Table of Contents
Overview
Lamatic 3.0 is a collaborative AI agent development platform designed to streamline the entire lifecycle of building, deploying, and managing agentic applications. Launched in November 2024, the platform emphasizes a developer-focused approach with visual workflow design, integrated version control through GitHub, and serverless edge deployment. By combining a low-code studio interface with enterprise-grade infrastructure management, Lamatic 3.0 enables cross-functional teams to create sophisticated AI agents and applications without the complexity of managing separate tooling for development, hosting, and orchestration.
Key Features
Lamatic 3.0 provides a comprehensive feature set for AI agent development and deployment:
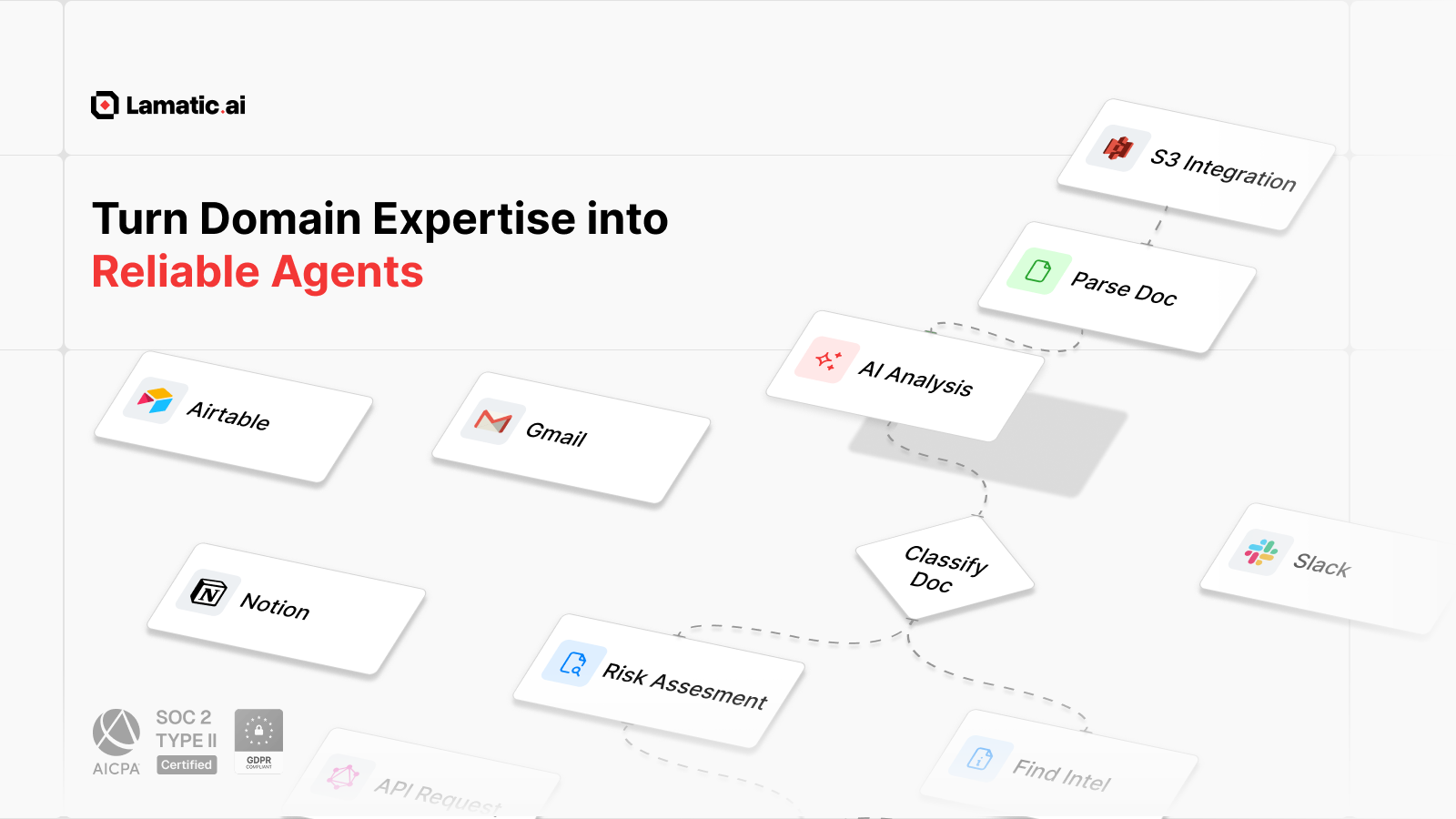
Visual Flow Builder: An intuitive drag-and-drop interface enables both technical and non-technical team members to design complex agentic workflows. The studio supports role-based access control, allowing different team members to collaborate on agent development with appropriate permissions. Users can construct flows by connecting nodes representing AI models, data sources, logic operations, and external integrations.
Managed Vector Database: The platform integrates Weaviate, an open-source vector database, providing fully managed vector storage for Retrieval-Augmented Generation applications. Users can connect multiple data sources including Google Drive, AWS S3, Notion, Slack, and PostgreSQL, with automatic data ingestion, vectorization using various embedding models, and incremental updates to keep knowledge bases current.
Serverless Edge Deployment: Lamatic 3.0 deploys applications to Cloudflare Workers for global edge execution, ensuring low latency and automatic scaling. Once a flow is built, the platform generates a federated GraphQL API, REST endpoints, and webhooks, eliminating manual infrastructure configuration. This serverless architecture removes the operational burden of managing servers, load balancers, and scaling policies.
Comprehensive SDK Ecosystem: The platform provides an open-source SDK with support for JavaScript and Python, enabling developers to integrate Lamatic flows into existing applications programmatically. The auto-generated GraphQL API provides strongly-typed queries and mutations for interacting with deployed agents, while REST API support ensures compatibility with any programming environment.
GitHub-Native Version Control: Lamatic 3.0 features deep GitHub integration, allowing teams to manage agent development using familiar Git workflows. Users can create branches for feature development, submit pull requests for code review, and maintain separate environments for development, staging, and production. This integration supports automated deployments on commit, enabling continuous delivery practices.
AgentKit Templates: The platform includes pre-built agent templates called AgentKits, which bundle frontend interfaces, proven agentic flows, and integration configurations for common use cases. These templates enable one-click deployment of complete AI solutions, dramatically reducing time from concept to production.
Prompt IDE and Testing Tools: An integrated development environment for prompt engineering allows users to design, test, and debug AI prompts within the platform. Built-in testing capabilities enable validation of flows before deployment, with real-time logs and traces for observability.
Multi-Model Support: Lamatic 3.0 connects to over 20 model providers including OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, Cohere, Hugging Face, and xAI, allowing teams to select optimal models for specific tasks or implement fallback strategies across providers.
Agent Optimization Toolkit: The platform includes capabilities for improving agent reliability through fallback configurations, retry logic, A/B testing between different prompts or models, and parallel model execution to compare responses.
How It Works
The Lamatic 3.0 development workflow follows a structured process:
Teams begin by accessing the visual Studio interface, where they design agentic flows by dragging and connecting nodes. These nodes can represent AI models, data transformations, conditional logic, external API calls, or integrations with business tools. For RAG applications, users configure the integrated Weaviate vector database by connecting data sources and selecting embedding models for automatic vectorization.
Once a flow is designed, users can test it directly within the Studio using the built-in testing interface. The platform provides real-time execution logs and traces, allowing developers to debug issues before deployment.
When ready for deployment, users commit their flow to a GitHub repository through the native version control integration. Lamatic 3.0 automatically generates the necessary API endpoints and deploys the application to Cloudflare Workers for global edge execution. The platform handles all infrastructure provisioning, scaling, and monitoring.
Development teams can create separate branches for feature work, test changes in isolated environments, and merge updates to production through standard GitHub pull request workflows. The platform supports environment-specific configurations, allowing different settings for development, staging, and production deployments.
External applications interact with deployed agents through the auto-generated GraphQL API, REST endpoints, or webhooks. Lamatic also provides embeddable widgets for chat and search interfaces that can be integrated into websites or applications with minimal code.
Use Cases
Lamatic 3.0 supports diverse AI agent applications across industries:
Intelligent Knowledge Assistants: Organizations build internal AI assistants that answer employee questions by retrieving information from corporate knowledge bases, documentation repositories, and business applications. The platform’s RAG capabilities enable accurate, context-aware responses grounded in company-specific data.
Customer Support Automation: Businesses deploy conversational agents that handle customer inquiries by accessing support documentation, CRM systems, and order databases. Multi-step workflows can escalate complex issues to human agents while automating routine questions.
Data Processing Pipelines: Teams create automated workflows that extract insights from unstructured data sources, transform information into structured formats, and trigger downstream actions based on analysis results.
Multi-Agent Systems: The platform enables development of supervisor agents that coordinate multiple specialized sub-agents, each handling specific aspects of complex tasks. This architecture supports sophisticated workflows requiring task decomposition and parallel execution.
Rapid Prototyping and MVPs: Startups and product teams use AgentKit templates to launch AI-powered features in days rather than months, accelerating market validation and customer feedback cycles.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
Lamatic 3.0 offers several compelling benefits for AI agent development:
The all-in-one architecture significantly reduces integration complexity by providing visual flow building, managed infrastructure, vector database, and deployment automation within a unified platform. Teams avoid the overhead of integrating separate tools for each component of the AI stack.
The GitHub-native version control enables professional software development practices including code review, branching strategies, and continuous deployment. This approach makes AI agent development feel familiar to engineering teams accustomed to modern DevOps workflows.
Cloudflare Workers-based edge deployment ensures low-latency global access to AI agents while automatic scaling handles traffic spikes without manual intervention. The serverless model eliminates infrastructure management responsibilities.
The collaborative design between technical and non-technical team members accelerates iteration cycles. Domain experts can modify prompts and business logic through the visual interface while engineers maintain control through version control and custom code integration.
Strong RAG support with managed Weaviate simplifies building knowledge-intensive applications. Automatic data ingestion, vectorization, and incremental updates remove significant engineering work typically required for production RAG systems.
Disadvantages
Lamatic 3.0 faces several considerations that may impact adoption:
The integrated, opinionated architecture may limit flexibility for teams requiring highly customized infrastructure or preferring alternative technology choices. Organizations with existing investments in specific databases, hosting platforms, or orchestration frameworks may find migration challenging.
Pricing transparency remains limited, with the enterprise tier reported at \$30,000 annually but detailed pricing for mid-market customers not extensively documented. Cost predictability concerns may affect budget planning for growing teams.
The platform represents a relatively new entrant launched in November 2024, meaning the production track record and ecosystem maturity lag behind established alternatives. Organizations with conservative technology adoption policies may prefer platforms with longer operational histories.
Vendor lock-in considerations emerge from the tightly integrated stack. While Lamatic provides open-source SDKs, migrating complex agent workflows to alternative platforms would require substantial re-engineering effort.
How Does It Compare?
Lamatic 3.0 competes in the rapidly evolving AI agent development platform space, distinguishing itself through its tightly integrated, end-to-end approach. Below is a structured comparison with current competitors across different categories:
Visual AI Workflow Builders
Flowise: Open-source visual AI workflow builder based on LangChain (Node.js/TypeScript). Offers drag-and-drop interface with extensive pre-built components and marketplace templates. Best for teams prioritizing flexibility and open-source customization. Compared to Lamatic, Flowise provides greater component-level control but requires more manual setup for deployment and production infrastructure.
Langflow: Python-based visual AI development platform with clean interface optimized for rapid prototyping. Excels in simplicity and quick iteration for smaller projects. Supports custom Python components for extensibility. Less comprehensive than Lamatic for production deployment workflows, requiring additional tooling for enterprise version control and managed hosting.
n8n: General-purpose workflow automation platform with AI/LLM node integration. Stronger in traditional API orchestration and business process automation than AI-specific features. Offers both cloud and self-hosted options. Compared to Lamatic, n8n provides broader non-AI automation capabilities but less sophisticated agent-specific features like multi-agent coordination and specialized RAG pipelines.
Dify: Open-source LLMOps platform combining no-code interface with backend-as-a-service capabilities. Offers similar managed approach to Lamatic with visual prompt orchestration, multi-model support, and RAG features. Key difference: Dify emphasizes rapid prototyping and accessibility for non-technical users, while Lamatic 3.0 targets professional development teams with GitHub integration and enterprise workflows.
Enterprise Agent Platforms
Retool Agents: Enterprise-grade platform combining agent development with Retool’s internal tool building ecosystem. Provides form-based agent configuration, human-in-the-loop controls, and production observability. Best for organizations already using Retool for internal tools. Lamatic differentiates through visual flow design and edge deployment versus Retool’s focus on internal business process automation.
Zapier Agents: No-code agent builder integrated with Zapier’s 8,000+ app ecosystem. Enables non-technical users to create automation agents with browser extension for triggering from any website. Optimized for business user accessibility rather than developer-centric workflows. Lamatic offers more sophisticated agent orchestration and custom logic capabilities for technical teams.
Vertex AI Agent Builder (Google Cloud): Enterprise platform from Google Cloud for building custom AI agents with strong GCP integration, governance features, and compliance capabilities. Targets large enterprises with complex regulatory requirements. Compared to Lamatic, Vertex emphasizes security and compliance over development velocity and cross-functional collaboration.
Microsoft Copilot Studio: Microsoft’s enterprise agent development platform with deep Microsoft 365 and Azure integration. Ideal for organizations heavily invested in Microsoft ecosystem. Lamatic differentiates through technology-agnostic approach supporting multiple cloud providers and model vendors.
AI Agent Frameworks and Orchestration
LangChain/LangGraph: Popular open-source frameworks for building LLM-powered applications and agentic workflows. Provides maximum flexibility and control through code-first approach. Requires significant engineering effort to build production infrastructure, deployment pipelines, and observability tooling that Lamatic provides out of the box.
CrewAI: Multi-agent orchestration framework focused on role-based agent collaboration. Excels in scenarios requiring specialized agents working together on complex tasks. Code-centric approach appeals to developers comfortable with Python. Lamatic offers similar multi-agent capabilities through visual interface with lower barrier to entry.
AutoGen (Microsoft): Multi-agent conversation framework supporting autonomous and human-in-the-loop workflows. Strong for academic and research contexts. Compared to Lamatic, AutoGen provides greater architectural flexibility but requires substantially more implementation work for production deployment.
Low-Code Development Platforms
BuildShip: Visual backend builder with AI workflow capabilities and serverless deployment. Combines general backend development with AI features. Broader use case coverage than Lamatic but less specialized for complex agentic workflows.
Stack AI: Enterprise-focused platform for building AI applications with emphasis on data integration and team collaboration. Offers similar managed infrastructure approach. Differentiation less pronounced compared to Lamatic’s GitHub-native version control and edge deployment strategy.
Bubble with AI Integrations: General-purpose no-code application builder with AI capabilities through integrations and plugins. Best for full-stack application development where AI is one component. Lamatic specializes exclusively in AI agent development with deeper platform-level optimizations.
Key Differentiators
Lamatic 3.0 distinguishes itself through several unique combinations:
The GitHub-native version control integration enables professional software development practices uncommon in visual AI builders, bridging the gap between low-code accessibility and enterprise development standards.
Serverless edge deployment via Cloudflare Workers provides global low-latency execution without infrastructure management, differentiating from platforms requiring self-hosted deployment or traditional cloud regions.
The all-in-one approach bundling visual builder, managed vector database, edge hosting, and monitoring reduces tool sprawl compared to frameworks requiring separate solutions for each component.
AgentKit templates with one-click deployment accelerate time-to-production for common use cases, competing with the ease-of-use found in no-code tools while maintaining developer-friendly customization options.
The subscription model bundles infrastructure, vector database, and platform access into unified pricing, potentially simplifying procurement compared to assembling separate services.
Pricing and Availability
Lamatic 3.0 operates on a freemium business model. The platform offers a free tier with limited features, allowing teams to experiment and prototype without upfront investment. For production use and enterprise capabilities, pricing information indicates an Enterprise plan at approximately \$30,000 per year. Mid-tier pricing details are not extensively documented in public materials. Prospective users should contact Lamatic directly for detailed pricing tailored to their usage requirements, team size, and feature needs.
Final Thoughts
Lamatic 3.0 presents a well-integrated solution for organizations seeking to build and deploy AI agents with minimal infrastructure complexity. The platform successfully addresses common pain points in agent development: fragmented tooling, deployment challenges, and collaboration friction between technical and business stakeholders. The GitHub-native version control and serverless edge deployment represent genuine innovations in making professional software development practices accessible within visual AI builders.
The platform appears particularly well-suited for product teams at startups and mid-sized companies that value rapid iteration and want to avoid managing infrastructure, yet need more control and production-readiness than purely no-code solutions provide. Enterprises with substantial Microsoft or Google Cloud investments may find ecosystem-specific alternatives more natural fits, while organizations prioritizing open-source flexibility might prefer Flowise or Langflow despite their greater configuration requirements.
As a November 2024 launch, Lamatic 3.0 remains relatively new, meaning prospective users should evaluate production stability and community ecosystem maturity against their risk tolerance. However, the technical architecture is sound, and the value proposition of unified agent development, version control, and deployment addresses genuine market needs. For teams currently struggling with integrating LangChain, managing vector databases, and deploying agent workflows to production, Lamatic 3.0 offers a compelling alternative worth evaluating, particularly given the free tier availability for hands-on assessment.