Table of Contents
Overview
Imagine a future where robots seamlessly understand and execute your commands, adapting to new situations without needing constant retraining. Figure AI’s Helix is bringing that vision closer to reality. This innovative Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model is designed to give humanoid robots the ability to perceive, understand, and act on the world around them, all through the power of natural language. Let’s dive into what makes Helix a game-changer in the world of robotics and embodied AI.
Key Features
Helix boasts a powerful set of features that enable it to perform complex tasks with remarkable adaptability:
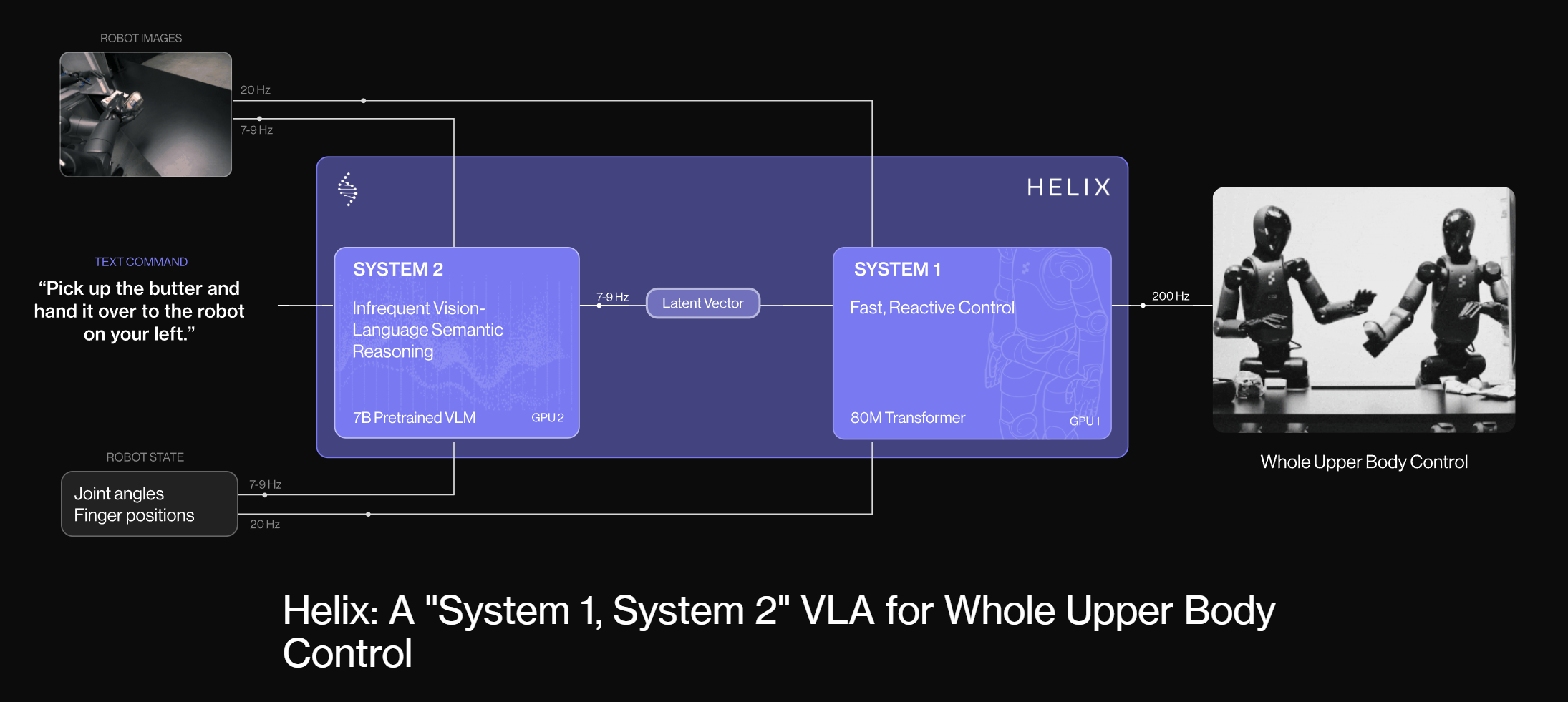
- Vision-Language-Action (VLA) architecture: A unified neural network that integrates visual and linguistic inputs to generate appropriate actions.
- Zero-shot task generalization: The ability to perform new tasks without requiring specific retraining, allowing for rapid adaptation to novel environments and situations.
- Full upper-body humanoid control: Enables precise and coordinated control of a humanoid robot’s arms, hands, and torso.
- Operates on embedded GPUs: Designed for efficient deployment on resource-constrained embedded systems, making it suitable for real-world applications.
- Multimodal perception: Processes information from various sensors, including cameras and potentially other modalities, to understand the environment.
- Real-time language grounding: Accurately interprets natural language instructions and grounds them in the physical world, enabling intuitive human-robot interaction.
How It Works
Helix functions by processing visual and linguistic information through its VLA architecture. It essentially “sees” and “hears” the world, interpreting commands and understanding the context of its environment. This understanding is then translated into precise control signals that drive the humanoid’s actuators, allowing it to execute tasks with remarkable accuracy. The key is its ability to generalize; it can adapt to unseen scenarios and objects without needing to be specifically trained on them, making it incredibly versatile.
Use Cases
The potential applications of Helix are vast and span various industries. Here are a few key areas where this technology could make a significant impact:
- Robotic assistance in homes and factories: Imagine robots helping with household chores or assisting workers on assembly lines, responding to simple voice commands.
- Human-robot interaction in service industries: Helix could power robots that provide customer service, assist in retail environments, or offer support in healthcare settings.
- Research in embodied AI: Provides a powerful platform for researchers to explore the intersection of AI, robotics, and human-computer interaction.
- Complex task automation: Automating intricate processes that require both perception and dexterity, such as sorting objects, assembling components, or performing delicate manipulations.
Pros & Cons
Like any cutting-edge technology, Helix has its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these can help you determine if it’s the right solution for your needs.
Advantages
- Advanced generalization without retraining: Significantly reduces the need for extensive training data and allows for rapid deployment in new environments.
- Efficient deployment on embedded hardware: Enables real-time operation on resource-constrained devices, making it practical for real-world applications.
- Supports complex tasks: Capable of handling intricate tasks that require both perception and manipulation.
Disadvantages
- Limited to upper-body control currently: While powerful, Helix currently focuses on upper-body movements, limiting its ability to perform tasks requiring full-body mobility.
- Requires sophisticated sensor integration: To fully leverage its capabilities, Helix needs to be integrated with high-quality sensors, which can add to the overall system complexity and cost.
How Does It Compare?
When considering advanced robotics platforms, it’s important to understand how Helix stacks up against the competition.
- Tesla Optimus: While Tesla Optimus aims for general-purpose humanoid robotics, Helix excels in zero-shot learning and efficient deployment on embedded hardware, potentially offering faster adaptation and easier integration.
- Boston Dynamics Atlas: Atlas is renowned for its impressive physical agility and dynamic movements. However, Helix focuses on cognitive control via language and vision, prioritizing intelligent task execution over pure physical prowess.
Final Thoughts
Helix represents a significant leap forward in the field of embodied AI. Its ability to understand and execute natural language commands, coupled with its zero-shot generalization capabilities, makes it a powerful tool for a wide range of applications. While still under development, Helix has the potential to revolutionize how we interact with robots and automate complex tasks, paving the way for a future where robots are truly intelligent and adaptable assistants.