Table of Contents
Overview
In the rapidly expanding landscape of no-code automation and AI agent development platforms, Ekinox emerges as a visual workflow builder specifically designed for building, deploying, and monitoring production-ready AI agent systems. Launched on October 19-21, 2025 with a Product Hunt debut on October 21, Ekinox positions itself as a purpose-built platform for agentic workflows rather than a general automation tool retrofitted with AI capabilities. The platform enables users to design sophisticated multi-step AI agent workflows through an intuitive drag-and-drop canvas interface, connecting AI models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and others with productivity tools, databases, communication platforms, and custom APIs—all without writing code.
Ekinox distinguishes itself through several key architectural decisions: serverless infrastructure enabling instant deployment without server management, real-time collaboration allowing distributed teams to co-edit workflows simultaneously, built-in AI Copilot providing context-aware assistance during workflow development, and open-source foundations ensuring transparency and community-driven development. The platform targets businesses, developers, and teams seeking to automate complex processes involving AI decision-making, data processing, customer support, marketing workflows, and internal operational orchestration while maintaining enterprise-grade security through SOC2 compliance and bank-level encryption.
With pricing starting from a free tier providing 10 workflow executions per minute and extending through Pro (\$29/month), Business (\$99/month), and custom Enterprise plans, Ekinox aims to serve organizations ranging from individual developers and startups to enterprise teams requiring advanced collaboration, governance, and scale.
Key Features
Ekinox delivers a comprehensive feature set optimized specifically for AI agent workflow development and production deployment:
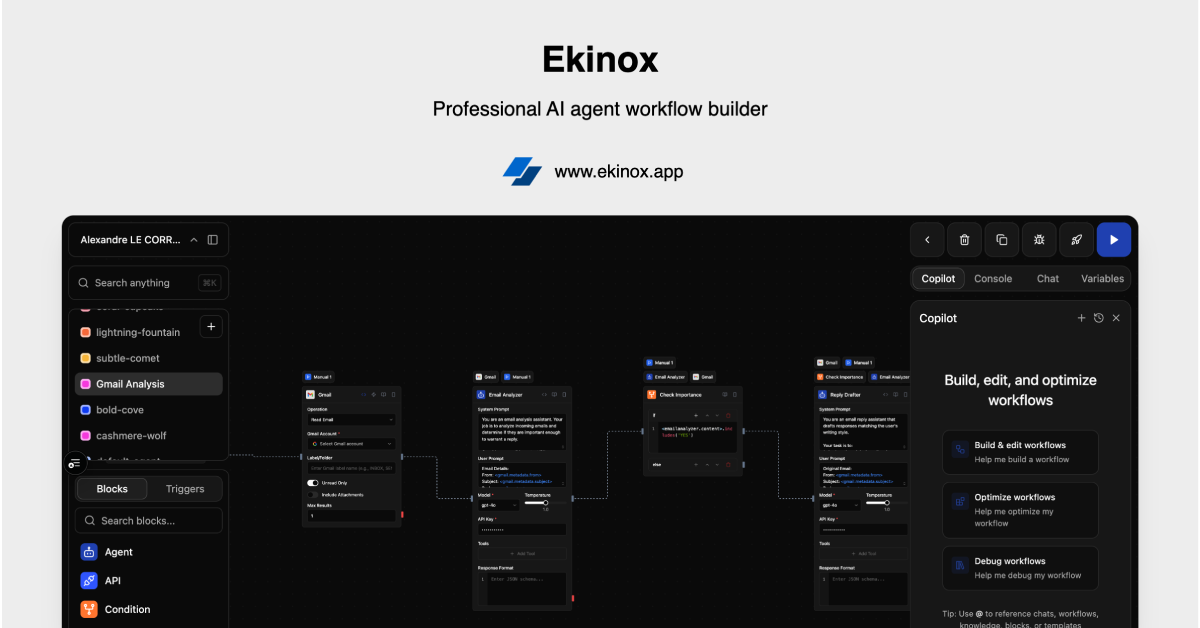
Visual No-Code Workflow Canvas: The platform provides an intuitive drag-and-drop interface where users design workflows by connecting blocks representing different functions—AI model invocations, API calls, database queries, conditional logic, loops, data transformations, and output handlers. This visual paradigm makes complex multi-step automation accessible to non-developers while providing sufficient power for sophisticated agentic systems, eliminating the need for traditional programming while maintaining logical precision.
Extensive Integration Ecosystem (80-100+ Services): Ekinox offers pre-built connectors to major AI model providers including OpenAI (GPT-4o, GPT-4 Turbo, o1), Anthropic (Claude Sonnet 4, Opus), Google (Gemini), Groq, Cerebras, and local Ollama models. Beyond AI, the platform integrates with communication tools (Gmail, Slack, Microsoft Teams, Telegram, WhatsApp), productivity platforms (Notion, Google Sheets, Airtable, Monday.com), development tools (GitHub, Jira, Linear), search and web services (Google Search, Perplexity, Firecrawl, Exa AI), and databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, Supabase, Pinecone, Qdrant). Note: Documentation indicates “80+ services” while marketing materials claim “100+ integrations”—a minor variance likely explained by counting methods (services vs. total integration endpoints).
Built-In AI Copilot for Workflow Development: Unlike most workflow builders requiring users to manually design every step, Ekinox includes an intelligent AI assistant accessible via @ context menu throughout the editor. This Copilot understands entire workspace context including workflows, blocks, knowledge bases, documentation, templates, and execution logs, enabling it to explain complex concepts, suggest best practices, generate workflow suggestions, make changes with user approval, and debug issues by analyzing execution logs. This accelerates development significantly compared to building workflows from scratch without assistance.
Real-Time Team Collaboration: The platform supports simultaneous co-editing where multiple team members work on the same workflow with real-time synchronization, role-based permissions management controlling access and modification rights, shared workspace environments centralizing team projects, and collaborative debugging through shared execution log access. This team-centric architecture differentiates Ekinox from individual-focused automation tools, addressing enterprise collaboration requirements.
Multiple Trigger Mechanisms: Workflows can initiate through various entry points including chat interfaces for conversational AI agents, REST API endpoints enabling external system integration, webhooks for event-driven automation, scheduled cron jobs for periodic execution, and external service events from platforms like Slack and GitHub. This trigger flexibility supports diverse use cases from user-facing chatbots to backend automation and scheduled data processing.
Advanced Workflow Logic Capabilities: Beyond simple linear automation, Ekinox supports sophisticated control flow including conditional branching based on runtime data, iterative loops for batch processing, parallel execution for concurrent operations, data routers distributing workflow paths, error handling and retry logic, and variable management for state persistence across workflow steps. These capabilities enable complex business logic implementation matching traditional programming paradigms without code.
Serverless Instant Deployment Architecture: Workflows deploy immediately to Ekinox’s managed cloud infrastructure without requiring server provisioning, configuration, or maintenance. The serverless model provides automatic scaling based on execution demand, 99.9% uptime SLA according to marketing materials, lightning-fast execution through optimized infrastructure, and zero operational overhead—users focus on workflow logic rather than infrastructure management.
Production-Grade Security and Compliance: Ekinox implements SOC2 Type II compliance meeting enterprise security requirements, bank-grade AES-256 encryption for data at rest and TLS for data in transit, advanced access controls with role-based permissions and SSO support (likely in Enterprise tier), automatic backups ensuring data durability, and audit logging for compliance and debugging. These enterprise features position Ekinox beyond hobbyist tools toward production business-critical deployment.
Comprehensive Monitoring and Analytics: The platform provides deep observability into workflow performance including execution history with detailed logs, performance metrics tracking execution times and bottlenecks, cost optimization insights showing AI model usage and expenditure, predictive scaling recommendations based on usage patterns, and real-time debugging tools enabling live workflow inspection during development.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Integration: Ekinox supports MCP enabling custom integrations with external services beyond pre-built connectors, allowing users to connect any API-accessible service and extending platform capabilities without vendor dependency.
How It Works
Ekinox implements a streamlined workflow from design through production deployment optimized for rapid iteration and collaboration. Users begin by accessing the web-based platform and creating or opening a workspace project. The visual canvas presents a blank design surface where workflow construction begins by dragging blocks from the component library onto the canvas.
Blocks represent distinct functional units: Input/Trigger blocks defining how workflows initiate (chat, API, webhook, schedule), Processing blocks performing core logic (AI model calls to GPT-4, Claude, or Gemini; API requests to external services; database queries; data transformations), Logic blocks controlling flow (conditional if/then, loops, routers, error handlers), and Output blocks defining responses (JSON responses for APIs, chat messages for users, database writes, external notifications).
Users connect blocks by drawing edges between output and input ports, creating directed acyclic graphs representing execution flow and data dependencies. Each block exposes configuration panels where users set parameters—selecting specific AI models and prompts, defining API endpoints and authentication, configuring database connection strings and queries, or specifying conditional logic expressions—all through visual forms without code syntax.
The built-in AI Copilot assists throughout this process. Users can type @ to invoke the assistant, ask questions (“how do I implement retry logic?”), request workflow modifications (“add error handling to this API call”), or debug issues (“why is this execution failing?”). The Copilot analyzes entire workspace context including previous executions and suggests specific solutions, sometimes offering to implement changes directly with user approval.
Once workflows reach testable states, users execute them directly from the editor with test inputs, observing results in real-time through execution logs displaying each block’s inputs, outputs, execution time, and any errors. This immediate feedback enables rapid debugging and iteration without deployment delays. Multiple team members can simultaneously edit workflows with changes synchronizing in real-time, supporting collaborative design and review workflows.
When workflows reach production-ready maturity, deployment occurs instantly—clicking “Deploy” makes workflows immediately available via their trigger mechanisms (API endpoints receive URLs for external calls, scheduled workflows begin executing on defined intervals, chat interfaces become accessible to end users). The serverless infrastructure handles scaling automatically—low-traffic workflows consume minimal resources; high-traffic workflows scale transparently without manual intervention or configuration.
Post-deployment, the monitoring dashboard provides visibility into workflow execution including frequency, success/failure rates, execution duration distribution, AI model token consumption and costs, error patterns, and performance trends—enabling continuous optimization and proactive issue resolution.
Use Cases
Ekinox addresses diverse automation and AI agent deployment scenarios across organizational functions:
Intelligent Customer Support Automation: Businesses can build AI-powered support agents that receive customer inquiries through chat interfaces, search knowledge bases for relevant information, invoke AI models to generate contextual responses, create support tickets in systems like Jira or Linear when escalation is needed, and notify human agents via Slack for complex issues—automating tier-1 support while maintaining quality and appropriate human involvement for nuanced situations.
CRM and Sales Workflow Integration: Sales teams can automate lead qualification by triggering workflows when new leads enter CRM systems, enriching lead data through external APIs (LinkedIn, Clearbit), scoring leads using AI analysis of company information and engagement signals, routing qualified leads to appropriate sales representatives via CRM updates and Slack notifications, and scheduling follow-up reminders—streamlining lead-to-opportunity conversion without manual data entry or coordination.
AI-Driven Data Processing and Analysis: Organizations can implement automated data pipelines that periodically extract data from databases or APIs, clean and transform data using custom logic blocks, analyze patterns and generate insights using AI models, populate dashboards and reports in tools like Notion or Google Sheets, and send summary notifications to stakeholders—transforming manual data analyst work into automated intelligence production.
Marketing Campaign Automation and Personalization: Marketing teams can trigger workflows when users complete specific actions (sign-ups, purchases, content downloads), segment users using AI analysis of behavior and demographics, generate personalized email or SMS content through LLM-based writing tailored to each segment, send communications through appropriate channels (Gmail, SendGrid, Twilio), track engagement and optimize campaigns based on performance data—enabling sophisticated marketing automation without expensive dedicated platforms.
Internal Process Orchestration and Employee Productivity: Companies can automate routine operational workflows including employee onboarding (creating accounts across systems, sending welcome messages, scheduling orientation meetings), expense approval routing (extracting data from submissions, applying policy rules, requesting manager approval via Slack, updating financial systems), document generation (collecting data from forms or databases, populating templates, distributing outputs), and meeting preparation (gathering relevant documents, generating briefings using AI summarization, distributing materials)—eliminating repetitive administrative burden and accelerating organizational velocity.
Multi-Agent Research and Analysis Systems: Advanced users can build sophisticated multi-agent architectures where specialized agents perform focused tasks—one agent searches the web for information, another analyzes and summarizes findings, a third generates reports, and a coordinator agent orchestrates the workflow—enabling complex analytical capabilities traditionally requiring significant development investment.
Pros \& Cons
Advantages
Purpose-Built for AI Agent Workflows: Unlike general automation platforms adding AI as afterthought, Ekinox was designed from inception specifically for agentic systems. Every feature—the visual canvas, execution logging, AI Copilot, monitoring—optimizes for AI agent development rather than general task automation. This focus provides superior developer experience for AI-specific use cases including better default templates, AI-aware debugging tools, and LLM-optimized execution infrastructure compared to retrofitted alternatives.
Intelligent AI Copilot Dramatically Accelerating Development: The built-in AI assistant providing context-aware suggestions, workflow generation, and debugging support represents significant innovation beyond bare workflow editors. Users can describe desired behaviors conversationally and receive implementation suggestions or automated generation, dramatically reducing time from concept to working agent. This productivity multiplier particularly benefits non-technical users lacking workflow design expertise or developers wanting to prototype rapidly.
Extensive Pre-Built Integration Ecosystem: The 80-100+ service connectors spanning AI models (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, local models), productivity tools (Notion, Airtable, Google Sheets), communication platforms (Slack, Teams, Telegram, WhatsApp), databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, Supabase, vector databases), and development tools (GitHub, Jira) provide immediate connectivity to enterprise technology stacks. This breadth eliminates integration development overhead and accelerates time-to-value compared to platforms requiring custom connector development or expensive third-party iPaaS solutions.
Real-Time Collaboration for Distributed Teams: The simultaneous multi-user editing, role-based permissions, and shared workspace architecture directly addresses enterprise requirements where workflow development involves multiple stakeholders—engineers, product managers, domain experts—across geographies. This collaborative capability differentiates Ekinox from individual-focused tools requiring serial handoffs or manual change coordination, improving team velocity and reducing coordination friction.
Production-Ready Security and Compliance: The SOC2 compliance, bank-grade encryption, access controls, and 99.9% uptime SLA provide enterprise-ready operational characteristics often absent in early-stage platforms or developer-focused tools. Organizations with compliance requirements, security policies, or production-grade service level needs can adopt Ekinox without requiring extensive security reviews or accepting unacceptable risk—critical for business-critical automation deployment.
Open-Source Foundation Ensuring Transparency: The open-source architecture provides code visibility enabling security audits, community-driven feature development and bug fixes, freedom from vendor lock-in through self-hosting options (likely available given open-source positioning), and confidence in long-term platform availability regardless of company trajectory. This transparency appeals to technical organizations prioritizing control and auditability over fully proprietary alternatives.
Serverless Deployment Eliminating Operational Complexity: The instant deployment without server provisioning, automatic scaling without capacity planning, zero infrastructure maintenance, and pay-per-execution economics remove traditional DevOps burden. Small teams and individual developers can deploy production-grade AI agents without platform engineering expertise or infrastructure management resources that typically gate such deployments.
Disadvantages
Extremely Recent Launch with Minimal Track Record: Ekinox’s October 19-21, 2025 launch means the platform has essentially zero production deployment history—literally days old as of this writing. This extreme youth creates substantial risks including undiscovered bugs and edge cases, immature documentation and learning resources, limited community knowledge and troubleshooting guidance, unproven scalability under diverse workload patterns, uncertain long-term platform viability and company sustainability, and potential feature instability as product evolves rapidly based on early user feedback. Organizations deploying business-critical workflows assume significant risk with such nascent platforms regardless of technical promise.
Requires Understanding of Workflow Logic and Automation Concepts: Despite no-code interfaces, Ekinox requires users to conceptualize processes as structured workflows with explicit logic, data flow, error handling, and state management—concepts unfamiliar to many non-technical users. The platform cannot automatically transform vague process descriptions into working workflows; users must decompose problems into discrete steps, understand conditional logic and iteration, grasp API concepts for integrations, and debug execution failures. This cognitive requirement limits accessibility compared to fully automated AI platforms where users simply describe outcomes without understanding implementation details.
Variable Costs Scaling with Automation Volume: The execution-based pricing model where free tier provides 10 executions per minute and paid tiers scale with usage creates cost unpredictability for high-volume workflows. Organizations running frequent scheduled jobs, high-traffic API endpoints, or intensive batch processing may encounter substantial monthly costs depending on execution volumes and AI model token consumption. Unlike flat-rate subscriptions providing cost certainty, usage-based pricing requires careful monitoring and optimization to prevent budget overruns—particularly challenging for organizations without established FinOps practices or cost prediction models.
Integration Count Ambiguity: Minor inconsistency exists between “100+ integrations” in marketing materials and “80+ services” in documentation. While likely explained by counting methodology differences (total integration points vs. distinct service categories), this variance creates uncertainty about exact connector availability and may lead to disappointment if specific required services fall outside the stated range. Organizations should verify specific integration needs against actual connector list before committing to platform adoption.
Limited Information on Enterprise Features and Customization: While SOC2 compliance and security features are highlighted, detailed specifications regarding enterprise requirements remain unclear including SSO/SAML authentication options, on-premise or private cloud deployment for air-gapped environments, data residency controls for regulatory compliance (GDPR, HIPAA), custom SLA guarantees beyond stated 99.9% uptime, dedicated support channels and response time commitments, and pricing models for very high-volume enterprise deployments. Organizations with specific enterprise requirements must conduct detailed vendor discussions to validate capability alignment.
Competitive Market with Established Dominant Players: The workflow automation and AI agent building space includes well-funded, mature platforms with substantial market share including Zapier (5+ million users), Make (formerly Integromat), n8n (open-source community), Flowise (focused AI workflow builder), and Microsoft’s AutoGen Studio. These competitors provide extensive documentation, large user communities, proven reliability, and established ecosystems. Ekinox must differentiate sufficiently and achieve critical mass adoption to justify organizational switching costs from existing tools—challenging regardless of technical merit given market maturity.
How Does It Compare?
The no-code AI agent and workflow automation landscape in late 2025 features diverse platforms each optimizing for different user needs, technical sophistication, and deployment scenarios:
n8n: Represents the leading open-source workflow automation platform with 45,000+ GitHub stars and extensive community adoption. n8n provides visual workflow design through node-based canvas, 400+ pre-built integrations, self-hosting capabilities for data sovereignty, and thriving community contributing custom nodes and templates. Pricing ranges from free self-hosted to \$25/month cloud starter plans scaling to enterprise. n8n’s strength lies in open-source maturity, massive integration library, and deployment flexibility. Compared to Ekinox, n8n offers greater integration breadth and established reliability but was designed for general automation rather than AI-specific workflows—lacking purpose-built AI agent features, native LLM integration optimization, and AI Copilot assistance. Ekinox differentiates through AI-first design, built-in intelligent assistance, and optimized AI agent debugging, while n8n provides broader automation coverage and proven production stability. Users choosing between them weigh AI specialization (Ekinox) against general automation maturity (n8n).
Flowise: Purpose-built for LLM orchestration and AI workflow development, Flowise provides visual design for LangChain and LlamaIndex applications, chatbot creation, document processing pipelines, and agent workflows. The platform emphasizes AI-specific capabilities including conversational memory, vector database integration, custom agent tools, and prompt engineering interfaces. Flowise offers open-source community edition and cloud-hosted managed service. Compared to Ekinox, Flowise and Ekinox compete directly in the AI-first workflow builder segment, with differentiation primarily through user experience, specific feature implementations, and ecosystem positioning. Flowise emphasizes LangChain ecosystem integration appealing to developers familiar with that framework; Ekinox emphasizes visual-first design, AI Copilot assistance, and broader integration ecosystem beyond AI-specific tools. Direct feature-by-feature comparison requires hands-on evaluation as both target similar use cases with comparable capabilities.
MindStudio: Provides no-code AI agent and application development with over 1,000 pre-built integrations, multiple deployment options (web apps, email-triggered agents, browser extensions, autonomous scheduled agents, API endpoints, MCP servers), and emphasis on business user accessibility. MindStudio targets non-technical business users building AI-powered tools without developer involvement. Pricing information remains unclear from public sources. Compared to Ekinox, MindStudio emphasizes broader deployment flexibility (browser extensions, email triggers) and business user simplicity, while Ekinox provides more sophisticated workflow control, developer-friendly debugging, and team collaboration features. MindStudio appeals to business users wanting packaged AI solutions; Ekinox targets teams building complex production workflows requiring granular control.
Zapier: Dominates the general automation market with 5+ million users, 7,000+ app integrations, and strong consumer and SMB adoption. Zapier provides simple trigger-action workflows (“Zaps”), multi-step automations, filters and formatters, and recently added AI capabilities through partnerships with OpenAI. Pricing ranges from free limited tier to \$19.99/month starter plans scaling to hundreds monthly for teams and businesses. Zapier’s strengths include massive integration ecosystem, user-friendly interfaces, extensive templates and community knowledge, and brand recognition driving adoption. However, Zapier was architected for simple point-to-point integrations rather than complex agentic workflows—lacking sophisticated control flow, advanced logic branching, native AI model flexibility, and developer-grade debugging. Ekinox targets more technical users and complex use cases that exceed Zapier’s capabilities, while Zapier serves broader market with simpler automation needs and superior integration breadth.
Make (formerly Integromat): Provides visual automation through flow-chart-style workflows, 1,800+ app integrations, advanced data manipulation, and complex logic capabilities exceeding Zapier’s simplicity. Make appeals to power users wanting sophisticated automation control without coding. Pricing starts at \$9/month for individual plans scaling to hundreds monthly for teams. Compared to Ekinox, Make offers established reliability, extensive integration library, and proven complex workflow capabilities, but lacks AI-first design, native LLM integration, and purpose-built agent features. Make serves users wanting powerful general automation; Ekinox serves users specifically building AI agent systems.
LangFlow: An open-source visual framework specifically for LangChain application development, providing drag-and-drop components for chains, agents, prompts, and tools. LangFlow appeals to LangChain developers wanting visual development interfaces while maintaining framework familiarity and flexibility. As open-source tool, LangFlow provides maximum customization and control but requires greater technical sophistication and self-management compared to managed services. Ekinox offers more comprehensive managed service experience with collaboration, monitoring, and enterprise features beyond LangFlow’s core workflow editor, trading customization depth for operational simplicity.
AutoGen Studio (Microsoft): Microsoft’s no-code interface for building multi-agent systems using the AutoGen framework, emphasizing agent-to-agent conversation, declarative workflow specification, interactive evaluation and debugging, and reusable agent galleries. AutoGen Studio targets sophisticated multi-agent architectures and research workflows. Compared to Ekinox, AutoGen Studio provides Microsoft ecosystem integration and advanced multi-agent capabilities but requires greater technical sophistication and lacks general business process integration breadth. AutoGen Studio serves AI researchers and developers; Ekinox serves business teams building practical automation.
Stack AI and Similar Emerging Platforms: Numerous newer platforms including Stack AI, Relevance AI, Cassidy, and others provide AI agent building with varying feature focuses. These platforms generally offer visual builders, LLM integration, workflow orchestration, and business automation capabilities similar to Ekinox. The primary differentiators among these emerging tools involve specific feature implementations, integration ecosystems, pricing models, and target market positioning rather than fundamental capability differences. Prospective users should evaluate multiple platforms hands-on against specific use cases rather than relying solely on marketing positioning.
Ekinox occupies a specific niche emphasizing AI-first workflow design purpose-built for agentic systems, intelligent AI Copilot acceleration, real-time team collaboration, open-source transparency, and production-ready security compliance. Its primary competitive advantages include workflow builder optimized specifically for AI agents rather than retrofitted general automation, built-in AI assistance dramatically accelerating development cycles, comprehensive integration ecosystem spanning AI models and business tools, enterprise-grade security and compliance for production deployment, and open-source foundations ensuring transparency and avoiding proprietary lock-in. However, users must carefully weigh these strengths against extreme platform youth creating adoption risk, established competitors with proven reliability and larger ecosystems, execution-based pricing creating cost unpredictability for high-volume scenarios, and workflow logic learning requirements limiting pure no-code accessibility. The platform serves teams specifically building AI agent workflows prioritizing purpose-built tooling, collaborative development, and enterprise readiness over general automation breadth or maximum simplicity.
Final Thoughts
Ekinox enters the competitive workflow automation and AI agent building market with genuinely distinctive positioning: a purpose-built platform designed from inception specifically for agentic AI systems rather than general automation retrofitted with LLM capabilities. The platform’s intelligent AI Copilot providing context-aware development assistance, real-time collaborative editing enabling distributed team workflows, comprehensive integration ecosystem spanning AI models and business tools, open-source foundation ensuring transparency, and enterprise-grade security compliance demonstrate thoughtful product design addressing real market needs in the rapidly maturing AI agent development space.
However, prospective adopters must navigate one overwhelmingly significant caveat: Ekinox launched literally days ago on October 19-21, 2025. This extreme youth means the platform has essentially zero production deployment history, minimal real-world testing across diverse use cases, sparse user-generated documentation and community knowledge, unproven reliability under actual workload patterns, and uncertain long-term platform viability. The contrast between sophisticated feature claims and days-old platform maturity creates exceptional early-adopter risk that cannot be overstated—mission-critical business workflows deployed on such nascent platforms assume risks many organizations cannot accept regardless of technical promise.
The competitive landscape presents both opportunities and formidable challenges. Established players including Zapier (5+ million users), Make, n8n (45,000+ GitHub stars), and specialized AI workflow builders like Flowise possess substantial advantages including proven reliability, extensive documentation, large user communities, comprehensive integration ecosystems, and brand recognition. Ekinox must differentiate sufficiently through its AI-first design, Copilot assistance, and collaborative features while overcoming the significant inertia favoring incumbent tools already embedded in organizational workflows. Success requires not just technical superiority but exceptional execution across product development, community building, documentation creation, and go-to-market strategy—uncertain outcomes for any startup.
The platform’s technical claims warrant careful verification. The minor inconsistency between “100+ integrations” marketing and “80+ services” documentation highlights the importance of validating specific integration availability against actual organizational needs rather than assuming coverage. The execution-based pricing model creating variable costs depending on workflow volume and AI token consumption requires careful estimation and monitoring to prevent budget surprises—particularly for organizations accustomed to predictable SaaS subscription pricing. Enterprise feature details including SSO authentication, data residency controls, custom SLAs, and dedicated support remain unclear, necessitating detailed vendor discussions before enterprise commitments.
The original content’s competitive comparison listing only Flowise, MindStudio, and n8n while omitting dominant players like Zapier, Make, AutoGen Studio, LangFlow, Stack AI, and numerous other relevant alternatives represents incomplete market assessment. Prospective users should evaluate Ekinox against comprehensive competitive set through hands-on testing rather than relying on selective positioning.
Ideal Ekinox users include innovative early-adopter teams comfortable with platform risk seeking purpose-built AI agent tooling, technical organizations valuing open-source transparency and security auditability, distributed teams benefiting from real-time collaborative workflow development, developers wanting intelligent AI assistance accelerating agent development, and organizations specifically building AI-driven automation where specialized tooling justifies adopting nascent platforms. The platform is less suitable for risk-averse enterprises requiring proven stability for business-critical workflows, non-technical business users expecting fully automated no-code experiences without workflow logic understanding, high-volume organizations concerned about execution-based pricing unpredictability, companies with specific enterprise requirements requiring detailed feature validation, and organizations already successfully using incumbent tools without compelling reasons to assume migration risk.
For those considering Ekinox, rigorous proof-of-concept evaluation is absolutely essential given platform youth. Leverage the free tier to test workflow builder usability, AI Copilot effectiveness, and integration quality for specific use cases. Build representative workflows matching actual business needs rather than toy examples to assess production readiness. Evaluate execution speeds, reliability under realistic loads, debugging capabilities, and monitoring adequacy. Compare hands-on against direct competitors including Flowise, n8n, and Make for equivalent workflows to validate claimed differentiation. Assess documentation comprehensiveness, support responsiveness, and community resources available for troubleshooting. Most critically, conduct honest risk assessment regarding platform youth—can your organization tolerate potential bugs, feature gaps, or even platform discontinuation if Ekinox fails to achieve market traction? Experimental projects and non-critical workflows provide appropriate early-adopter opportunities; mission-critical business-essential automation warrants established alternatives until Ekinox demonstrates sustained reliability and market viability.
Ekinox demonstrates promising innovation in AI-first workflow design, intelligent development assistance, and collaborative team features addressing genuine needs in the maturing AI agent development market. However, realizing this potential requires surviving the perilous early-stage period where most startups fail, building substantial user base achieving network effects and sustainable business model, demonstrating production-grade reliability across diverse real-world deployments, and competing effectively against well-funded incumbents with years of refinement and ecosystem development. Until these fundamentals mature through market validation and operational time, Ekinox remains best suited for experimental adoption by risk-tolerant early adopters, technical teams building innovative AI applications comfortable with bleeding-edge tools, and developers contributing to open-source community development—while production-critical enterprise deployments warrant established alternatives with proven track records until Ekinox graduates from days-old startup to mature, reliable platform.
https://www.ekinox.app/