Table of Contents
Polyvia
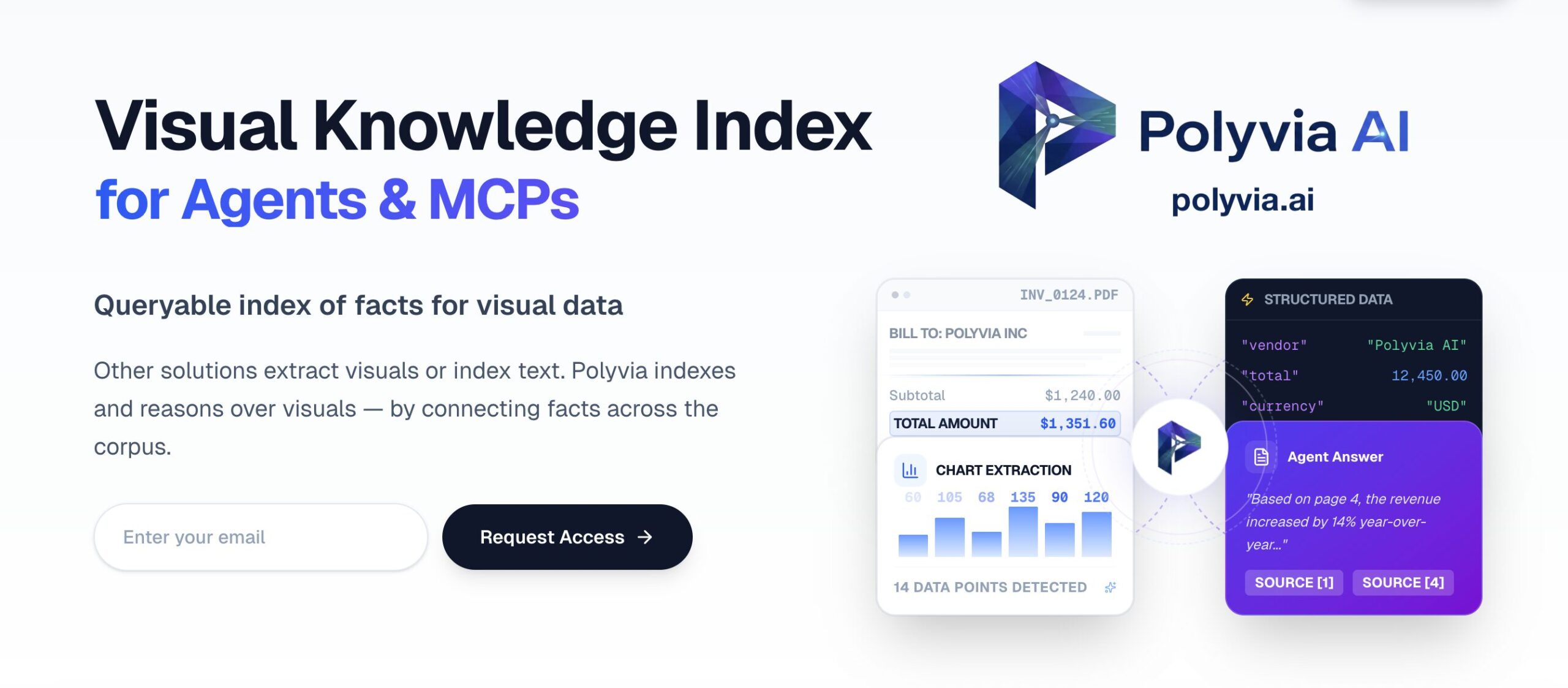
Polyvia is a specialized AI infrastructure platform designed to solve the “Visual RAG” (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) problem. While traditional tools treat images as static files or simple text captions, Polyvia functions as a Visual Knowledge Index. It ingests complex visual documents—such as financial slides, engineering diagrams, and healthcare charts—and converts them into a queryable knowledge graph. This allows AI agents to “reason” across visual data (e.g., comparing trend lines between two different PDF charts) rather than just retrieving keyword matches.
Core Features
- VLM-OCR Extraction: Uses Vision Language Models to extract not just text, but the logic from charts, tables, and infographics (e.g., understanding that a bar is “higher” than another).
- Graph-Based Fact Indexing: Disambiguates entities across documents (e.g., realizing “Q3 Revenue” in Doc A is the same metric as “3rd Quarter Sales” in Doc B) to build a connected knowledge graph.
- MCP Server Integration: Natively supports the Model Context Protocol, allowing Claude, Cursor, and other AI agents to connect to Polyvia as a plug-and-play tool.
- Audit-Ready Citations: Every answer generated provides visual citations that point back to the exact pixel coordinates or slide section of the source document.
- Scale: Engineered to handle massive enterprise repositories (10,000+ documents) without performance degradation.
How It Works
Users upload visual-heavy datasets (PDFs, PPTs, images). Polyvia’s VLM-OCR pipeline extracts structured facts and relationships from the visuals. Instead of storing these as flat vector embeddings, it indexes them into an ontology—a map of connected facts. When a developer’s agent queries the system (via API or MCP), Polyvia retrieves the answer by tracing the logic across multiple visuals and returns the result with a verifiable source link.
Use Cases
- Multimodal AI Agents: empowering coding agents (like in Cursor) to read and implement architecture diagrams directly from technical documentation.
- Financial Analysis: Automating the extraction and comparison of trend data from thousands of earnings call presentation slides.
- Compliance & Audit: Verifying that claims made in marketing materials match the data in technical specification charts.
- Scientific Research: Querying specific data points buried in scatter plots across hundreds of research papers.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Solves the specific failure mode of standard RAG on complex charts/tables; Native MCP support makes it instantly usable with modern agent frameworks; Graph-based approach allows for multi-hop reasoning that simple vector search cannot do; Traceability is critical for enterprise use (no hallucinations without sources).
- Cons: Early Stage: Currently in Private Beta (as of Feb 2026) with “Request Access” barriers; Niche: Overkill for simple text documents; Cost: Likely higher than standard OCR tools due to the compute cost of running Vision Models (VLMs) at scale.
Pricing
- Private Beta: Currently accessible via waitlist/request only.
- Free Tier: Limited tier available for testing (details subject to change during beta).
- Enterprise: Custom volume pricing for large-scale document indexing.
How Does It Compare?
Polyvia positions itself as a “Visual Knowledge Index,” effectively replacing the complex “DIY” pipeline of stitching together OCR, Vector DBs, and LLMs.
- Reducto AI
Reducto is a direct competitor in the “Visual Extraction” space, known for using VLMs to parse complex layouts better than standard OCR. However, Reducto primarily focuses on the extraction layer (getting clean JSON from PDFs). Polyvia goes a step further by indexing and connecting those facts into a graph for reasoning, rather than just outputting the raw data. - ColPali (Hugging Face)
ColPali is a state-of-the-art open-source model approach that retrieves documents based on visual embeddings (looking at the “image” of the page). While ColPali is a powerful building block for developers building their own system, Polyvia is a fully managed platform that handles the infrastructure, citation logic, and graph connections out of the box. Unstructured.io / LlamaParse
These are the industry standard ETL tools for RAG. They excel at cleaning data and chunking it for vector stores. Polyvia competes by arguing that for visual data, simple chunking is insufficient. You don’t just need to “clean” the chart; you need to “index the meaning” of the chart, which Polyvia’s VLM-centric approach prioritizes.Pinecone / Weaviate (Vector DBs)
These are storage engines. To build a Polyvia equivalent with Pinecone, you would need to build your own VLM extraction pipeline, write your own reasoning logic, and manage your own citation system. Polyvia wraps all of that into a single API.
Final Thoughts
Polyvia is an essential evolution in the “Agent Stack.” As AI models move from simple chatbots to autonomous agents that do work, they need to “see” documents the way humans do—understanding the flow of a diagram or the trend in a chart. For developers building agents that need to read technical manuals or financial reports, Polyvia offers a massive shortcut by packaging Visual Perception and Knowledge Graph reasoning into a single, agent-ready server.