Table of Contents
Overview
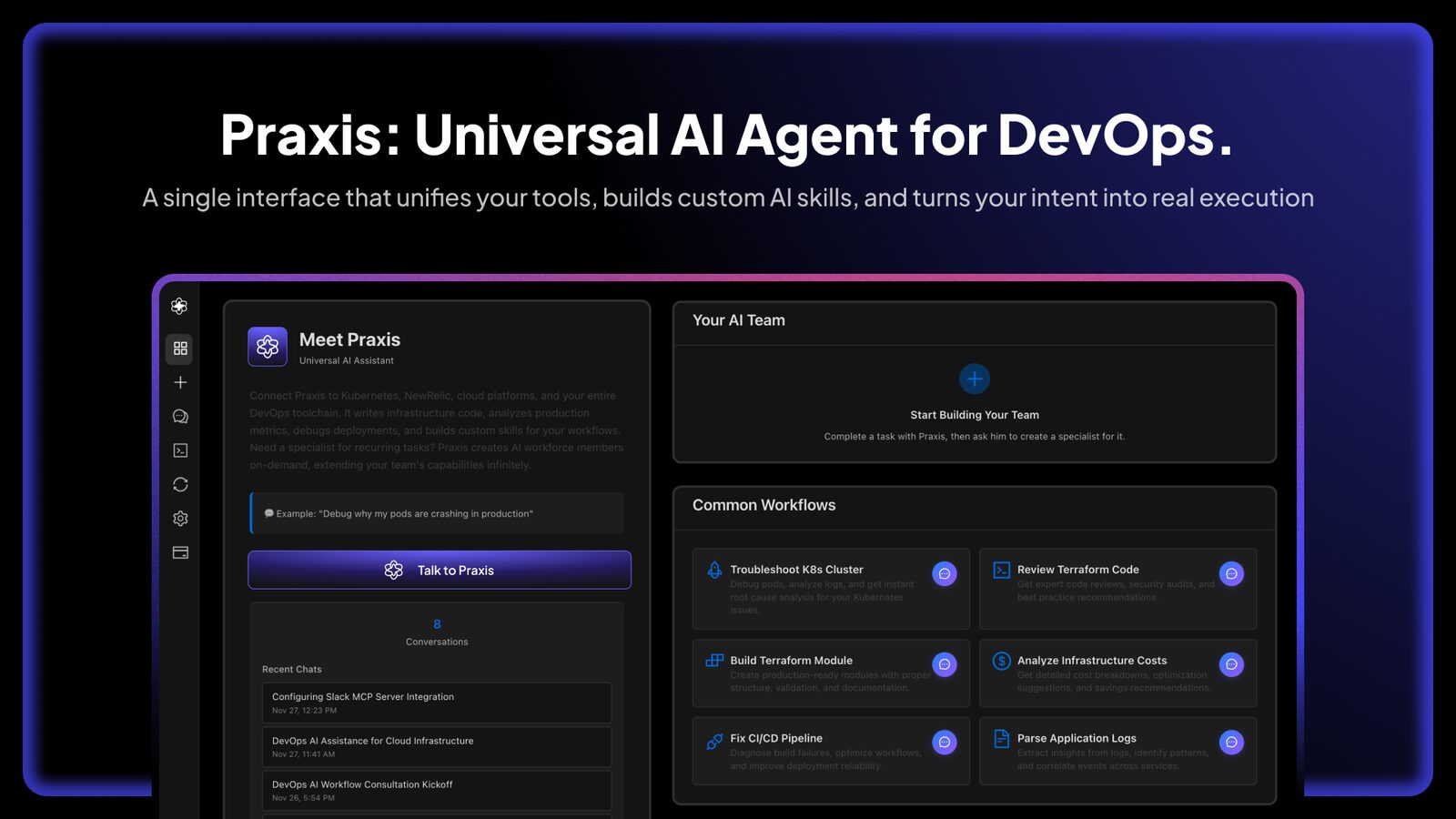
Praxis by Facets.cloud is a universal AI agent platform for DevOps that executes infrastructure operations, troubleshoots incidents, and automates workflows through natural language conversation. Launched on Product Hunt on December 4, 2025 (exact upvote count not publicly available at time of research), Praxis addresses a fundamental friction in modern engineering organizations: the context-switching tax and tooling fragmentation where DevOps teams juggle 30+ disconnected platforms (Kubernetes, Terraform, AWS, Datadog, PagerDuty, Jira) requiring deep expertise in each tool’s CLI syntax, API patterns, and operational peculiarities—creating bottlenecks that delay incident resolution, slow releases, and block entire organizations when DevOps engineers become unavailable.
Built by Facets.cloud (YC-backed cloud orchestration platform trusted by enterprise customers), Praxis represents the company’s evolution from infrastructure standardization into AI-native operations. Unlike generic AI chatbots or simple command wrappers, Praxis implements Model Context Protocol (MCP) integrations enabling secure, credential-managed connections to production infrastructure where AI agents execute read-write operations (kubectl commands, Terraform applies, CI/CD triggers, metric queries) with proper authorization and audit trails. The system combines a universal general-purpose agent handling ad-hoc requests with the ability to create dedicated “Specialist” agents for recurring workflows—essentially hiring AI teammates trained on your organization’s specific operational patterns, tools, and tribal knowledge.
The platform has been production-validated through customer deployments including ZeonAI’s GCP migration (first environment live in 1 week, 3 daily releases established) demonstrating real-world operational acceleration. Praxis targets the emerging “agentic DevOps” paradigm where AI systems don’t just suggest fixes or generate code snippets—they autonomously investigate alerts, execute remediation runbooks, optimize infrastructure configurations, and resolve incidents in minutes rather than hours by directly interfacing with the same tools human operators use.
Key Features
Praxis is packed with powerful features designed to eliminate DevOps toil and accelerate incident response:
- Natural Language DevOps Commands Through Conversational Interface: Users interact with Praxis via Slack, web interface, or IDE integrations by describing operational goals in plain English rather than memorizing tool-specific syntax. Example queries: “Why is the payment service pod crashing in prod?”, “Show me CPU utilization for the last hour”, “Apply the Terraform changes in staging”, “Create a new Kubernetes namespace for the marketing team”. The AI interprets intent, determines which underlying tools to invoke (kubectl, Terraform, cloud CLIs, monitoring APIs), executes necessary commands with proper error handling, and returns synthesized results explaining what it found and what actions it took. This natural language abstraction eliminates the cognitive overhead of context-switching between tools, remembering arcane command flags, and translating business requirements into technical operations.
- Integration with Kubectl, Terraform, Datadog, NewRelic, and 30+ DevOps Tools: Praxis implements Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers providing standardized interfaces to major DevOps platforms including Kubernetes (kubectl commands, Helm operations, pod logs), infrastructure-as-code (Terraform plan/apply, configuration generation), cloud platforms (AWS, GCP, Azure resource management), CI/CD systems (Jenkins, ArgoCD, GitHub Actions), monitoring and observability (Datadog, NewRelic, Prometheus, Grafana metrics and logs), and ticketing systems (Jira, ServiceNow). The MCP architecture ensures consistent authentication, secure credential management, and uniform error handling across heterogeneous tooling. Teams connect existing tools through simple configuration without rewriting integrations or exposing credentials directly to AI models—credentials remain secured in Praxis’s infrastructure with policy-based access controls determining which operations agents can execute.
- AI FinOps Analysis and Cloud Cost Optimization: The platform analyzes cloud spending patterns across AWS, GCP, and Azure by querying cost APIs, resource utilization metrics, and infrastructure configurations to identify optimization opportunities. Praxis generates actionable recommendations including rightsizing over-provisioned instances, identifying idle resources (unused load balancers, unattached volumes, orphaned snapshots), recommending reserved instance or savings plan purchases based on usage patterns, and detecting cost anomalies signaling configuration drift or abuse. The AI explains potential savings in business terms (“We could save \$3,200/month by downsizing these 12 staging instances to t3.medium”) rather than dumping raw billing data, enabling non-technical stakeholders to understand infrastructure economics. Automated workflows can implement approved optimizations (scheduled instance resizing, automated resource cleanup) converting analysis into realized savings.
- Custom “DevOps Specialist” Agents for Recurring Workflows: Beyond the universal agent handling ad-hoc queries, Praxis enables creating dedicated Specialist agents trained on specific operational workflows through conversational teaching. Users describe desired specialist behavior (“I need an agent that handles database migration approvals: check staging test results, verify rollback plan exists, notify #data-team channel, and apply migrations during maintenance windows”). Praxis captures these requirements, generates agent workflows, tests execution paths, and deploys autonomous specialists that activate based on triggers (Slack mentions, API calls, scheduled cron, alert webhooks). Specialists accumulate organizational knowledge including tool preferences, approval patterns, escalation procedures, and learned optimizations—essentially codifying DevOps tribal knowledge into reusable AI teammates that scale operational capacity without proportional headcount growth.
- Automated Infrastructure Troubleshooting with Root Cause Analysis: When incidents occur (pod crashes, elevated error rates, latency spikes), Praxis conducts automated investigations following expert troubleshooting methodologies: developing hypotheses about potential causes, gathering evidence from logs/metrics/traces supporting or refuting each hypothesis, iterating through diagnostic steps, and producing structured reports summarizing findings with confidence scores. The system queries Kubernetes for pod status and restart history, retrieves application logs showing error patterns, checks resource utilization (memory/CPU exhaustion), validates configuration correctness (environment variables, secrets), tests network connectivity, and correlates across monitoring systems. Results present to engineers as “here’s what I found, here’s what likely caused the issue, here are the commands I ran to reach this conclusion”—enabling quick validation rather than starting investigations from scratch.
- Infrastructure-as-Code Generation and Management: Praxis generates production-ready Terraform configurations, Kubernetes manifests, Helm charts, and CI/CD pipeline definitions from natural language requirements. Engineers describe desired infrastructure (“I need a PostgreSQL 15 instance with 500GB storage, automatic backups, read replicas in two regions, and connection pooling”) and receive validated IaC outputs incorporating organizational standards, security policies, tagging conventions, and cost controls. The system modifies existing configurations by understanding semantic diffs (“change the API service from 3 replicas to 5 without downtime”), generates migration paths for infrastructure changes, and applies best practices (encryption at rest, least-privilege IAM, network segmentation) automatically. This accelerates infrastructure delivery from days/weeks spent writing Terraform to minutes spent reviewing generated configs.
- Real-Time Incident Debugging Reducing Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR): During production incidents, Praxis functions as on-call augmentation gathering context across distributed systems faster than human operators switching between dashboards. The system receives alerts from monitoring systems, immediately begins automated investigation, surfaces relevant information (recent deployments, configuration changes, correlated failures), suggests probable root causes ranked by likelihood, and recommends remediation actions with risk assessment. Engineers interact conversationally (“show me error logs for the auth service”, “compare current pod resource usage vs. yesterday”, “what changed in the last hour?”) receiving instant answers without manually querying multiple tools. This conversational debugging maintains flow state rather than forcing mental model reloading across tool boundaries.
- MCP-Powered Extensibility with Secure Credential Management: The Model Context Protocol architecture enables teams to extend Praxis with custom integrations to proprietary internal tools, specialized monitoring systems, or vertical-specific platforms through MCP server implementations. Organizations write MCP adapters exposing tool capabilities to AI agents while maintaining centralized authentication, authorization, and audit logging. Credentials never expose directly to LLMs—instead, the MCP layer manages secrets, enforces RBAC policies, and logs all operations for compliance. This security-first approach enables giving AI agents production access without creating credential sprawl or uncontrolled blast radius.
- Policy-Driven Access Controls and Approval Workflows: Praxis enforces organization-defined policies determining which operations require approval, who can approve, and under what conditions. Examples: production changes require two-engineer approval; budget thresholds above \$1000 escalate to finance; critical infrastructure modifications notify security team; junior engineer requests route through senior review. The system integrates approval workflows directly into conversational interfaces—when an agent proposes restricted actions, it automatically requests approval from designated stakeholders via Slack/Teams, blocks execution pending authorization, and maintains audit trails for compliance. This governance framework enables safely delegating operational authority to AI agents without sacrificing organizational controls.
- Self-Enhancing Through Operational Learning: Praxis improves over time by learning from successful operations, failed attempts, and engineer corrections. When agents make mistakes or engineers override suggestions, the system captures feedback refining future behavior. Specialist agents become more accurate as they execute workflows repeatedly, learning organizational preferences (preferred instance families, networking patterns, naming conventions), context-specific edge cases, and operational nuances impossible to pre-program. This continuous learning enables agents to evolve beyond their initial training, eventually matching or exceeding junior operator capabilities for routine tasks.
How It Works
Praxis operates through sophisticated AI orchestration combining LLMs with specialized DevOps tooling:
Stage 1: User Request via Natural Language Interface
Engineers interact with Praxis through Slack channels, web dashboards, or API endpoints by describing operational goals in conversational language. The system accepts both simple commands (“show pod status in production namespace”) and complex multi-step requests (“investigate the payment service latency spike, identify root cause, and recommend fixes”). Users reference infrastructure using business terminology rather than technical identifiers—Praxis maps colloquial names to actual resources through organizational context graphs tracking naming patterns and relationships.
Stage 2: Intent Classification and Task Planning
The AI agent parses natural language queries to extract operational intent, required parameters, target resources, and success criteria. The system employs large language models fine-tuned on DevOps domain knowledge to understand technical terminology, infrastructure patterns, and operational best practices. For complex requests requiring multiple steps, Praxis generates execution plans decomposing goals into actionable sub-tasks (e.g., “investigate latency spike” becomes: query recent deployments, check error logs, analyze resource metrics, examine network issues, synthesize findings). The planning stage incorporates organizational context including tool preferences, access permissions, and known operational constraints ensuring feasible execution paths.
Stage 3: MCP Tool Selection and Credential Acquisition
Based on required operations, Praxis identifies relevant MCP servers providing necessary capabilities (kubectl for Kubernetes operations, Terraform CLI for infrastructure changes, Datadog API for metrics, etc.). The system retrieves appropriate credentials from secure storage (HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, native key management) based on requesting user’s identity and RBAC policies. Credential acquisition happens transparently without exposing secrets to LLMs or user interfaces—the MCP layer maintains authentication tokens, rotates credentials per security policies, and logs all access for audit compliance.
Stage 4: Parallel Tool Execution with Error Handling
Praxis executes operations against infrastructure through MCP integrations, often invoking multiple tools in parallel to accelerate information gathering. The system implements robust error handling including automatic retries for transient failures, graceful degradation when tools are unavailable, and fallback strategies switching between alternative information sources. Each operation captures detailed telemetry including executed commands, returned output, timing information, and success/failure status enabling troubleshooting when automated workflows encounter issues. The orchestration layer ensures atomic operations for destructive changes—rolling back partial modifications if any step fails to prevent inconsistent infrastructure states.
Stage 5: Result Synthesis and Natural Language Response
Raw tool outputs (JSON API responses, kubectl logs, Terraform plan diffs) undergo AI-powered synthesis translating technical data into human-comprehensible explanations. The system highlights actionable insights, explains significance of findings, provides context for non-obvious patterns, and recommends next steps. For troubleshooting scenarios, Praxis structures results as investigation reports showing hypotheses tested, evidence gathered, eliminated possibilities, and remaining root cause candidates with confidence scores. The natural language generation adapts to audience—technical details for engineers, business impact for executives, procedural summaries for compliance audits.
Stage 6: Optional Action Execution with Approval Gating
When Praxis recommends actions (scaling deployments, applying Terraform changes, modifying configurations), the system evaluates organizational policies determining whether proposed operations require approval. Low-risk read-only operations proceed immediately. Moderate-risk changes enter approval workflows notifying designated reviewers via Slack/Teams with action summaries, estimated impact, and rollback procedures. High-risk production modifications require multi-party approval with security/compliance verification. Engineers approve, reject, or modify proposals conversationally—approved actions execute automatically with comprehensive logging while rejections capture reasoning for agent learning.
Stage 7: Specialist Agent Creation Through Conversational Training
For recurring workflows, engineers create dedicated Specialist agents by describing desired behavior patterns through conversation. Praxis guides users through defining trigger conditions (Slack keywords, API webhooks, scheduled cron, alert patterns), required operations (which tools to invoke with what parameters), decision logic (approval requirements, error handling, escalation paths), and success criteria. The system generates agent code implementing specified behavior, deploys to production with monitoring, and iterates based on execution outcomes. Specialists become organizational assets embedded with tribal knowledge—essentially scaling DevOps expertise without linear headcount growth.
Stage 8: Continuous Learning and Performance Optimization
Praxis captures telemetry across all operations including success rates, execution latency, accuracy of predictions, and engineer feedback. The system identifies patterns indicating areas for improvement—frequently corrected mistakes, commonly requested capabilities lacking automation, bottlenecks in multi-step workflows. Machine learning models fine-tune over time using organizational operational data as training signals, improving intent classification accuracy, tool selection logic, and result synthesis quality. This continuous improvement cycle ensures Praxis becomes more valuable as adoption increases, eventually matching organizational operational patterns with minimal explicit configuration.
Use Cases
Given its specialized capabilities, Praxis addresses various scenarios where DevOps operations create organizational bottlenecks:
Automating Routine DevOps Tickets Reducing Toil:
- Self-service infrastructure provisioning where product teams request new environments (“create staging environment for mobile-v2 app”) without DevOps manual intervention
- Automated user access management granting engineers appropriate permissions based on roles without ticket queues
- Regular operational tasks (log rotation, certificate renewal, backup verification) executing on schedules without human execution overhead
- Common troubleshooting workflows (restart crashed pods, clear disk space, reset rate limits) delegated entirely to AI agents
Real-Time Incident Debugging Accelerating MTTR:
- On-call engineers receiving pre-investigated incident reports showing probable root causes, relevant context, and suggested remediations within minutes of alert firing rather than starting investigations from scratch
- Conversational troubleshooting during incidents maintaining flow state (“show me logs around the error timestamp”, “compare this deployment to the previous version”) without switching between terminals, dashboards, and wikis
- Automated correlation across distributed systems identifying cascading failures, infrastructure degradation, or configuration drift causing symptoms
- Post-incident learning where resolved issues train specialist agents preventing similar incidents through proactive monitoring
Cloud Cost Analysis and Reduction Improving Unit Economics:
- CFOs and finance teams querying cloud spending conversationally (“why did AWS costs spike 40% last month?”) receiving business-focused explanations without technical jargon
- Automated cost anomaly detection alerting teams to unexpected usage patterns indicating bugs, abuse, or configuration mistakes before month-end invoices
- Rightsizing recommendations implemented automatically during off-peak hours (downscaling development environments overnight, removing unused resources, consolidating underutilized instances)
- Budget enforcement where infrastructure requests exceeding thresholds trigger approval workflows preventing runaway spending
Infrastructure-as-Code Generation and Management:
- Product teams describing infrastructure requirements in business terms (“we need a Redis cache with 10GB memory, multi-AZ deployment, and daily backups”) receiving production-ready Terraform without writing code
- Platform engineering standardizing infrastructure patterns by codifying best practices into IaC generation templates ensuring consistency across teams
- Migration automation generating Terraform configurations from existing manually-created resources enabling infrastructure-as-code adoption without greenfield rebuilds
- Configuration drift detection and remediation where Praxis identifies deviations from IaC definitions and proposes corrective actions
Scaling DevOps Capacity Without Proportional Headcount:
- High-growth startups maintaining 10:1 developer-to-DevOps ratios by delegating routine operations to AI agents rather than hiring additional operators
- Enterprise platform teams supporting hundreds of product teams through self-service AI-mediated infrastructure access instead of centralized request processing
- Organizations entering new markets or launching products rapidly provisioning infrastructure through conversational interfaces without months-long DevOps onboarding
- Cross-timezone support where AI agents provide 24/7 operational coverage without requiring geographically distributed human operator teams
Pros \& Cons
Every powerful tool comes with its unique set of advantages and potential limitations:
Advantages
- Drastically Reduces Context Switching for DevOps Engineers: Conversational interface eliminates the cognitive overhead of switching between 30+ tools, remembering CLI syntax, navigating disconnected dashboards, and translating between tool-specific mental models. Engineers maintain flow state troubleshooting incidents, provisioning infrastructure, or analyzing metrics through unified natural language interface rather than constantly breaking concentration to look up commands or switch applications. This productivity gain compounds across hundreds of daily micro-interruptions.
- Unifies Disparate Tools (Monitoring, Infrastructure, Logs, CI/CD): Praxis provides integrated view across fragmented DevOps tooling through MCP abstraction layer, enabling cross-tool correlation impossible when each system operates in isolation. Engineers query spanning monitoring metrics, application logs, infrastructure state, and deployment history simultaneously receiving synthesized insights rather than manually correlating data across separate platforms. This unified visibility accelerates troubleshooting and reduces missed connections causing delayed root cause identification.
- Production-Validated Through Real Customer Deployments: ZeonAI’s GCP migration (first environment live in 1 week with 3 daily releases) and partnerships with enterprise customers demonstrate Praxis operates successfully in actual production environments rather than laboratory conditions. This real-world validation reduces adoption risk compared to experimental tools lacking production battle-testing—customers benefit from learned lessons, hardened error handling, and operational playbooks developed through live usage.
- MCP Standard Ensures Future-Proof Extensibility: Model Context Protocol represents Anthropic’s emerging standard for AI-tool integration supported by major development platforms (Claude, Cursor, GitHub Copilot). By building on MCP rather than proprietary integrations, Praxis ensures compatibility with evolving AI ecosystem without vendor lock-in risks. Organizations invest in MCP integrations that function across multiple AI platforms rather than rebuilding tool connections per vendor.
- Self-Enhancing Through Operational Learning: Unlike static automation scripts requiring manual updates, Praxis improves continuously by learning from operational outcomes, engineer corrections, and organizational patterns. Specialist agents become more accurate over time matching team-specific preferences, edge cases, and contextual nuances impossible to pre-program. This learning capability means ROI increases with adoption as agents accumulate tribal knowledge scaling operational expertise.
- Enables AI-Native Agentic DevOps Workflows: Praxis represents evolution beyond simple code generation or suggestion tools toward autonomous AI agents that independently investigate, diagnose, and remediate operational issues. This paradigm shift from “AI assists humans” to “AI executes operations with human oversight” enables order-of-magnitude productivity gains for routine workflows while freeing engineers for strategic initiatives requiring creativity and business context.
Disadvantages
- Requires High Trust Giving AI Agents Write-Access to Infrastructure: Delegating production infrastructure control to AI systems demands organizational trust overcoming justifiable concerns about autonomous systems making destructive changes. One misconfigured agent or poorly understood prompt could delete databases, terminate critical instances, or disrupt customer-facing services. While Praxis implements approval workflows and audit trails, psychological barriers to AI operational authority remain significant adoption friction especially in risk-averse enterprises or regulated industries.
- Effectiveness Depends on Quality of Underlying Tool Integrations: Praxis capabilities are constrained by MCP server implementation quality, API completeness, and tool-specific limitations. If Terraform provider lacks certain resource types, Datadog API doesn’t expose needed metrics, or Kubernetes RBAC prevents required operations, Praxis cannot overcome these upstream constraints. Organizations may discover workflow gaps requiring custom MCP development or tool upgrades before achieving desired automation levels.
- Learning Curve for Conversational Infrastructure Management: While natural language interfaces eliminate CLI memorization, they introduce different challenges around prompt engineering, understanding agent capabilities, and debugging when AI misinterprets requests. Engineers must learn effective prompting strategies, develop intuition for agent limitations, and recognize when to escalate to manual operations—skills orthogonal to traditional DevOps expertise potentially creating initial productivity dips during adoption.
- Pricing Model May Be Prohibitive for Small Teams: SaaS pricing starting around \$799/month (exact tiers not publicly disclosed) plus custom enterprise pricing targets mid-market and enterprise organizations rather than indie developers or early-stage startups with limited budgets. Small teams may find costs unjustifiable compared to existing manual workflows especially before realizing productivity gains, creating chicken-egg adoption challenges where benefits don’t materialize until sufficient usage amortizes subscription costs.
- Potential Security and Compliance Concerns: Centralizing infrastructure access through AI agents creates high-value security targets—compromised Praxis instances could provide attackers lateral movement across entire cloud estates. Organizations in regulated industries (healthcare, finance, government) face compliance uncertainty around AI-executed operations including audit trail adequacy, accountability assignment when agents make mistakes, and regulatory acceptance of autonomous infrastructure management.
- Early-Stage Tool Requiring Operational Maturity: Product Hunt launch December 2025 indicates recent market entry without extensive production track record beyond initial customer deployments. Early adopters may encounter undocumented edge cases, evolving APIs, integration gaps with niche tools, or operational playbook limitations requiring custom development. Organizations with low risk tolerance may prefer waiting for broader adoption, larger community, and maturity indicators before committing production operations to Praxis.
How Does It Compare?
Praxis by Facets.cloud vs. Kubiya
Kubiya is an AI-powered DevOps assistant using LLMs for conversational infrastructure management, integrated with Slack as primary interface.
Company Maturity:
- Praxis by Facets.cloud: Built by YC-backed Facets.cloud (established 2020) with enterprise customer base and production cloud orchestration platform
- Kubiya: Standalone startup founded 2022 with venture funding from Israel and Silicon Valley VCs
Platform Architecture:
- Praxis: Universal agent plus customizable Specialist agents; MCP-powered tool integrations; self-enhancing through operational learning
- Kubiya: Agent-actor framework with purpose-built templates; full-stack LLM solution with fine-tuned embedding and RAG for knowledge base
Tool Integration:
- Praxis: MCP standard supporting kubectl, Terraform, NewRelic, Datadog, cloud platforms; extensible through custom MCP servers
- Kubiya: Direct integrations with Kubernetes, AWS, GitHub, Jira, CI/CD, ticketing; speaks platform-specific languages (Boto3, JQL, kubectl)
AI Capabilities:
- Praxis: Root cause analysis, automated troubleshooting, IaC generation, FinOps analysis, specialist agent creation
- Kubiya: Task automation, knowledge retrieval, natural language policy creation, Terraform module generation, cluster troubleshooting
Pricing:
- Praxis: SaaS starting ~\$799/month with custom enterprise pricing
- Kubiya: Custom pricing not publicly disclosed; positioned for enterprise DevOps teams
Target Audience:
- Praxis: Platform engineering teams, DevOps organizations, enterprises seeking unified AI orchestration layer
- Kubiya: DevOps teams reducing toil, organizations improving developer experience, platform engineers automating workflows
When to Choose Praxis: For organizations already using Facets.cloud, when MCP standard compliance matters, and for creating custom Specialist agents tailored to organizational workflows.
When to Choose Kubiya: For Slack-first teams, when established venture backing and longer operational track record reduce adoption risk, and for agent-actor framework with pre-built templates.
Praxis by Facets.cloud vs. Parity (YC S24)
Parity is an AI tool specifically for on-call Kubernetes engineers enabling automated investigation, root cause analysis, and intelligent runbook execution.
Scope:
- Praxis: Universal DevOps agent spanning infrastructure, monitoring, CI/CD, cloud management, cost optimization, and multi-platform operations
- Parity: Kubernetes-specific on-call automation focused on incident investigation and cluster troubleshooting
Primary Use Case:
- Praxis: Broad DevOps automation from infrastructure provisioning to cost optimization to general operational workflows
- Parity: On-call incident response specifically for Kubernetes clusters reducing MTTR through automated root cause analysis
Technical Approach:
- Praxis: Multi-tool orchestration through MCP integrations executing operations across entire DevOps stack
- Parity: AI agents following human troubleshooting patterns (develop hypothesis, validate with logs/metrics, iterate) specialized for Kubernetes
Capabilities:
- Praxis: Infrastructure-as-Code generation, multi-cloud management, FinOps analysis, CI/CD automation, general DevOps tasks
- Parity: Root cause analysis, intelligent runbook execution with branching logic, read-only Kubernetes commands for investigation
Safety Model:
- Praxis: Policy-driven approval workflows enabling write operations with governance controls
- Parity: Exclusively read-only commands for safety; suggests remediations but doesn’t automatically apply fixes
Pricing:
- Praxis: ~\$799/month SaaS with custom enterprise pricing
- Parity: Custom pricing for YC-backed startup; typical SaaS model
When to Choose Praxis: For comprehensive DevOps automation beyond Kubernetes, when infrastructure provisioning and cost optimization matter equally to incident response.
When to Choose Parity: For on-call teams primarily managing Kubernetes requiring specialized incident investigation, when read-only safety model aligns with risk tolerance.
Praxis by Facets.cloud vs. K8sGPT
K8sGPT is an open-source Kubernetes diagnostic tool combining codified SRE knowledge with Generative AI to explain cluster issues in plain English.
Commercial Model:
- Praxis: Commercial SaaS platform with subscription pricing and enterprise support
- K8sGPT: Open-source (CNCF Sandbox project) with free CLI tool and optional enterprise Operator
Scope:
- Praxis: Universal DevOps automation across infrastructure, monitoring, CI/CD, cloud platforms, and operational workflows
- K8sGPT: Kubernetes-exclusive diagnostic tool for cluster scanning, issue detection, and plain-English explanations
Operational Capability:
- Praxis: Executes operations (apply Terraform, scale deployments, modify configurations) through MCP integrations with write access
- K8sGPT: Diagnostic and explanatory tool that identifies issues and suggests fixes but doesn’t execute remediation commands
Integration:
- Praxis: MCP-powered connections to 30+ DevOps platforms with centralized credential management and RBAC
- K8sGPT: Kubernetes API server connection; integrates with monitoring (Grafana, Prometheus); LLM backends (OpenAI, Azure, Cohere, local models)
Deployment:
- Praxis: Cloud-hosted SaaS with managed infrastructure and enterprise-grade SLAs
- K8sGPT: Self-hosted CLI or in-cluster Operator requiring infrastructure management and maintenance
AI Architecture:
- Praxis: Agent-based system with learning capabilities, custom Specialists, and multi-tool orchestration
- K8sGPT: Rule-based analyzers codifying SRE knowledge enriched with LLM-generated explanations; prevents hallucinations through staged analysis
Pricing:
- Praxis: Subscription pricing starting ~\$799/month
- K8sGPT: Free open-source; LLM API costs (OpenAI, Azure) or self-hosted local models
When to Choose Praxis: For commercial support, broad DevOps automation, write operations with governance, and learning agents adapting to organizational patterns.
When to Choose K8sGPT: For open-source preference, Kubernetes-only environments, budget constraints favoring free tools, and when diagnostic-only capability suffices without operational automation.
Praxis by Facets.cloud vs. Manual DevOps Operations
Manual operations involve human engineers executing DevOps tasks through tool-specific interfaces, CLI commands, and dashboard-driven workflows.
Operational Speed:
- Praxis: Minutes to resolve incidents through automated investigation and pre-analyzed root causes; seconds to provision infrastructure from natural language
- Manual: Hours investigating incidents switching between tools; days provisioning infrastructure writing IaC from scratch
Context Switching:
- Praxis: Unified conversational interface eliminating tool-switching cognitive overhead
- Manual: Constant interruptions switching between terminals, dashboards, documentation, and communication tools fragmenting focus
Scalability:
- Praxis: AI agents handle unlimited concurrent requests without capacity constraints; Specialist agents scale operational expertise beyond human headcount
- Manual: Linear scaling requiring proportional DevOps hiring as infrastructure complexity and engineering team size grow
Consistency:
- Praxis: Specialist agents execute workflows identically every time following organizational standards and learned best practices
- Manual: Human variance in troubleshooting approaches, forgotten steps, undocumented tribal knowledge, and inconsistent implementations
Learning Curve:
- Praxis: Natural language interface accessible to engineers with minimal DevOps expertise; lowers barrier for self-service operations
- Manual: Steep learning curves mastering each tool’s CLI, API, mental model, and operational patterns requiring months-long onboarding
Cost:
- Praxis: ~\$799+/month subscription plus implementation costs
- Manual: DevOps engineer salaries (\$120,000-180,000/year) multiplied by headcount required for operational coverage
When to Choose Praxis: For nearly all organizations beyond smallest teams; automation ROI justifies investment through productivity gains, reduced MTTR, and operational scalability.
When to Choose Manual: Only for smallest teams (<3 engineers) with simple infrastructure, when AI trust barriers are insurmountable, or when regulatory constraints prohibit autonomous operations.
Final Thoughts
Praxis by Facets.cloud represents a watershed moment in DevOps evolution by realizing the long-promised “infrastructure-as-conversation” paradigm where natural language replaces CLI memorization and AI agents execute operations rather than merely suggesting them. The December 4, 2025 Product Hunt launch and production validation through customer deployments (ZeonAI’s successful GCP migration) position it as practical implementation of agentic DevOps rather than experimental vaporware—addressing documented pain points (tooling fragmentation, context-switching overhead, operational bottlenecks) through working software deployed in production environments.
What makes Praxis particularly compelling is its recognition that DevOps suffers from fundamental scaling limitations: human operators don’t parallelize well, expertise doesn’t replicate instantly, and tribal knowledge exists only in individuals’ heads creating bus factor risks and onboarding friction. By codifying operational patterns into learnable AI agents, Praxis enables organizations to scale DevOps capacity through software rather than linear headcount growth—creating “AI teammates” that eventually match junior operator capabilities for routine tasks while freeing senior engineers for strategic initiatives requiring creativity and business context.
The Model Context Protocol integration specifically deserves emphasis as forward-looking architectural decision. MCP represents Anthropic’s emerging standard for AI-tool connections supported by major platforms (Claude, Cursor, GitHub Copilot), creating industry-wide interoperability rather than proprietary vendor lock-in. By building on MCP, Praxis ensures compatibility with evolving AI ecosystem, protects customer investment in tool integrations, and contributes to broader agentic DevOps standards benefiting entire industry.
The tool particularly excels for:
- High-growth startups maintaining unsustainable developer-to-DevOps ratios (10:1, 20:1) by delegating routine operations to AI agents rather than hiring additional operators they can’t afford
- Enterprise platform teams supporting hundreds of product teams through self-service AI-mediated infrastructure access instead of ticket-queue bottlenecks delaying entire organizations
- Organizations experiencing DevOps burnout where on-call rotations, operational toil, and context-switching overhead drive attrition requiring retention initiatives beyond compensation
- Companies adopting cloud-native architectures (Kubernetes, microservices, multi-cloud) where operational complexity exploded beyond human capacity to manually manage
- Engineering leadership seeking quantifiable productivity gains justifying AI investment through measurable metrics (MTTR reduction, infrastructure provisioning speed, self-service adoption)
For Kubernetes-exclusive environments requiring specialized incident investigation, Parity’s focused on-call automation provides deeper cluster troubleshooting capabilities despite narrower overall scope. For open-source preference or budget constraints, K8sGPT offers free diagnostic capabilities for Kubernetes though without operational automation or broad tool coverage. For organizations not yet ready for AI-executed operations, Kubiya’s longer operational track record and agent-actor framework may reduce adoption risk despite potentially higher pricing.
But for the specific intersection of “universal DevOps automation,” “MCP-powered extensibility,” and “custom Specialist agents encoding organizational knowledge,” Praxis addresses genuine operational bottlenecks through specialized capabilities competitors don’t replicate. The platform’s primary limitations—requiring organizational trust for AI write-access, effectiveness dependent on integration quality, and relatively recent market entry—reflect expected early-stage constraints and fundamental tradeoffs of autonomous operational AI rather than tool-specific flaws.
The critical strategic question isn’t whether AI will transform DevOps (operational complexity growth rates prove human-only approaches unsustainable), but whether organizations will adopt purpose-built agentic platforms like Praxis or attempt building equivalent capabilities internally. The economics strongly favor buy-versus-build given development costs, ongoing maintenance, and opportunity costs of DevOps teams building AI infrastructure instead of serving organizational needs.
If your DevOps team drowns in toil preventing strategic work, if context-switching between 30+ tools fragments productivity, if organizational scaling demands accelerating infrastructure operations without proportional headcount growth, or if incident response delays cascade into customer-impacting outages, Praxis provides accessible specialized solution worth evaluating. The production validation through customer success stories, MCP standard compliance ensuring future compatibility, and backing by established Facets.cloud platform reduce adoption risks compared to unproven alternatives.