Table of Contents
Ray 3.0 by Spatie
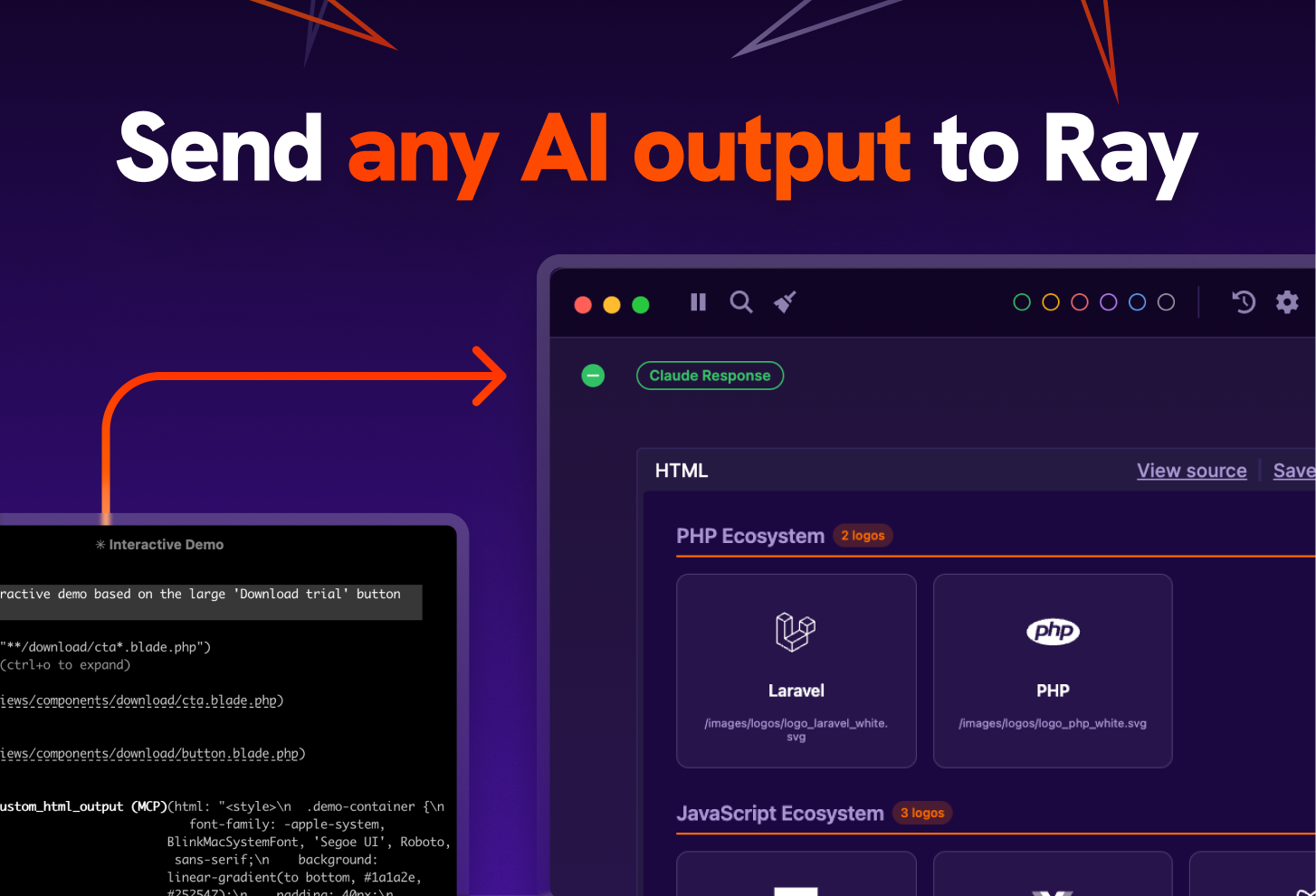
Ray is a dedicated desktop debugging tool that renders output from your code and AI agents in a readable, interactive window. It solves the problem of reading messy logs in terminal windows by providing a structured interface for HTML, arrays, diagrams, and rich text. With its new Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, AI agents can directly send formatted results, prototypes, and debug data to Ray instead of dumping them into a chat interface.
Key Features
- Dedicated Debug Window: A floating desktop window that stays on top of your IDE, collecting logs without cluttering your browser or terminal.
- MCP Server Integration: Acts as a local MCP server, allowing AI agents (like Claude Desktop or IDE-based agents) to send output, prototypes, and code directly to Ray.
- Rich Content Rendering: Renders HTML, CSS, JSON, and images instantly; also supports Mermaid.js for visualizing database schemas and flowcharts.
- Cross-Platform: Native applications available for macOS, Windows, and Linux.
- Language Agnostic: Official SDKs for Laravel, PHP, JavaScript, TypeScript, Go, Ruby, and more.
- Advanced Debugging: Features include “Pause code execution,” measurement of execution time, and click-to-source navigation (clicking a log opens the file in your IDE).
- Theme Support: Fully customizable appearance to match your dark/light mode preferences.
How It Works
Developers install the Ray application and the corresponding package for their programming language (e.g., npm install node-ray or composer require spatie/ray). Once running, Ray listens on a specific local port.
For AI workflows, Ray runs a local MCP (Model Context Protocol) server. When you ask an AI agent to “visualize the user flow” or “debug this array,” the agent can use the MCP tool to send the data to Ray. Ray then parses this incoming payload and renders it—turning a raw JSON string into an interactive tree, or raw HTML into a rendered preview—inside its dedicated window.
Use Cases
- AI Output Visualization: AI agents can “draw” diagrams or render HTML prototypes in a separate window while you continue chatting in the main interface.
- Backend Debugging: Inspecting large arrays, objects, and database queries in PHP/Laravel without using
var_dumpor breaking the page layout. - Remote Debugging: Debugging code running on a remote SSH server while viewing the logs locally on your desktop.
- Performance Tuning: Measuring exactly how long a specific query or function takes to execute.
- Visual Regression: Quickly previewing emails or UI components generated by code/AI without a full browser refresh.
Pros & Cons
Pros:
– Decouples debug output from the browser console, keeping web views clean.
– Excellent AI integration via MCP allows for “dual-monitor” style workflows with agents.
– Highly polished UI that is significantly easier to parse than raw text logs.
– “Click-to-code” feature saves time by jumping straight to the file causing the log.
– Works offline and locally, respecting privacy.
Cons:
– Paid Product: Unlike browser tools, Ray requires a paid license (though a free trial is available).
– Setup Required: Requires installing both the desktop app and language-specific dependencies.
– Learning Curve: Users must learn specific syntax (e.g., ray($variable)) to utilize it fully.
– MCP Complexity: Setting up the MCP integration requires an AI client that supports the protocol (e.g., Claude Desktop).
Pricing
Ray is a premium tool with a license model. Pricing typically falls around €49 per year or a €100+ lifetime license, often bundled with other Spatie products. A free trial is available, usually limited by the number of items you can log per session.
How Does It Compare?
Ray occupies a niche between simple loggers and complex IDE debuggers.
- vs. Browser DevTools (
console.log)- Browser DevTools: Free and built-in, but logs are transient (lost on refresh) and cluttered mixed with browser errors.
- Ray: Persistent history that survives page reloads. It formats server-side code (PHP/Node) just as beautifully as client-side code, which browser consoles cannot easily do for backend processes.
- vs. Xdebug
- Xdebug: The industry standard for “step debugging” (pausing code line-by-line). It is powerful but difficult to configure and slow.
- Ray: Focuses on “dump debugging.” It is faster to set up and better for visualizing data, but it doesn’t offer the granular breakpoint control of Xdebug (though it can pause execution).
- vs. LaraDumps
- LaraDumps: A free, open-source alternative heavily inspired by Ray.
- Ray: Offers a more polished, native cross-platform application (LaraDumps is Electron-based) and has official support/updates from a dedicated commercial team (Spatie). Ray’s AI/MCP integration is currently more advanced.
- vs. Claude Artifacts / ChatGPT Canvas
- Artifacts/Canvas: These render code/HTML inside the AI’s chat interface.
- Ray: Moves that rendering to your local desktop environment. This is crucial for local development where the AI needs to debug your actual running code, not just isolated snippets.
Final Thoughts
Ray 3.0 transforms debugging from a chore into a visually organized experience. While it was originally a tool for PHP/Laravel developers, the addition of the MCP server makes it a unique utility for the AI era—giving your AI agents a dedicated “screen” to show their work. For developers who find themselves constantly pasting code between their IDE, terminal, and AI chat, Ray bridges the gap by creating a unified, visual output channel.