Table of Contents
Overview
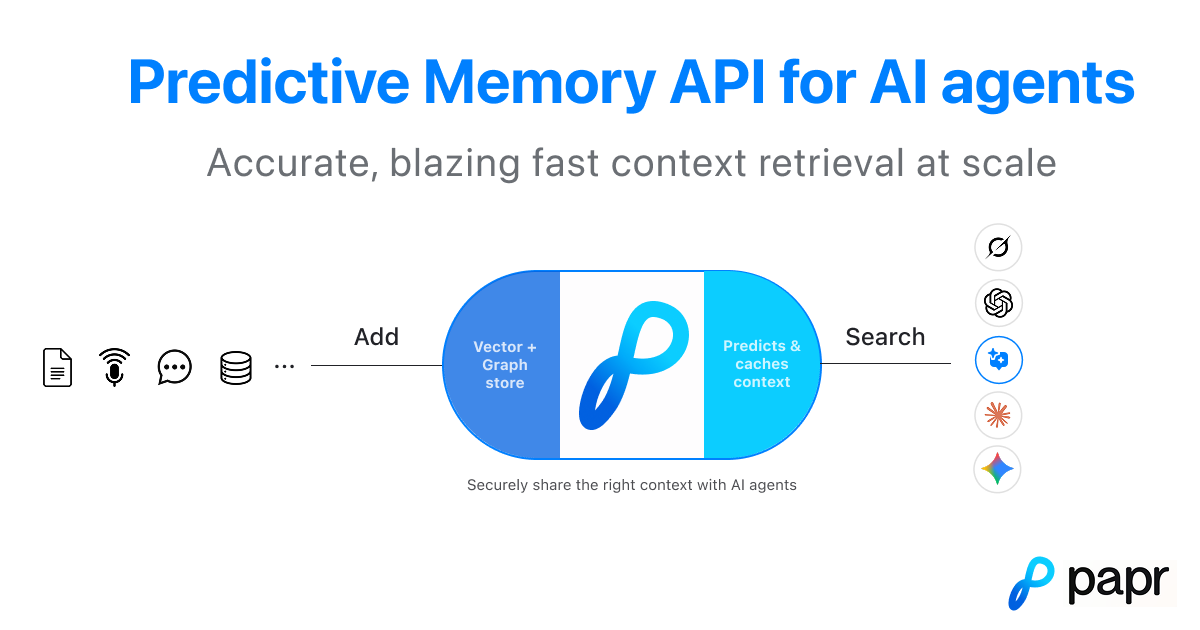
Papr is an AI-native memory infrastructure platform combining vector embeddings and knowledge graphs into unified API enabling production-ready Retrieval-Augmented Generation and long-term memory capabilities for AI agents and applications. Ranked #1 on Stanford’s STaRK benchmark with 91%+ retrieval accuracy and sub-100ms query latency, Papr addresses fundamental challenges AI systems face: agents hallucinate without access to relevant context, conversation history lives disconnected from documents and structured data, traditional RAG systems return text fragments rather than connected understanding, and scaling knowledge bases often degrades rather than improves retrieval performance creating unpredictable agent behavior.
Papr’s Predictive Memory Graph architecture maps real relationships across all data sources connecting code commits to support tickets, AI conversations to Slack threads, and design decisions to implementation creating interconnected knowledge story rather than isolated information silos. The platform automatically structures unstructured data from meetings, documents, conversations, and tools into hybrid memory combining vector similarity search with knowledge graph traversal enabling multi-hop retrieval surfacing insights users haven’t explicitly requested. Available as open-source self-hosted deployment or managed cloud service with identical APIs, Papr provides built-in access control lists, namespace boundaries, and permission management ensuring data privacy for multi-tenant applications.
The platform targets developers building AI assistants requiring cross-session context memory, enterprises deploying document Q\&A systems across large knowledge bases, customer experience teams automating multi-step support ticket resolution, SaaS companies implementing multi-tenant knowledge management, and researchers constructing domain-specific knowledge graphs for specialized applications. By treating memory as prediction challenge rather than search task, Papr scales performance as data grows contrary to traditional RAG systems experiencing degradation with increased knowledge base size.
Key Features
Ranked #1 on Stanford STaRK Benchmark: Papr achieves 91%+ retrieval accuracy on Stanford’s Semi-structured Retrieval Benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases, the authoritative evaluation framework assessing LLM-driven retrieval systems on semi-structured knowledge combining textual content with complex relational information. STaRK features natural-sounding queries requiring context-specific reasoning across product search, academic paper search, and biomedical inquiry domains with millions of entities and relationships. Papr’s top ranking demonstrates superior capability handling real-world retrieval scenarios where information spans unstructured text and structured entity relationships versus competitors focusing exclusively on vector similarity without graph-based context connections.
Sub-100ms Retrieval with Predictive Caching: Query response latency under 100 milliseconds through predictive memory engine anticipating what users will request next and pre-loading relevant context. This predictive approach contrasts with reactive retrieval waiting for explicit queries then searching indices; Papr analyzes interaction patterns, temporal access sequences, and entity relationships predicting probable information needs caching anticipated results enabling instant response when queries arrive. The low-latency performance proves critical for interactive AI applications where multi-second retrieval delays create unacceptable user experience or break conversational flow in chatbot scenarios.
Hybrid Vector Index Plus Knowledge Graph Architecture: Unified data structure combining semantic vector embeddings with explicit entity relationship graphs providing complementary retrieval modalities. Vector similarity search identifies semantically related content through high-dimensional embedding proximity; knowledge graph traversal follows explicit connections between entities understanding contextual relationships, hierarchies, temporal sequences, and references impossible capturing through embeddings alone. The hybrid approach enables sophisticated multi-hop retrieval connecting information across multiple independent sources answering complex queries requiring synthesis from disconnected knowledge fragments—capabilities exceeding pure vector databases or standalone graph systems.
Automatic Entity Extraction and Relationship Mapping: LLM-powered analysis transforms unstructured data from meeting transcripts, Slack conversations, documents, and tool outputs into structured knowledge graph based on defined ontologies. The system identifies entities (people, companies, projects, tasks, insights, opportunities, code snippets), extracts entity attributes and properties, infers relationships between entities, and maintains temporal ordering creating rich interconnected knowledge representation from raw text. This automatic structuring eliminates manual knowledge graph construction enabling continuous knowledge capture from everyday work artifacts without explicit data entry overhead.
GraphQL and Natural Language Query Interfaces: Dual query modalities serving different use cases: GraphQL enables structured queries for analytics, aggregations, and relationship analysis requiring precise control over traversal depth, filtering, and return shapes; natural language search accepts conversational queries receiving semantically relevant memories with automatic graph entity inclusion and intelligent reranking. The flexibility supports both technical users requiring programmatic access and end-users preferring conversational interfaces democratizing knowledge access across diverse stakeholder technical capabilities.
Built-In Access Controls and Multi-Tenant Architecture: Enterprise-grade permission management with access control lists, namespace boundaries preventing cross-tenant data leakage, and row-level security ensuring users only retrieve authorized information. The multi-tenant architecture enables SaaS providers hosting multiple customers’ knowledge bases within shared infrastructure maintaining complete data isolation and privacy guarantees. Permissions propagate through knowledge graph relationships preventing indirect information disclosure through entity connections bridging security boundaries addressing complex access control scenarios characteristic of enterprise knowledge management.
Unified RAG Plus Memory API: Single API surface combining document-based retrieval-augmented generation with conversational memory management eliminating integration complexity of maintaining separate vector databases, conversation stores, and document repositories. Developers store memories via POST /v1/memory, retrieve through POST /v1/memory/search, upload documents via POST /v1/document with automatic analysis and selective memory creation, and send conversation history with intelligent extraction of important information—all through consistent interface requiring minimal code for comprehensive AI memory capabilities.
Open Source and Managed Cloud Options: Platform availability as fully open-source self-hosted deployment providing complete control over infrastructure, data residency, and customization enabling organizations with strict security requirements, air-gapped environments, or specific compliance needs running Papr internally. Managed cloud offering provides turnkey solution eliminating operational overhead with same API compatibility ensuring seamless migration paths between deployment models as organizational needs evolve. The dual availability strategy addresses diverse enterprise requirements from cost-conscious startups to regulated industries.
User and Agent Memory Types: Support for both user-centric memories capturing preferences, history, context, conversations enabling personalization and agent-centric memories where AI documents own workflows, learnings, reasoning patterns enabling self-improvement. Both memory types stored and queried identically allowing agents not just personalizing for users but learning and enhancing own capabilities over time creating continuously improving AI systems through experiential learning captured as structured memories.
Real-Time Data Ingestion and Synchronization: Immediate addition and indexing of new memories ensuring knowledge base currency without batch processing delays or stale data problems characteristic of periodic reindexing approaches. The log-structured ingestion pipeline separates write operations from query processing enabling continuous data streaming while maintaining query consistency preventing read-your-writes anomalies. Real-time synchronization proves essential for operational use cases where outdated information creates incorrect decisions or customer-facing applications requiring immediate knowledge updates.
Intelligent Reranking and Hybrid Search: Advanced result ranking combining semantic similarity scores with graph relationship strengths, temporal relevance, contextual filters, and metadata matching producing final result sets optimized for query intent beyond simple embedding distance. Hybrid search functionality merges sparse retrieval methods (BM25-style keyword matching, learned-sparse models) with dense embeddings improving robustness and accuracy addressing limitations of pure semantic search missing exact terminology matches or specialized vocabularies. The sophisticated ranking ensures most relevant and contextually appropriate results surface despite massive knowledge bases.
How It Works
Papr operates through sophisticated integration combining vector embeddings, knowledge graph construction, predictive caching, and multi-modal retrieval creating comprehensive memory infrastructure:
Step 1: Data Ingestion Through Multiple Pathways
Developers add data via three input methods: direct memory creation (POST /v1/memory) explicitly storing information with full control suitable for agent self-documentation, document upload (POST /v1/document) for PDFs and Word files with automatic analysis and selective memory extraction, or message/chat ingestion sending conversation history with intelligent information extraction. This flexible ingestion accommodates diverse data sources from structured agent outputs to unstructured human communications.
Step 2: Automatic Structuring and Entity Extraction
LLMs analyze ingested content identifying entities (people, companies, projects, tasks, insights, opportunities, code), extracting entity attributes, inferring relationships based on context and co-occurrence patterns, and applying domain ontologies structuring knowledge consistently. For example, customer discovery meeting transcript transforms into structured entities representing discussed problems, associated customer company, mentioned competitor products, identified opportunities, and action items with temporal and reference relationships connecting elements creating queryable knowledge graph from unstructured recording.
Step 3: Vector Embedding and Graph Index Creation
Content generates semantic embeddings through chosen models (Papr’s hosted options or custom embeddings) capturing meaning in high-dimensional vector space enabling similarity search. Simultaneously, extracted entities and relationships populate knowledge graph with nodes representing entities and edges encoding connections. Both indices update dynamically as new data arrives maintaining currency without full reindexing enabling real-time knowledge evolution supporting operational workflows.
Step 4: Predictive Memory Engine Optimization
Background prediction models analyze access patterns, temporal sequences, entity co-occurrence, and user interaction histories identifying probable future queries. The system pre-computes result sets for anticipated requests, caches connected context subgraphs for frequent entity combinations, and prioritizes indexing for high-probability retrieval paths. This predictive optimization enables sub-100ms query response despite potentially traversing million-node graphs by preprocessing likely queries before explicit requests arrive.
Step 5: Hybrid Search and Multi-Hop Retrieval
Query requests trigger parallel search paths: vector similarity identifies semantically related memories through embedding proximity, keyword matching finds exact terminology through sparse retrieval, and graph traversal explores entity connections following relationships to discover contextually relevant information multiple hops distant from initial vector matches. For example, query about “weekend guest food preferences” might vector-match “Pen is coming” entry, graph-traverse to Pen’s profile discovering pasta preference, then connection-follow to specific menu items containing pasta yielding complete contextualized answer synthesized from multiple independent memories.
Step 6: Intelligent Result Reranking
Raw retrieval results from vector, keyword, and graph searches merge through reranking algorithm considering semantic relevance scores, relationship strengths and paths lengths, temporal recency and access frequency, metadata filter matching, and contextual coherence across result set. The reranking produces final ordered results optimizing for query intent extracting signal from diverse retrieval modalities ensuring most valuable information surfaces rather than simply closest embeddings.
Step 7: Permission-Aware Filtering
Before returning results, access control layer filters memories and entities checking requester permissions against ACLs, respecting namespace boundaries preventing cross-tenant exposure, and validating relationship traversal doesn’t leak restricted information through entity connections. This security enforcement operates transparently maintaining performance while ensuring data privacy and regulatory compliance requirements for enterprise deployments handling sensitive information.
Step 8: Continuous Learning and Model Updates
User interactions, relevance feedback, and query patterns feed prediction models improving anticipatory caching accuracy over time. The system identifies underperforming queries, analyzes failure modes revealing knowledge gaps or structuring issues, and adjusts entity extraction and relationship inference based on demonstrated information needs creating continuously improving memory infrastructure adapting to actual usage patterns.
Use Cases
Given specialization in unified RAG plus memory with knowledge graph integration, Papr addresses scenarios where connected context and persistent memory provide value:
Powering Long-Context Chatbots and Copilots:
Developers building AI assistants requiring memory beyond single conversation sessions leverage Papr storing user interactions, preferences, historical context, and learned information. The knowledge graph connections enable assistants understanding relationships between past conversations, referenced documents, and user-specific context surfacing relevant information without explicit reminders. Multi-hop retrieval answers complex queries synthesizing information from multiple conversation threads, documents, and structured data impossible with conversation history alone. The persistent memory transforms stateless chatbots into contextually-aware assistants understanding user needs and history creating personalized experiences.
Building Agents Remembering Users Across Sessions:
AI agent applications requiring user context persistence across multiple interactions use Papr maintaining user profiles, preference histories, past actions, learned behaviors, and interaction patterns. The memory enables agents personalizing responses based on demonstrated preferences, avoiding repeating previously provided information, referencing past conversations naturally, and building continuous relationship understanding user needs evolution. For example, coding assistant remembers developer’s preferred frameworks, coding style, project context, and past problem-solving approaches tailoring suggestions matching established patterns rather than providing generic advice.
Analytics and Insights UIs Querying Knowledge Graphs:
Business intelligence and analytics applications leverage GraphQL interface executing structured queries over knowledge graphs aggregating information, identifying patterns, and discovering insights. Complex analytical queries like “find all customer problems mentioned in discovery calls related to onboarding workflow efficiency” traverse meeting transcripts, extract problem entities, filter by topic, and aggregate results impossible with pure text search. The structured graph queries enable dashboards, reporting tools, and analytical UIs providing business insights from unstructured organizational knowledge without manual data extraction.
Reducing Hallucinations in Production LLM Applications:
Production AI applications suffering from LLM hallucinations when generating information absent from training data use Papr ensuring language models ground responses in verified factual context. The high retrieval accuracy and multi-hop capability surface relevant supporting information for queries enabling citation-backed responses verifiable against source documents. The knowledge graph connections help models understanding relationships and context reducing confabulation when dealing with ambiguous or incomplete information by providing structured context beyond isolated text fragments.
Enterprise Document Intelligence and Q\&A:
Organizations with large document repositories (contracts, reports, technical documentation, policies) deploy Papr enabling natural language querying across corpus. The automatic entity extraction identifies key terms, people, dates, requirements, obligations creating structured representation of document content. Multi-hop retrieval connects related information across documents answering questions requiring synthesis from multiple sources like “what are contract renewal terms for customers in healthcare sector” traversing customer entities, industry classifications, and contract clauses producing comprehensive answers.
Customer Support Automation and Multi-Step Ticket Resolution:
Customer experience teams automate support workflows through Papr memory storing customer interaction histories, product knowledge bases, troubleshooting procedures, and resolved ticket patterns. Support agents and AI assistants query knowledge accessing relevant context from past tickets, known issues, solution documentation, and customer-specific configurations. The graph relationships connect symptoms to root causes, solutions to prerequisite steps, and customers to product versions enabling accurate multi-step troubleshooting surpassing keyword search limitations.
Multi-Tenant SaaS Knowledge Management:
SaaS platforms serving multiple customers require secure knowledge isolation while maintaining operational efficiency. Papr’s multi-tenant architecture with built-in ACLs enables hosting all customer knowledge bases within shared infrastructure maintaining complete data separation and privacy. Each tenant benefits from improved retrieval performance as overall system scales contrary to traditional approaches where shared indices create cross-contamination risks necessitating separate deployments increasing operational complexity and costs.
Domain-Specific Knowledge Graph Construction:
Researchers and enterprises building specialized knowledge graphs for domains (healthcare, finance, legal, scientific research) leverage Papr’s automatic entity extraction and relationship mapping constructing graphs from unstructured domain literature, research papers, regulations, and expert documents. The resulting knowledge graphs enable sophisticated domain queries, relationship discovery, and insight generation supporting research, compliance, decision-making, and domain expertise amplification without manual graph curation.
Pros \& Cons
Advantages
Top-Ranked Retrieval Accuracy Validated by Independent Benchmark: The #1 position on Stanford STaRK benchmark with 91%+ accuracy provides objective third-party validation of Papr’s retrieval capabilities versus competitive solutions. Academic benchmarks eliminate vendor self-reported performance claims providing trustworthy comparative assessment critical for production deployment decisions where retrieval quality directly impacts application value and user experience.
Hybrid Architecture Combining Vector and Graph Strengths: The unified vector plus knowledge graph approach addresses fundamental limitations of pure vector databases (missing explicit relationships, inability to traverse connections, poor performance on structured queries) and standalone graph systems (weak semantic similarity, limited unstructured text handling) providing comprehensive solution handling diverse query patterns from semantic search to relationship analysis.
Sub-100ms Latency Enabling Real-Time Applications: The predictive caching and optimization delivering query responses under 100 milliseconds enables interactive AI applications where multi-second delays create unacceptable user experience. This performance proves critical for conversational interfaces, real-time decision support, and customer-facing applications requiring immediate responses maintaining engagement and utility.
Unified API Simplifying Integration Complexity: Single API surface combining RAG, conversational memory, document intelligence, and knowledge graph queries dramatically reduces integration effort versus cobbling together separate vector databases, conversation stores, graph systems, and document processors. The unified interface accelerates development, reduces maintenance burden, and creates consistent developer experience across diverse memory and retrieval needs.
Scales Performance as Knowledge Grows: The counter-intuitive property where increasing data improves rather than degrades retrieval performance through enhanced prediction models, richer entity relationships, and denser knowledge graphs addresses fundamental scaling challenges traditional RAG systems face. This positive scaling characteristic proves essential for long-term production deployments where knowledge bases continuously expand from operational usage.
Enterprise-Grade Security and Multi-Tenancy: Built-in ACLs, namespace isolation, and permission-aware retrieval enable secure multi-tenant SaaS deployments handling sensitive information without custom security layers. The enterprise focus differentiates Papr from developer-focused vector databases lacking production-grade access controls requiring extensive additional engineering for secure production deployment.
Open Source and Cloud Deployment Flexibility: Dual availability as self-hosted open source and managed cloud with API compatibility provides deployment flexibility matching diverse organizational requirements, compliance constraints, and cost structures. Organizations start with managed cloud then migrate to self-hosted as scale increases or reverse path enables rapid prototyping before committing infrastructure investment.
Automatic Structuring Reducing Manual Knowledge Engineering: LLM-powered entity extraction and relationship inference eliminates tedious manual knowledge graph construction enabling continuous knowledge capture from everyday artifacts without explicit data entry. This automation proves transformative versus traditional knowledge management requiring dedicated ontologists and manual curation limiting adoption and currency.
Disadvantages
Infrastructure Product Requiring Engineering Integration Effort: Papr represents developer-facing infrastructure platform rather than end-user application requiring engineering resources building integration layers, designing memory schemas, implementing data ingestion pipelines, and optimizing retrieval for specific use cases. This complexity may prove excessive for simple chatbot scenarios where dedicated solutions like ChatGPT plugins or simple vector databases suffice without infrastructure investment.
Limited Public Information About Production Deployments: As relatively new platform, comprehensive case studies, production deployment references, proven scalability under extreme load, and extensive community knowledge remain limited compared to established vector databases with years operational history. Early adopters face uncertainty about edge cases, failure modes, operational complexity, and long-term viability characteristic of nascent infrastructure technologies.
Pricing Structure Unspecified Creating Cost Uncertainty: While open-source self-hosted option exists, managed cloud pricing remains undisclosed preventing accurate cost forecasting for production deployments. Organizations cannot evaluate total cost of ownership, compare value propositions against alternatives with transparent pricing, or budget effectively for scaling creating procurement and financial planning challenges.
Stanford STaRK Benchmark Scope May Not Represent All Use Cases: While impressive, single benchmark performance doesn’t guarantee superior results across all retrieval scenarios, domains, or query patterns. Organizations must validate Papr against own datasets, query distributions, and performance requirements rather than relying exclusively on benchmark results potentially not representative of specific application characteristics.
Knowledge Graph Quality Depends on LLM Extraction Accuracy: Automatic entity extraction and relationship inference susceptibility to LLM errors, ambiguities, or misinterpretations creates risk of incorrect knowledge graph structure propagating through retrieval results. Over-reliance on automatic structuring without validation may introduce subtle errors accumulating over time degrading knowledge base quality requiring human review mechanisms.
Learning Curve for Advanced Features and Optimization: Maximizing Papr’s capabilities requires understanding vector embeddings, knowledge graph concepts, query optimization, memory schema design, and predictive caching mechanisms. Organizations lacking AI/ML expertise may struggle extracting full platform value or may under-utilize advanced features settling for basic retrieval missing opportunities for sophisticated multi-hop queries and graph analytics.
Young Ecosystem with Limited Third-Party Integrations: Compared to established vector databases with extensive connector ecosystems, monitoring tools, administrative interfaces, and community resources, Papr’s tooling and integration ecosystem remains nascent. Early adopters build custom solutions for common operational needs like monitoring, backup/restore, migration tools, or observability potentially duplicating effort across deployments.
Dependency on External LLMs for Entity Extraction: The automatic knowledge graph construction requiring LLM API calls creates external dependencies on OpenAI, Anthropic, or other providers introducing latency, cost per ingestion operation, rate limiting, and potential service outages. Organizations requiring complete self-contained deployment may face challenges if preferred local models lack sufficient capability for high-quality entity extraction.
How Does It Compare?
Papr vs Pinecone (Leading Managed Vector Database)
Pinecone is established fully-managed vector database serving major enterprises providing real-time semantic search, hybrid search combining dense and sparse embeddings, metadata filtering, serverless architecture with automatic scaling, and comprehensive SDK support across Python, JavaScript, Java, .NET launched 2019 processing billions of vectors for thousands of customers.
Architecture Approach:
- Papr: Hybrid vector index plus knowledge graph with entity relationships and multi-hop traversal
- Pinecone: Pure vector database optimized for approximate nearest neighbor search with metadata filtering
Retrieval Capabilities:
- Papr: Multi-hop graph traversal connecting information across entity relationships; 91%+ accuracy on STaRK benchmark
- Pinecone: High-performance vector similarity with hybrid search (dense + sparse embeddings); optimized for recall and latency
Knowledge Graph:
- Papr: Built-in knowledge graph with automatic entity extraction and relationship mapping core to architecture
- Pinecone: No native knowledge graph; pure vector storage requiring external graph solutions if needed
Query Interfaces:
- Papr: GraphQL for structured queries and natural language for semantic search
- Pinecone: REST API for vector operations; no native GraphQL or complex query language
Access Control:
- Papr: Built-in ACLs, namespace boundaries, row-level permissions with graph-aware security
- Pinecone: Namespace isolation, API key-based auth, metadata filtering for access control
Deployment Options:
- Papr: Open-source self-hosted or managed cloud with identical APIs
- Pinecone: Managed cloud only (serverless or pod-based); no self-hosted option
When to Choose Papr: For applications requiring knowledge graph relationships, multi-hop retrieval connecting entities, GraphQL analytical queries, or validated STaRK benchmark performance on semi-structured knowledge.
When to Choose Pinecone: For pure vector similarity workloads, established managed infrastructure with proven enterprise scale, comprehensive ecosystem integrations, transparent pricing, or avoiding self-hosting operational complexity.
Papr vs Weaviate (Open-Source AI-Native Vector Database)
Weaviate is open-source vector database emphasizing developer experience with GraphQL interface, modular vectorization connecting popular embedding models (OpenAI, Cohere, Hugging Face), hybrid search combining vector and keyword (BM25), and production-ready clustering for horizontal scaling serving millions of developers since 2016.
Open Source Model:
- Papr: Open source with dual licensing supporting self-hosted and managed cloud
- Weaviate: Fully open source (BSD-3-Clause) with optional Weaviate Cloud Services managed offering
Graph Capabilities:
- Papr: Native knowledge graph with entity extraction and multi-hop relationship traversal
- Weaviate: Vector database with cross-references between objects; no true knowledge graph or automatic entity extraction
Search Methods:
- Papr: Hybrid vector + graph + keyword with intelligent reranking combining modalities
- Weaviate: Hybrid vector + BM25 keyword search; generative search for RAG; no graph traversal
Module Ecosystem:
- Papr: Focused API with integrated features; limited third-party module ecosystem
- Weaviate: Extensive module system connecting 20+ services (OpenAI, Cohere, VoyageAI, Hugging Face) for vectorization and generation
Benchmark Performance:
- Papr: #1 Stanford STaRK with 91%+ accuracy on semi-structured retrieval
- Weaviate: Strong ANN benchmark performance; no specific STaRK ranking published
Scalability Approach:
- Papr: Predictive caching and optimization; multi-tenant architecture
- Weaviate: Horizontal scaling through sharding; replication for fault tolerance
When to Choose Papr: For knowledge graph requirements, entity relationship extraction from unstructured data, multi-hop retrieval, or validated semi-structured benchmark leadership.
When to Choose Weaviate: For mature open-source ecosystem, extensive module integrations with AI services, pure vector workloads, established community support, or avoiding new platform adoption risks.
Papr vs LlamaIndex (RAG Framework and Orchestration)
LlamaIndex is open-source data framework for connecting custom data sources to LLMs providing data connectors for diverse sources (APIs, PDFs, SQL databases), flexible indexing strategies, query engines, and modular architecture enabling RAG pipeline experimentation serving as industry-standard framework for RAG development launched 2022.
Product Category:
- Papr: Infrastructure platform providing unified memory database with API
- LlamaIndex: Application framework and orchestration library for building RAG systems
Deployment Model:
- Papr: Hosted service (cloud or self-hosted) providing database infrastructure developers query via API
- LlamaIndex: Library integrated into application code; developers choose backend vector stores, LLMs, embedding models
Data Management:
- Papr: Manages storage, indexing, retrieval, knowledge graph construction as infrastructure service
- LlamaIndex: Orchestrates data pipelines connecting chosen storage (Pinecone, Weaviate, Chroma) with retrieval and generation
Knowledge Graph:
- Papr: Native knowledge graph with automatic entity extraction integrated into memory platform
- LlamaIndex: Knowledge Graph Index as optional index type; requires manual graph construction or external tools
Developer Control:
- Papr: Opinionated integrated platform abstracting retrieval implementation details
- LlamaIndex: Highly flexible framework enabling custom retrieval strategies, index types, query engines
When to Choose Papr: For managed infrastructure solution handling storage and retrieval, automatic knowledge graph construction, or preference for unified API over framework integration.
When to Choose LlamaIndex: For maximum flexibility choosing storage backends, complete control over RAG pipeline implementation, experimentation with diverse strategies, or existing vector database investments requiring orchestration layer.
Papr vs MemGPT / Mem0 (Memory-Focused RAG Solutions)
MemGPT and Mem0 are specialized memory layers for LLM applications emphasizing long-term memory persistence, user personalization, and conversation context management. MemGPT uses virtual context management with tiered memory hierarchy; Mem0 provides memory infrastructure with user preferences, interaction history, and incremental learning.
Architecture Focus:
- Papr: Hybrid vector + knowledge graph for comprehensive retrieval and memory with predictive caching
- MemGPT/Mem0: Memory-first design emphasizing conversation continuity and user personalization
Knowledge Graph:
- Papr: Native knowledge graph with entity relationships enabling multi-hop retrieval and analytics
- MemGPT/Mem0: Vector-based memory without explicit knowledge graph; relationship inference through embeddings
Benchmark Validation:
- Papr: #1 Stanford STaRK ranking with 91%+ semi-structured retrieval accuracy
- MemGPT/Mem0: No STaRK benchmark results published; focus on memory quality and personalization
Query Capabilities:
- Papr: GraphQL structured queries and natural language; analytics and aggregations
- MemGPT/Mem0: Natural language memory retrieval; limited complex query or analytics interfaces
Enterprise Features:
- Papr: Built-in ACLs, multi-tenancy, namespace isolation for production SaaS deployments
- MemGPT/Mem0: Varying enterprise readiness; Mem0 offers multi-tenancy; MemGPT research-focused
When to Choose Papr: For knowledge graph analytics, GraphQL querying, validated benchmark performance, or enterprise multi-tenant requirements.
When to Choose MemGPT/Mem0: For memory-first LLM applications prioritizing conversation continuity, simpler integration focused on personalization, or specialized memory management features.
Papr vs Milvus (Open-Source Vector Database)
Milvus is mature open-source vector database designed for billion-scale similarity search supporting multiple index types (IVF, HNSW, DiskANN), GPU acceleration, distributed architecture with cloud-native design, and comprehensive language SDKs launched 2019 with large production deployments.
Maturity and Scale:
- Papr: Newer platform with STaRK benchmark validation; growing production adoption
- Milvus: Established with 1000+ production deployments; proven billion-scale performance
Knowledge Graph:
- Papr: Integrated knowledge graph with entity extraction and multi-hop traversal
- Milvus: Pure vector database; no knowledge graph capabilities requiring external graph systems
Index Variety:
- Papr: Hybrid vector + graph optimized for unified retrieval
- Milvus: Multiple specialized indexes (IVF, HNSW, DiskANN, FLAT) with GPU acceleration options
Query Language:
- Papr: GraphQL and natural language interfaces
- Milvus: Expression-based filtering with Boolean and arithmetic operators; no GraphQL
Benchmark Results:
- Papr: #1 STaRK semi-structured retrieval
- Milvus: Strong ANN Benchmarks performance; no published STaRK results
Ecosystem Maturity:
- Papr: Young ecosystem with core platform focus
- Milvus: Mature ecosystem with Attu visualization tool, backup utilities, monitoring integrations, extensive documentation
When to Choose Papr: For knowledge graph requirements, GraphQL queries, semi-structured retrieval workloads matching STaRK benchmark, or unified memory plus retrieval API.
When to Choose Milvus: For pure vector workloads, proven billion-scale deployments, GPU acceleration needs, mature tooling ecosystem, or avoiding newer platform adoption risks.
Final Thoughts
Papr represents significant advancement in AI memory infrastructure addressing fundamental limitations plaguing RAG systems: traditional vector databases treat knowledge as isolated text fragments missing entity relationships and context connections, pure graph systems handle structured data poorly without semantic search capabilities, and scaling knowledge bases typically degrades retrieval performance creating unpredictable agent behavior as information grows. The December 2025 platform demonstrates viability of unified hybrid architectures combining vector embeddings with knowledge graphs validated through #1 Stanford STaRK benchmark ranking with 91%+ accuracy on semi-structured retrieval tasks requiring contextual reasoning across textual and relational information.
The Predictive Memory Graph treating memory as prediction challenge rather than search task enables counter-intuitive scaling property where increased data improves performance through richer relationship networks and enhanced prediction models contrary to traditional RAG degradation patterns. Sub-100ms query latency through predictive caching enables real-time interactive applications impossible with reactive multi-second retrieval characteristic of naive implementations. Automatic entity extraction and relationship inference from unstructured sources eliminates manual knowledge engineering enabling continuous knowledge capture from operational artifacts creating living knowledge bases evolving with organizational information flows.
The platform particularly excels for sophisticated AI applications requiring cross-session context memory connecting conversations with documents and actions, enterprise document intelligence synthesizing answers from multiple sources through multi-hop retrieval, customer support automation accessing interaction histories with product knowledge through graph connections, multi-tenant SaaS knowledge management maintaining secure isolation with built-in ACLs, and domain-specific knowledge graphs constructed automatically from specialized literature rather than manual curation.
For users requiring pure vector workloads without knowledge graph needs, Pinecone provides established managed infrastructure with proven enterprise scale, transparent pricing, and comprehensive ecosystem. For maximum RAG pipeline flexibility preferring framework over managed service, LlamaIndex offers modular orchestration choosing storage backends and strategies. For open-source vector database with mature tooling ecosystem, Weaviate delivers production-ready platform with extensive module integrations. For memory-first applications prioritizing conversation continuity, MemGPT/Mem0 specialize in personalization-focused memory management.
But for the intersection of unified vector plus knowledge graph retrieval, validated benchmark leadership on semi-structured knowledge, multi-hop entity traversal, GraphQL analytical queries, enterprise access controls, and treating memory as prediction enabling positive scaling, Papr addresses capability combination no established alternative provides comprehensively. The platform’s primary limitations—infrastructure product requiring engineering integration versus end-user application, limited public production deployment references given newness, undisclosed managed cloud pricing preventing cost forecasting, benchmark performance potentially not representing all use cases, LLM-dependent entity extraction quality, learning curve for advanced optimization, and young ecosystem lacking mature tooling—reflect expected constraints of ambitious new infrastructure pioneering hybrid memory architectures.
The critical value proposition centers on connected knowledge and predictive performance: if applications require entity relationship understanding beyond text similarity; if multi-hop retrieval synthesizing information across disconnected sources provides value; if scaling knowledge bases currently degrades rather than improves retrieval creating production issues; if GraphQL structured queries enable analytics and insights impossible with pure vector search; or if validated benchmark performance on semi-structured knowledge matters for production confidence—Papr provides compelling solution worth serious evaluation despite infrastructure complexity and early-stage maturity common among next-generation database technologies.
The platform’s success depends on demonstrating sustained production reliability at scale, building ecosystem of connectors and operational tooling, providing transparent managed cloud pricing enabling cost evaluation, and growing community knowledge through case studies, best practices, and reference architectures reducing adoption friction. For organizations prioritizing retrieval quality and connected knowledge over operational simplicity, accepting infrastructure engineering investment, and valuing benchmark-validated performance, Papr delivers on promise: transforming AI memory from isolated fragment retrieval toward predictive connected knowledge infrastructure enabling agents remembering context across sessions, synthesizing multi-source insights, and improving performance as knowledge accumulates—creating foundation for sophisticated AI applications impossible with traditional RAG approaches.