Table of Contents
Overview
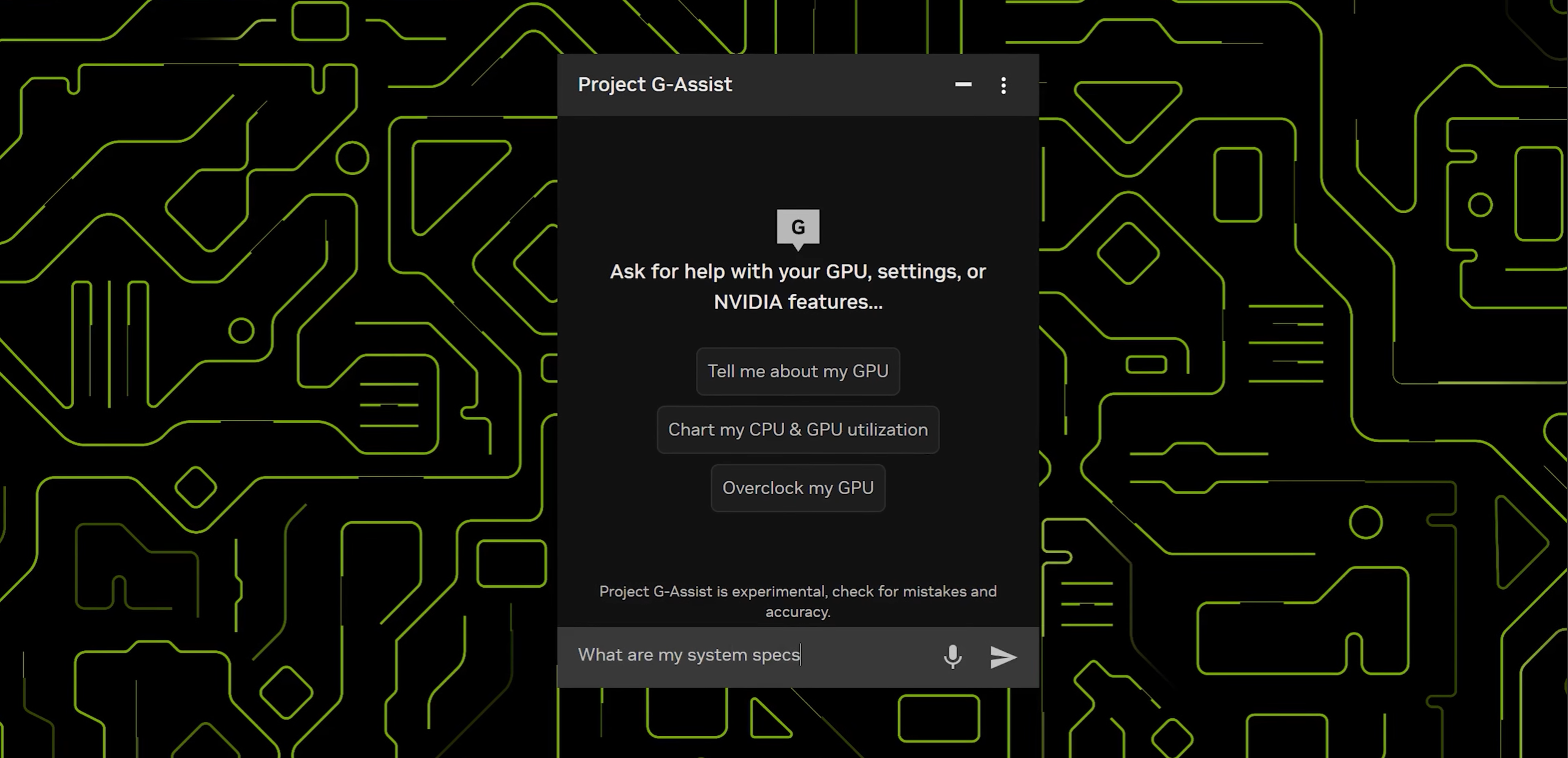
Tired of digging through endless menus to optimize your gaming rig? NVIDIA’s Project G-Assist might just be the answer. This innovative AI assistant, designed specifically for GeForce RTX PCs, promises to put you in complete control of your system with simple voice or text commands. Imagine tweaking game settings, monitoring performance, and even customizing your peripherals, all without lifting a finger (well, almost!). Let’s dive into what makes G-Assist a potential game-changer.
Key Features
Project G-Assist boasts a compelling set of features designed to streamline your PC experience:
- Local AI Processing on GeForce RTX GPUs: Executes AI tasks directly on your GPU, ensuring low latency and privacy by avoiding cloud reliance.
- Voice and Text Command Support: Allows users to interact with the system using natural language, making adjustments intuitive and hands-free.
- System Optimization and Diagnostics: Provides tools to analyze and optimize system performance, identifying potential bottlenecks and suggesting improvements.
- Game Setting Adjustments: Enables users to quickly adjust in-game graphics settings for optimal performance or visual quality.
- Peripheral Customization: Offers options to customize settings for connected peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, and headsets.
- Plugin Support for Extended Functionalities: Allows developers to create plugins that extend G-Assist’s capabilities, integrating it with other applications and services.
How It Works
G-Assist operates seamlessly within the NVIDIA app. At its core is a locally hosted Small Language Model (SLM). When you issue a command, either through voice or text, the SLM interprets your request. It then interacts with NVIDIA and third-party APIs to execute the task. For example, if you ask G-Assist to “optimize settings for Cyberpunk 2077,” it will analyze your system and adjust the game’s graphics settings accordingly. Similarly, it can overclock your GPU, adjust fan speeds, or even change the lighting on your keyboard, all based on your natural language instructions.
Use Cases
The applications of Project G-Assist are diverse and cater to a wide range of user needs:
- Enhancing Gaming Performance: Optimize in-game settings for smoother frame rates and improved visual fidelity.
- System Diagnostics and Optimization: Identify and resolve performance bottlenecks to ensure your system is running at its peak.
- Customizing Hardware Settings: Fine-tune hardware settings, such as GPU overclocking and fan speeds, to achieve optimal performance and cooling.
- Automating Routine PC Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks, such as launching applications or adjusting system settings, to save time and effort.
- Integrating with External Applications via Plugins: Extend G-Assist’s functionality by integrating it with other applications and services through plugins.
Pros & Cons
Like any new technology, Project G-Assist has its strengths and weaknesses. Let’s break them down:
Advantages
- Operates offline with local processing, ensuring privacy and low latency.
- Enhances user control over system settings, providing a more personalized experience.
- Extensible through plugin support, allowing for future expansion and customization.
Disadvantages
- Currently limited to desktop RTX GPUs, excluding laptop users and those with older cards.
- Requires significant VRAM (approximately 10GB), potentially limiting its usability on lower-end RTX cards.
How Does It Compare?
While other software solutions offer performance optimization, Project G-Assist distinguishes itself with its integrated AI assistant. Intel Deep Link provides performance optimization features but lacks the natural language interface and AI-driven assistance of G-Assist. AMD Radeon Software offers system tuning tools, but similarly, it doesn’t incorporate AI-powered assistance for a more intuitive user experience. G-Assist’s focus on natural language control and AI-driven optimization sets it apart from the competition.
Final Thoughts
Project G-Assist represents a significant step forward in PC system management. Its ability to understand and execute natural language commands, combined with its local AI processing, offers a compelling alternative to traditional system tuning methods. While the VRAM requirement and desktop-only limitation are drawbacks, the potential for future expansion through plugins and broader GPU support makes G-Assist a promising tool for gamers and PC enthusiasts alike. Keep an eye on this one – it could revolutionize how we interact with our PCs.