Table of Contents
Overview
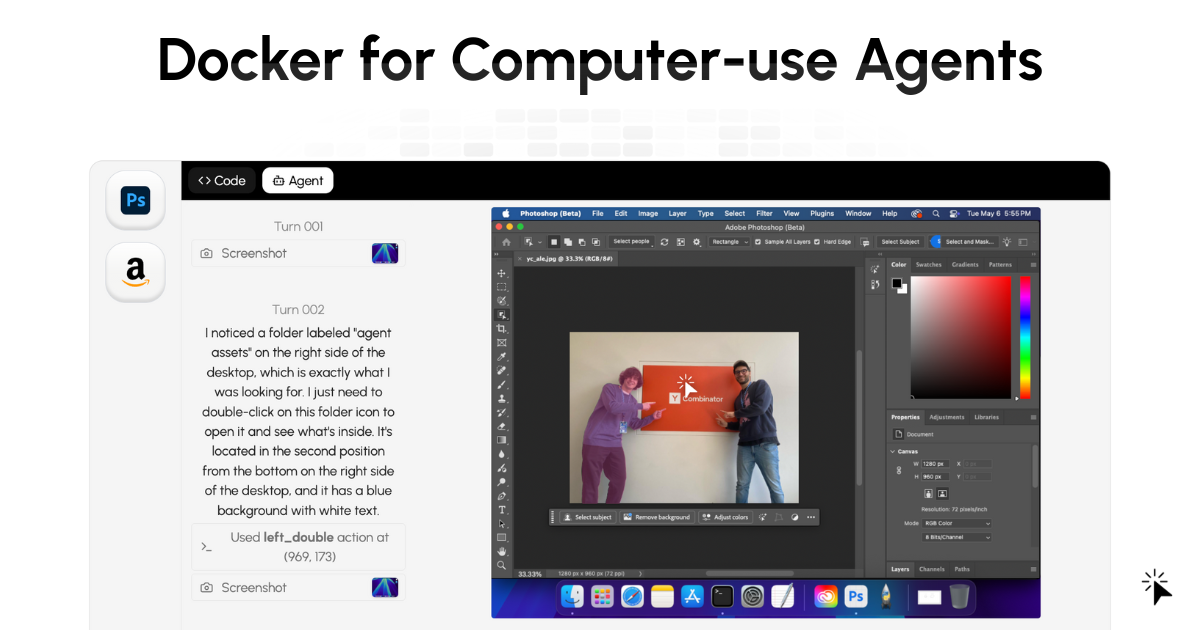
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI, the ability to train and test agents in realistic environments is crucial. Enter Cua, an open-source framework that’s revolutionizing how AI agents interact with operating systems. Think of it as a playground where AI can learn and experiment without the risk of impacting real-world systems. Dubbed the ‘Docker for Computer-Use Agents,’ Cua offers a secure and efficient way to virtualize entire operating systems for AI control. Let’s dive deeper into what makes Cua a game-changer.
Key Features
Cua boasts a powerful set of features designed to empower AI developers and researchers:
- Full OS virtualization for AI agents: Provides a complete operating system environment within a container, allowing agents to interact with software and files as if they were on a real machine.
- Lightweight, high-performance containers: Ensures efficient resource utilization and fast execution, crucial for training and testing complex AI models.
- Open-source with community support: Offers transparency, flexibility, and the potential for collaborative development and improvement.
- Secure sandboxed execution: Isolates AI agents from the host system, preventing unintended consequences and ensuring a safe testing environment.
- Developer tools for custom agent behavior: Provides the necessary tools and APIs to tailor agent behavior and integrate them seamlessly with the virtualized environment.
How It Works
Cua’s magic lies in its ability to create isolated, containerized OS instances that AI agents can interact with. It essentially launches a virtual computer within a container. Agents communicate with this virtual computer through standard I/O interfaces and APIs. This allows them to execute commands, manipulate the user interface, and receive system feedback, just like a human user. Developers can integrate their AI agents using plugins or remote control protocols, making the integration process flexible and adaptable to various architectures. This allows for seamless interaction and control of the virtualized environment.
Use Cases
Cua’s versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Training autonomous AI agents: Provides a safe and controlled environment for agents to learn and improve their skills through trial and error.
- Simulating complex digital workflows: Enables the creation of realistic simulations of real-world processes, allowing AI agents to optimize and automate them.
- Secure AI testing environments: Offers a sandboxed environment for testing AI agents without the risk of compromising sensitive data or systems.
- Building multi-agent systems: Facilitates the development and testing of collaborative AI systems where multiple agents interact and coordinate their actions.
- Automating software testing: Allows AI agents to automatically test software applications, identifying bugs and vulnerabilities more efficiently.
Pros & Cons
Like any tool, Cua has its strengths and weaknesses. Let’s take a look at the advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Highly customizable: Allows developers to tailor the environment and agent behavior to their specific needs.
- Efficient resource usage: Leverages lightweight containers to minimize resource consumption and maximize performance.
- Ideal for research and development: Provides a flexible and powerful platform for exploring new AI concepts and applications.
Disadvantages
- Requires technical setup: May require some technical expertise to set up and configure the environment.
- Limited Windows support: Primarily focused on Linux-based systems, with limited support for Windows.
- Small user community: Being a relatively new project, the user community is still growing.
How Does It Compare?
When evaluating Cua, it’s helpful to consider its alternatives and how it stacks up against them.
- Auto-GPT: While Auto-GPT aims for broader goal automation, Cua focuses specifically on providing a controlled OS environment.
- Docker: Docker operates at a lower abstraction level, primarily focused on containerizing applications rather than entire operating systems for AI agent interaction.
- Ansible: Ansible is a configuration management tool, whereas Cua is designed for agent-based interaction with a virtualized OS.
Final Thoughts
Cua presents a compelling solution for developers and researchers seeking a robust and flexible platform for training and testing AI agents. Its open-source nature, combined with its focus on security and performance, makes it a valuable tool for pushing the boundaries of AI development. While it may require some technical expertise to get started, the potential benefits of Cua are undeniable. As the AI landscape continues to evolve, Cua is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of autonomous agents.