Table of Contents
Overview
Designed to bridge the gap in native Linux accessibility, NexTalk leverages modern local-AI architectures to process audio data without an internet connection. By utilizing a transparent “capsule” UI that overlays the screen only during active speech, it minimizes visual clutter while maintaining a high degree of responsiveness. Its architecture is specifically optimized for modern Linux environments, offering full compatibility with Wayland and X11 through a native Fcitx5 integration. This ensures that text is injected into terminals, code editors, and browsers with sub-20ms latency, making voice dictation feel as natural and secure as physical typing.
Key Features
- 100% Offline AI Inference: Uses the high-efficiency Sherpa-onnx engine to perform all speech recognition locally, ensuring that private conversations never leave the device.
- Native Fcitx5 Integration: Communicates directly with the Linux input method framework via Unix Domain Sockets, avoiding the lag and reliability issues associated with virtual keyboard hacks.
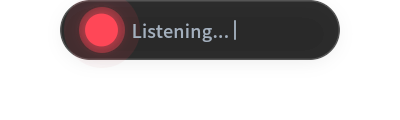
- Minimalist Capsule UI: Features a sleek, Flutter-based transparent overlay that appears when summoned by a hotkey and vanishes instantly upon completion.
- Sub-20ms Ultra-Low Latency: Optimized for real-time performance, delivering processed text into the focused window with virtually no perceptible delay.
- Full Wayland & X11 Support: Built from the ground up to work seamlessly across all major Linux desktop environments, including GNOME and KDE.
- Bilingual Support (English/Mandarin): Ships with optimized models for highly accurate transcription in both English and Mandarin Chinese.
- Zero-Hassle Installation: Distributed as a native Linux package that integrates with existing system shortcuts and input managers.
- Developer-Friendly Architecture: Open-source design allowing for custom command integration and integration into larger accessibility workflows.
How It Works
The workflow begins with the user pressing a configurable hotkey (default: Alt + Space). This action wakes the “NexTalk Capsule”—a small, semi-transparent window that stays on top of all other applications. As the user speaks, the audio is processed locally using the Sherpa-onnx model. The resulting text is streamed through a high-speed C++ plugin to the Fcitx5 input method server. Fcitx5 then injects the characters directly into the focused text area, whether it’s a Slack message, a line of code in VS Code, or a terminal command. When the user stops speaking or presses the hotkey again, the capsule vanishes, and the input process concludes.
Use Cases
- Privacy-Sensitive Dictation: Drafting emails or legal documents in environments where data security and offline operation are mandatory.
- Voice Coding & Development: Speeding up code writing or terminal commands using hands-free input, integrated directly into IDEs.
- Wayland-Native Accessibility: Providing a robust voice typing solution for users on modern Wayland-based distros like Fedora or Ubuntu 24.04+.
- Low-Bandwidth Productivity: Enabling consistent, high-speed dictation for users with unstable or restricted internet connections.
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Unmatched privacy and security due to local-only processing. Native integration provides a much smoother experience than “keystroke simulation” tools. Extremely lightweight and visually unobtrusive.
- Cons: Exclusively built for the Linux ecosystem (no Windows or macOS support). Requires the Fcitx5 input method framework to be installed on the system.
Pricing
- Free & Open Source: NexTalk is available for free under the MIT License, with its full source code hosted on GitHub for community contributions and auditing.
How Does It Compare?
- Nerd-dictation: A popular Python-based offline tool. While Nerd-dictation is highly hackable, NexTalk offers a much more polished UI and superior system-level integration through Fcitx5 and Unix sockets.
- Dragon (Nuance): The long-standing king of Windows dictation. Dragon is highly accurate but expensive and cloud-heavy. NexTalk provides a comparable speed for Linux users while being completely free and offline.
- Google Docs Voice Typing: High accuracy but requires a persistent cloud connection and only works within the browser. NexTalk works across every application on the Linux desktop.
- Vosk / Whisper (Local setups): These are raw AI models. NexTalk is a “finished product” that packages these types of models into a user-friendly application with a dedicated UI and system integration.
- Utterly: A cloud-based voice agent tool. Utterly focuses on call handling and business transcripts, whereas NexTalk is a dedicated “typing tool” for personal productivity.
Final Thoughts
NexTalk is a transformative tool for the Linux community, finally delivering a professional-grade voice input experience that respects the platform’s core values of privacy and efficiency. By successfully combining a modern UI (Flutter) with a high-performance backend (Sherpa-onnx), it moves Linux voice input from the realm of “hacker projects” into a mainstream productivity utility. As AI continues to evolve, NexTalk stands as a model for how specialized, local-first applications can outperform cloud giants in both speed and trust. For any Linux user looking to automate their typing or enhance their accessibility, NexTalk is an essential, zero-cost addition to their software library.

