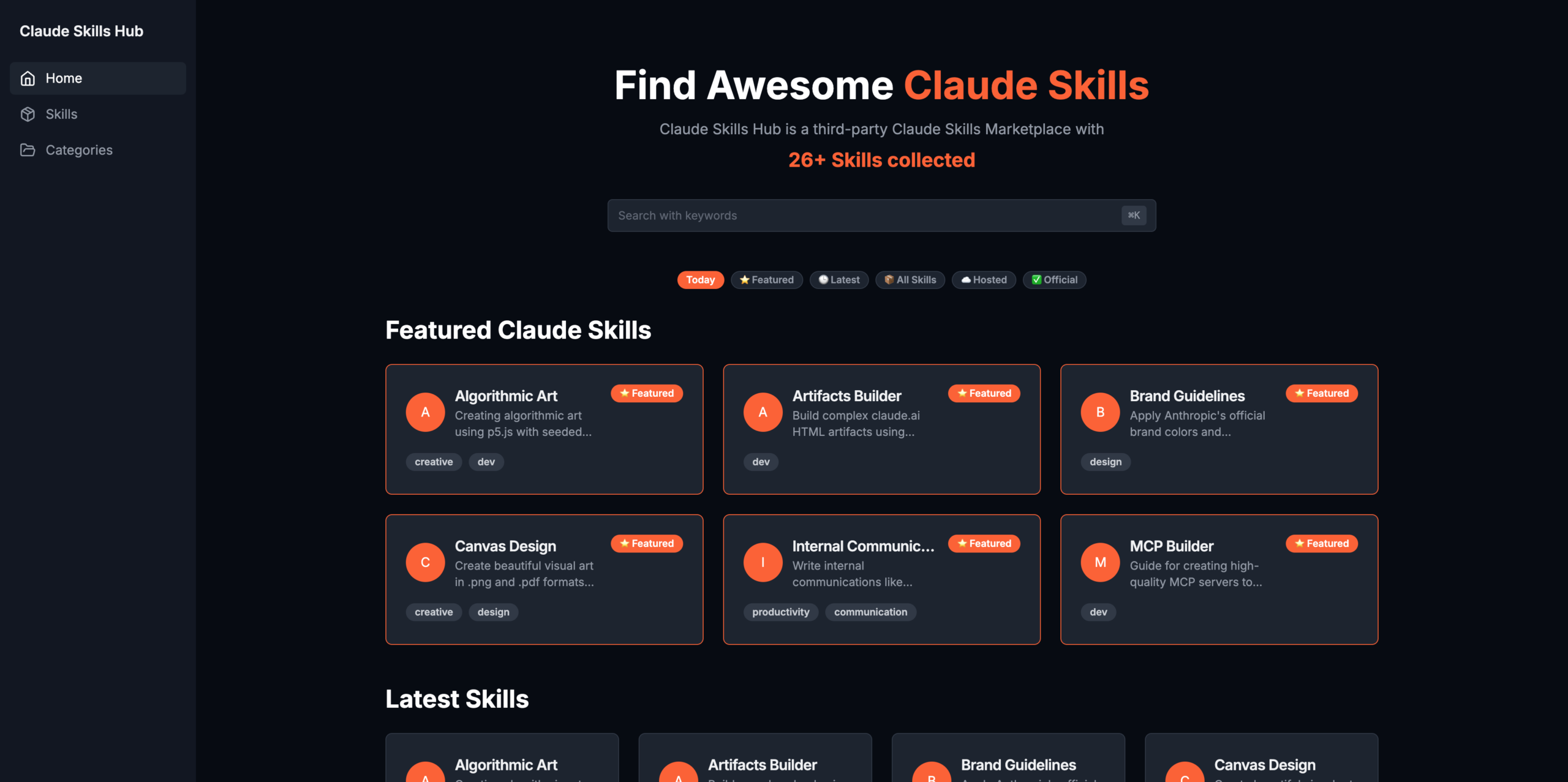
Claude Skills Hub delivers focused functionality designed to accelerate skill discovery and adoption within the Claude ecosystem:
Comprehensive Skill Search: Navigate an expanding catalog using MiniSearch-powered search that queries skill names, descriptions, categories, and tags. The search interface enables rapid discovery when you need specific capabilities like “Excel analysis,” “brand guidelines,” or “API integration,” surfacing relevant skills instantly from the aggregated collection.
Advanced Category Filtering: Browse skills organized by functional categories including data analysis, document generation, coding assistance, design tools, automation workflows, and communication templates. Tag-based filtering further refines results, allowing users to narrow searches by programming language, file format, industry vertical, or skill complexity level.
Instant ZIP Downloads: Access complete skill packages through one-click ZIP downloads containing the full directory structure with SKILL.md files, scripts, and resources. These packages integrate immediately into Claude Code’s filesystem-based skills directory or upload to Claude.ai through the web interface, eliminating manual file assembly.
Curated Official and Community Skills: The hub currently aggregates all 15 official Anthropic pre-built Agent Skills covering document creation in .docx, .xlsx, and .pptx formats, alongside community contributions from established collections including BehiSecc’s awesome-claude-skills repository with specialized tools and travisvn’s curated skill library. The catalog expands continuously as new community skills emerge.
Embedded Sandbox Testing: An in-development feature that will enable users to test skills in a dedicated sandbox environment connected directly to Claude’s API before downloading. This preview capability ensures skills meet expectations and function correctly within your specific use case, reducing trial-and-error integration cycles.
GitHub Direct Submission: A planned feature allowing developers to contribute their own Claude Skills by submitting GitHub repository links. This submission workflow will enable community growth while maintaining quality through review processes, fostering a collaborative ecosystem where expertise becomes shareable infrastructure.
Serverless Architecture: Built entirely on Cloudflare’s edge infrastructure with Pages for hosting, D1 for database operations, and R2 for skill package storage. This serverless foundation ensures global availability, minimal latency, and cost-efficient operation while maintaining open-source compatibility for community contributions and transparency.
Detailed Skill Metadata: Each listed skill displays comprehensive information including creator attribution, last update timestamps, download counts, category classifications, compatibility notes, and usage examples. This metadata helps users evaluate skill quality and relevance before integration.
How It Works
Claude Skills Hub operates as an aggregation and distribution layer connecting skill creators with Claude users through a streamlined discovery workflow.
The platform continuously monitors multiple source repositories including Anthropic’s official skills repository and prominent community collections on GitHub. Automated processes extract skill metadata from SKILL.md files, including names, descriptions, categories, and tags. This information populates a searchable D1 database that powers the hub’s discovery interface.
When users visit Claude Skills Hub, they encounter a clean catalog interface presenting available skills with preview information. The MiniSearch-powered search engine enables natural language queries that match against skill metadata, returning ranked results based on relevance. Category and tag filters provide alternative navigation paths for exploratory browsing when users aren’t certain which specific skill they need.
Upon identifying a relevant skill, users can download the complete skill package as a ZIP file. This package contains the full directory structure required for Claude Skills, including the SKILL.md configuration file with YAML frontmatter and instructions, any executable scripts referenced by the skill, supporting documents or reference materials, and folder organization that matches Claude’s expected structure.
For Claude Code users who prefer filesystem-based skills, the downloaded package extracts directly into either personal skills directories at ~/.claude/skills/skill-name/ for cross-project availability, or project-specific skills at .claude/skills/skill-name/ within individual project directories. Claude Code automatically discovers these skills through filesystem scanning, making them immediately available.
For Claude.ai users on Pro, Max, Team, or Enterprise plans with code execution enabled, skills upload through Settings > Features > Skills as ZIP files. The web interface validates the skill structure, extracts metadata, and makes the skill available across conversations. Custom skills remain individual to each user rather than organization-wide, though Enterprise deployments may eventually support central management.
Once integrated, skills enhance Claude’s capabilities through the three-level progressive disclosure mechanism. At session start, Claude preloads lightweight metadata from all available skills, typically consuming 20-50 tokens per skill regardless of complexity. This minimal context awareness enables Claude to identify potentially relevant skills without performance impact. When a user request semantically matches a skill’s domain based on the loaded metadata, Claude loads the full SKILL.md instructions and any referenced documents, applying this specialized knowledge to the task. For skills containing executable code, Claude invokes these scripts as tools at its discretion, running calculations, processing data, or making API calls with programmatic reliability.
The planned sandbox testing feature will extend this workflow by enabling preview execution before download. Users would select a skill, configure any required parameters or API keys, and watch Claude apply the skill to sample tasks within an isolated environment. This preview capability will surface compatibility issues, clarify skill behavior, and validate expectations before committing to full integration.
Use Cases
Claude Skills Hub enables practical applications across diverse workflows where specialized, repeatable Claude capabilities deliver value:
Brand Consistency Enforcement: Download skills that encode your organization’s brand guidelines, tone of voice, visual standards, and communication templates. Rather than explaining brand requirements in every conversation, Claude automatically applies your established standards when generating presentations, emails, social media content, or marketing materials. Teams maintain consistency across AI-generated content without constant supervision.
Specialized Data Analysis: Acquire skills containing custom formulas, statistical methods, or analytical frameworks specific to your industry or role. Financial analysts can install skills that apply proprietary valuation models. Data scientists can integrate skills with specialized data cleaning routines. Healthcare professionals can leverage skills that parse medical terminology or calculate clinical metrics according to established protocols.
Code Generation Standards: Implement skills that teach Claude your team’s coding conventions, architectural patterns, testing requirements, and documentation standards. Development teams ensure AI-generated code adheres to established practices without manual review cycles. Skills can encode framework-specific patterns, security requirements, accessibility guidelines, or performance optimization techniques.
Document Generation Automation: Utilize skills for creating recurring document types with consistent structure and formatting. Generate quarterly business reviews that follow your template. Produce client proposals matching your standard sections. Create meeting notes with your preferred organization. Transform raw discussion transcripts into polished executive summaries using established frameworks.
API Integration Workflows: Deploy skills containing authentication patterns, endpoint documentation, and integration logic for your frequently used services. Skills can abstract complex API interactions into simple natural language commands, enabling Claude to fetch data from your CRM, post updates to project management tools, retrieve analytics from business intelligence platforms, or synchronize information across your tool ecosystem.
Creative Brief Development: Install skills that guide Claude through your creative process, asking the right questions, organizing responses into your brief template, and ensuring all required elements are captured. Design agencies can codify their discovery process. Content teams can standardize campaign planning. Product managers can structure feature specifications using proven frameworks.
Educational Content Creation: Leverage skills designed for curriculum development, lesson planning, assessment design, or learning material adaptation. Educators can build skills that format content according to pedagogical principles, adjust complexity for different learning levels, or generate practice problems following specific instructional theories.
Custom Workflow Automation: Combine multiple skills to orchestrate complex, multi-step workflows. A content publication workflow might stack skills for research synthesis, outline generation, first draft creation, brand guideline application, and SEO optimization. Each skill handles its specialized component while Claude coordinates the overall sequence.
Skill Modification and Learning: Download existing skills as starting points, then modify them to precisely fit your unique requirements. Study well-designed skills to understand effective instruction patterns. Evolve your skill library organically as workflows mature and requirements change.
Pros \& Cons
Advantages
Centralized Discovery for Emerging Ecosystem: Claude Skills Hub solves the immediate problem that emerged following Anthropic’s Skills launch: scattered resources across GitHub repositories, Discord channels, and social media make finding relevant skills time-consuming. The hub aggregates skills from multiple authoritative sources into a searchable, categorized directory that eliminates discovery friction.
Free Access and Community-Driven Growth: The platform operates without subscription fees, paywalls, or usage limitations, making skill discovery accessible to all Claude users. The community-driven model with planned GitHub submission enables organic growth where the collective expertise of Claude users becomes shared infrastructure benefiting the entire ecosystem.
Immediate Integration Through ZIP Downloads: Ready-to-use ZIP packages eliminate manual file assembly, folder structure creation, or YAML formatting. Users download complete, validated skill packages that integrate directly into Claude Code or Claude.ai, reducing the technical barriers that might otherwise prevent skill adoption among non-developer users.
Quality Signal Through Curation: By aggregating from established collections like BehiSecc’s and travisvn’s repositories rather than accepting arbitrary submissions, Claude Skills Hub provides an initial quality filter. Users can trust that listed skills come from vetted sources, reducing concerns about malicious or poorly designed skills.
Serverless Architecture Ensures Availability: The Cloudflare infrastructure provides global edge distribution, automatic scaling, and high reliability without operational overhead. Users experience fast load times regardless of geographic location, and the platform remains accessible even during traffic spikes following new Anthropic feature announcements.
Open-Source Friendly Foundation: The serverless architecture and community focus create an environment conducive to transparency and contribution. The platform’s technical choices suggest willingness to open development processes, potentially enabling community participation in roadmap decisions and feature implementation.
Disadvantages
Early Development Stage With Incomplete Features: Launched merely a week after Anthropic introduced Skills, Claude Skills Hub remains in active development with critical features like sandbox testing and GitHub direct submission still in progress as of late October 2025. Users may encounter evolving interfaces, changing organization schemes, or gaps in functionality as the platform matures.
Limited to Claude Ecosystem: The platform serves exclusively Claude users on Pro, Max, Team, or Enterprise plans with code execution enabled. This limits the addressable audience compared to cross-platform tools and creates no value for users of other AI models like GPT-4, Gemini, or open-source alternatives. Organizations committed to model diversity may find skills lock them further into Anthropic’s ecosystem.
No Quality Validation or Testing Beyond Source Reputation: While aggregating from established collections provides some quality signal, Claude Skills Hub does not currently validate that skills function as described, contain secure code, or follow best practices. Users download skills based on descriptions and creator reputation without objective quality metrics or peer review processes.
Dependency on External Repositories: The hub’s value depends on the continued maintenance and growth of source repositories like BehiSecc’s and travisvn’s collections. If these community maintainers lose interest, experience burnout, or pivot to other projects, Claude Skills Hub’s catalog could stagnate. No clear sustainability model ensures long-term curation.
Unclear Relationship With Anthropic: As an independent community project rather than an official Anthropic platform, Claude Skills Hub’s long-term position remains uncertain. Anthropic could launch an official skills marketplace that supersedes the hub, leaving early adopters on a deprecated platform. The lack of formal partnership or recognition creates strategic risk.
Individual User Skills Only: Skills uploaded to Claude.ai remain individual to each user without organization-wide deployment or central administration capabilities. Enterprise teams cannot currently push curated skill libraries to all employees, requiring each team member to manually discover, download, and upload skills independently. This limits enterprise adoption efficiency.
How Does It Compare?
Claude Skills Hub occupies a unique position in the AI customization landscape, addressing needs distinct from existing platforms while facing competition from both community efforts and potential official alternatives:
GitHub Direct Repositories like BehiSecc’s awesome-claude-skills and travisvn’s collections represent the decentralized alternative. These curated lists provide direct access to skill repositories with full source code visibility and Git version control. However, GitHub requires users to manually browse repository READMEs, clone or download individual skills, and assemble folder structures correctly. There’s no unified search across collections, no standardized metadata presentation, and no preview or testing capability. Claude Skills Hub aggregates these repositories while adding search, categorization, and packaged downloads that streamline adoption.
OpenAI’s GPTs Marketplace offers conceptual similarities as a discovery platform for customized AI capabilities. However, GPTs operate on a fundamentally different architecture. GPTs are self-contained, closed-source configurations hosted entirely on OpenAI’s infrastructure with revenue sharing for creators and centralized quality control. Skills are open, portable directory structures that users control and modify. GPTs require no local setup but offer no code visibility or modification capability. The comparison highlights philosophical differences between platform-controlled customization and user-owned capability extension.
Model Context Protocol Servers represent an alternative pattern for extending AI capabilities through external tool integration. MCP requires running separate server processes that Claude connects to via defined protocols, enabling dynamic data access and action execution. Skills differ fundamentally by being self-contained folders with instructions and code that Claude loads directly without external infrastructure. As Simon Willison noted, Skills may prove “a bigger deal than MCP” precisely because their simplicity and portability lower adoption barriers. Claude Skills Hub doesn’t address MCP server discovery, focusing exclusively on the simpler Skills pattern.
Anthropic’s Official Skills Repository at github.com/anthropics/skills contains the 15 pre-built Agent Skills and serves as the authoritative source for official capabilities. While comprehensive for Anthropic-created skills, the official repository doesn’t aggregate community contributions, provide advanced search beyond GitHub’s native features, or offer packaged downloads. Claude Skills Hub extends the official repository by incorporating community skills and adding discovery layer optimizations.
Prompt Libraries and Marketplaces like PromptBase, FlowGPT, or Snack Prompt represent an older customization paradigm. These platforms share text prompts that users copy-paste into conversations. Skills fundamentally differ through persistence across conversations, automatic activation based on context, executable code capabilities, and structured folder organization. Prompts require manual invocation and lack the composability and efficiency advantages that Skills’ three-level progressive disclosure enables.
Potential Official Anthropic Marketplace: The strategic risk Claude Skills Hub faces is Anthropic eventually launching an official, integrated skills marketplace within Claude.ai with revenue sharing, quality certification, and deep platform integration. Such a marketplace would leverage Anthropic’s direct relationship with users, brand authority, and technical capabilities to provide seamless discovery and management. Claude Skills Hub’s sustainability depends on carving a niche that an official marketplace wouldn’t serve, such as radical transparency, community governance, or specialized curation.
Claude Skills Hub differentiates through its combination of community aggregation across multiple sources, lightweight architecture providing fast global access, open approach encouraging transparency and contribution, and early-mover timing capturing the market immediately following Skills launch. Its primary limitations stem from early-stage development, lack of quality validation mechanisms, and uncertain positioning relative to potential official Anthropic initiatives.
The platform serves users best when they need quick discovery across multiple community sources, prefer downloading complete packages over manual assembly, want a simple interface over GitHub repository navigation, and seek to explore the Skills ecosystem without commitment. It’s less suitable for users requiring quality guarantees, enterprise-wide skill deployment, or tight integration with existing development workflows beyond basic filesystem or ZIP upload patterns.
Final Thoughts
Claude Skills Hub represents a community response to genuine need, emerging within days of Anthropic’s Skills announcement to address the discovery challenge inherent in any new ecosystem. The platform recognizes a fundamental truth: powerful capabilities scattered across repositories and social channels deliver limited value if users cannot easily find, evaluate, and integrate them.
The timing matters significantly. By launching on October 22, 2025, barely a week after Anthropic introduced Skills, Claude Skills Hub captured early adopter attention during the initial exploration phase when the community actively seeks resources to understand and leverage the new capability pattern. This first-mover advantage establishes the hub as a reference point for skill discovery, potentially creating network effects as more users contribute and reference the platform.
However, realistic assessment requires acknowledging substantial uncertainties. As an independent community project without formal Anthropic affiliation, Claude Skills Hub’s long-term position remains unclear. Anthropic possesses both incentive and capability to launch an official, integrated marketplace that would likely supersede community efforts through superior platform integration, quality certification processes, and creator monetization. The gap between community initiative and official platform often proves temporary in technology ecosystems.
The incomplete feature set with sandbox testing and GitHub submission still in development as of late October 2025 reflects the platform’s early stage. Users should expect evolution in interface design, organization schemes, and functionality as the developer responds to community feedback and refines the roadmap. This dynamism enables rapid iteration but creates uncertainty about which current patterns will persist.
Quality validation represents the most significant gap. Without objective testing, peer review, or certification processes, users download skills based primarily on source repository reputation and description accuracy. As the Skills ecosystem grows and more creators contribute capabilities, distinguishing well-designed, secure, effective skills from poorly constructed or potentially malicious ones will become increasingly critical. Claude Skills Hub currently lacks mechanisms to provide this signal.
Yet within these limitations, the platform delivers genuine value. For users exploring Claude Skills for the first time, the hub provides accessible introduction through organized categories and search functionality that GitHub repositories don’t inherently offer. For regular Claude users seeking to expand their skill library, the aggregation across multiple collections saves discovery time. For the broader community, the platform demonstrates demand for centralized skill discovery, potentially influencing Anthropic’s own roadmap decisions.
Claude Skills Hub appears most valuable for users who actively experiment with AI customization, seek to understand skill design patterns through examples, need quick access to diverse skills without deep GitHub navigation, and accept early-stage platform evolution as natural. It’s less suitable for enterprise teams requiring compliance validation, users seeking long-term platform stability guarantees, or those needing advanced features like collaborative skill development, version management, or organizational deployment.
The platform’s ultimate significance may lie not in becoming the permanent home for Claude Skills but in demonstrating community need, establishing initial discovery patterns, and accelerating ecosystem growth during the critical early adoption phase. Whether Claude Skills Hub itself endures or gets superseded by official alternatives, its contribution to making Skills accessible during their launch window provides value to the community it serves.
For now, Claude Skills Hub offers the fastest path to explore what Skills enable, discover community creativity, and begin integrating specialized capabilities into Claude workflows. Users should engage with appropriate expectations: this is an early-stage community tool filling a temporary gap, not mature infrastructure with long-term guarantees. Within that context, it successfully lowers barriers to Skills adoption and deserves recognition as a constructive community contribution to the emerging Claude ecosystem.