Table of Contents
Overview
WarpGrep is a specialized context retrieval sub-agent developed by Morph (morphllm.com) designed specifically for coding agents to intelligently search large codebases and retrieve only relevant files and line ranges preventing “context rot” during extended development tasks. Launched in December 2024 as RL-trained agentic system inspired by Cognition’s proprietary SWE-Grep tool (which achieves 650 tokens/second throughput on Cerebras infrastructure), WarpGrep operates as specialized inference engine handling code search operations in parallel while primary coding agents (Claude Code, Codex, OpenCode, custom agents) focus on reasoning and implementation.
The platform addresses critical bottleneck in AI-assisted software engineering where traditional agents waste significant time and tokens on sequential grep operations, reading irrelevant files, and accumulating noise in context windows. Rather than each agent individually deciding what files to grep and maintaining sequential single-threaded search workflows, WarpGrep treats context retrieval as independent learned problem using reinforcement learning to optimize for two metrics: correctly identifying relevant files and pinpointing precise line ranges minimizing unnecessary context.
Available through dual access pathways (MCP/Model Context Protocol for seamless tool integration with Claude and compatible agents, or SDK for programmatic usage in custom agent frameworks), WarpGrep currently operates in beta free tier with planned usage-based pricing (\$0.40/1M tokens). Morph also offers complementary Fast Apply tool handling merge operations for AI-suggested code changes with 98% accuracy at 60x higher speed than naive full-file replacement approaches, positioning Morph as complete infrastructure layer for production-grade coding agents.
Key Features
RL-Trained Context Retrieval Optimization: Single month of reinforcement learning training taught system optimal grep query patterns, parallel execution strategies, result filtering thresholds, and line range boundaries for thousands of real coding tasks. The RL training used internal dataset of real repositories, user queries, and ground truth relevant files creating specialized retrieval policy matching human developer intuitions about relevant context without requiring manual heuristic engineering.
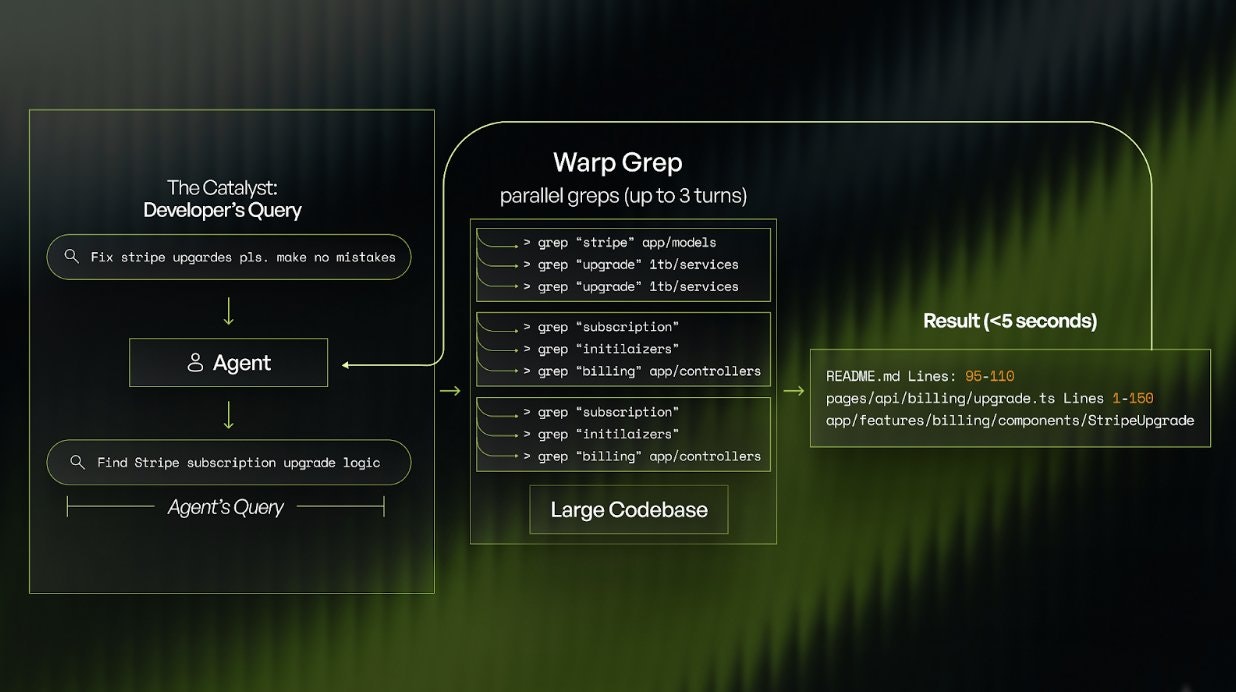
Parallel Multi-Turn Context Search: Executes up to eight parallel grep and file read operations per turn preventing sequential bottleneck traditional agents face. Within four-turn budget per context retrieval session, system plans comprehensive searches combining multiple strategies: pattern-based grep for specific implementations (database queries, API endpoints, authentication flows), semantic search for conceptual relationships, import tracing following dependencies, and file glob operations for discovering related modules. Parallel execution combined with strict turn budgets keeps latency under control.
Aggressive Context Filtering and “Context Rot” Reduction: Proprietary algorithms filter grep results keeping only truly relevant files and discarding irrelevant matches. WarpGrep demonstrates 70% reduction in context rot on long-horizon tasks compared to baseline approaches—crucial metric as agent tasks extend beyond 5-10 turns where accumulated context noise exponentially degrades reasoning quality. By preventing pollution of primary agent context with 40+ irrelevant files, subsequent reasoning steps operate on cleaner signal enabling better decision-making.
Precise Line Range Identification: Returns not just file names but specific line ranges (e.g., “authentication.ts:120-180”) where relevant code concentrates. This precision prevents agents reading entire 500-line files when relevant logic occupies 30 lines, significantly reducing token consumption and improving focus. The line range precision trained through RL on ground truth evaluations.
Strict Turn and Token Budgets: Hard constraints prevent runaway context retrieval burning unlimited budget searching increasingly marginal files. Four-turn maximum ensures retrieval completes rapidly, parallel operations ensure parallelizable work completes simultaneously rather than sequentially, and token budgets enforce cost discipline preventing “search forever” failure modes.
MCP Integration for Claude Code and Compatible Agents: Model Context Protocol implementation provides standardized tool interface enabling drop-in usage with Claude Code, Codex, and other MCP-compatible agents without requiring custom integration. Tools appear naturally in agent’s available capabilities enabling autonomous decision-making about when context retrieval needed.
SDK for Custom Agent Frameworks: Programmatic access for teams building proprietary agent frameworks or integrating with non-MCP systems. SDK handles tool communication, manages budgets and state, and provides callbacks for custom orchestration logic.
High Throughput Inference: Achieves 4500+ tokens/second throughput on modern GPU infrastructure enabling rapid context search completion. While slightly slower than Cognition’s proprietary SWE-Grep (650 tokens/second on Cerebras custom silicon) system remains substantially faster than Claude’s stock grep operations enabling meaningful latency improvements for end-to-end tasks.
Code-Specific Vector Embeddings: Complementary embeddings service trained on millions of Git commits enables semantic search supplementing pattern-based grep. Hybrid grep+semantic approach improves retrieval accuracy 31% on large codebases compared to either approach alone.
How It Works
Coding agent encounters situation requiring code exploration (needs to understand authentication middleware, find database query examples, trace API endpoint implementation). Rather than agent manually crafting grep patterns, WarpGrep invokes with natural language description (“How does the authentication system handle token refresh?”). WarpGrep plans multi-step search: pattern grep for “refresh_token” keywords, import following from auth module, semantic search for “token rotation patterns,” and file globbing through middleware directory. Parallel execution completes within seconds returning ranked results with line ranges. Agent consumes results maintaining cleaner context than from sequential manual grep producing irrelevant noise.
Use Cases
Speeding Up SWE-Bench Tasks: Research teams evaluating coding agents on SWE-Bench benchmarks benefit from 40% acceleration enabling faster iteration on agent design improvements. Reduced context rot particularly impacts long-horizon tasks requiring multi-file modifications where context management proves critical success factor.
Improving AI Coding Agent Accuracy: Cleaner context through aggressive filtering enables primary agents reasoning more effectively without distraction from irrelevant code. For complex tasks spanning multiple files across large repositories, context quality directly correlates with accuracy.
Reducing API Costs: Token-conscious pricing rewards aggressive context filtering. By reducing tokens necessary completing equivalent tasks, WarpGrep directly reduces inference costs particularly important for teams running coding agents at scale processing large codebases.
Enabling Long-Horizon Coding Tasks: Tasks requiring spanning dozens of files, understanding complex interdependencies, or iterative refinement across repository become practical with proper context management. WarpGrep’s RL training specifically optimizes for multi-turn scenarios where context rot prevention proves essential.
Improving Custom Agent Performance: Organizations building proprietary coding agents benefit from specialized retrieval layer rather than attempting general-purpose approaches. Replacing generic semantic search with WarpGrep immediately improves agent reliability and speed.
Pros \& Cons
Advantages
Solves Critical AI Coding Bottleneck: Context retrieval and management represents persistent pain point preventing scaling coding agents to real-world repository sizes. Specialized solution directly addressing this bottleneck provides immediate tangible benefits.
Significant Measured Speed Improvements: 40% faster task completion provides substantial productivity gains even compared to baseline agents, and improvements compound with task complexity as context rot becomes increasingly problematic.
Reduction in Context Pollution: 70% context rot reduction directly improves reasoning quality enabling better code generation and fewer erroneous modifications to unrelated files.
Seamless Integration Through MCP: Standard tool interface enables drop-in usage with existing Claude Code and compatible agents requiring minimal integration effort.
Transparent Performance Metrics: Published benchmarks on SWE-Bench with detailed ablations enable quantitative evaluation versus alternatives rather than relying on marketing claims.
Disadvantages
Slower Than Proprietary SWE-Grep: WarpGrep (4500+ tokens/second throughput) currently slower than Cognition’s closed-source SWE-Grep (650 tokens/second on Cerebras custom infrastructure) creating performance gap for teams prioritizing absolute speed. However, Morph emphasizes system remains trainable and actively optimizing performance.
Requires Coding Agent Integration: Standalone utility without embedded agent value requires compatible agent framework adoption. Not suitable for teams using incompatible agents or custom systems requiring substantial engineering integration effort.
Beta Status with Incomplete Optimization: December 2024 launch and active optimization mean potential for breaking changes, incomplete features, or stability issues. Production-critical workflows face risk of disruption if beta instability prevents reliable operation.
Specialized Tool with Limited Scope: Focuses exclusively on code retrieval not addressing other coding agent challenges (test generation, error recovery, architecture understanding) requiring complementary solutions for comprehensive agent development.
Limited Public Benchmarking: Published evaluations focus primarily on SWE-Bench Lite subset, lacking comprehensive evaluation across diverse codebases, programming languages, and real-world scenarios outside research benchmarks.
Pricing Uncertainty: While free during beta, post-beta pricing structure (\$0.40/1M tokens claimed) remains unconfirmed preventing accurate cost forecasting for production deployments scaling to large token volumes.
How Does It Compare?
WarpGrep vs SWE-Grep (Cognition AI)
SWE-Grep is Cognition’s proprietary context retrieval specialist trained through month-long RL process integrated within Windsurf IDE and Devin AI software engineer achieving 650 tokens/second throughput on Cerebras infrastructure with proven performance on internal engineering tasks and integrated with SWE-1.5 frontier coding model.
Training Approach:
- WarpGrep: Month-long RL training on diverse codebase collection
- SWE-Grep: Integrated training with Cognition’s broader SWE-1.5 ecosystem
Performance:
- WarpGrep: 4500+ tokens/second throughput; 40% speed improvement claimed
- SWE-Grep: 650 tokens/second on specialized Cerebras hardware; proven production performance
Availability:
- WarpGrep: Open beta accessible via MCP or SDK (\$0.40/1M tokens pricing TBD)
- SWE-Grep: Proprietary; available through Windsurf IDE subscription
Integration:
- WarpGrep: MCP-based drop-in tool; SDK for custom agents
- SWE-Grep: Integrated within Cognition’s product stack
Context Rot Reduction:
- WarpGrep: 70% reduction claimed on long-horizon tasks
- SWE-Grep: Context optimization claims less quantified; integrated within broader agent
When to Choose WarpGrep: For open access to specialized retrieval, MCP compatibility with Claude/custom agents, or evaluation of RL-trained retrieval approach.
When to Choose SWE-Grep: For integration with Windsurf/Devin ecosystem, proven production performance, or Cognition’s unified SWE-1.5 approach.
WarpGrep vs MemGPT (UC Berkeley)
MemGPT is context management system from UC Berkeley treating LLM context window as hierarchical memory resource similar to OS virtual memory enabling extended context through intelligent paging between fast context window and slower external storage.
Architecture:
- WarpGrep: Specialized RL-trained retrieval sub-agent for parallel code search
- MemGPT: Hierarchical memory management with paging between storage tiers
Primary Function:
- WarpGrep: Code retrieval optimization within agent workflows
- MemGPT: Extended context management for any LLM task
Use Cases:
- WarpGrep: Coding agents, repository navigation, context rot prevention
- MemGPT: Long document analysis, extended conversations, general-purpose context extension
Integration:
- WarpGrep: Tool-based integration within agent framework
- MemGPT: System-level context management replacing native context handling
Optimization Target:
- WarpGrep: Retrieval quality for code understanding
- MemGPT: Extended context for any domain
When to Choose WarpGrep: For specialized code retrieval within coding agents.
When to Choose MemGPT: For extending context windows broadly across diverse applications.
WarpGrep vs LlamaIndex (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
LlamaIndex is flexible framework for building retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications providing vector database integration, document chunking, semantic search, and query engines for connecting LLMs to enterprise data across diverse document types.
Scope:
- WarpGrep: Specialized code retrieval for software engineering
- LlamaIndex: General-purpose RAG across all data types
Optimization:
- WarpGrep: RL-trained specifically for source code retrieval
- LlamaIndex: Framework supporting diverse retrieval strategies
Agent Integration:
- WarpGrep: Tool within agent workflows
- LlamaIndex: Standalone framework or integrated component
Training:
- WarpGrep: RL-optimized retrieval policies
- LlamaIndex: Configurable retrievers using various embedding models
Use Cases:
- WarpGrep: Coding agent context management
- LlamaIndex: Enterprise knowledge assistants, document question-answering
When to Choose WarpGrep: For specialized code retrieval within coding agents.
When to Choose LlamaIndex: For general RAG applications across diverse data types.
Final Thoughts
WarpGrep represents targeted solution addressing specific persistent bottleneck plaguing coding agents: inefficient context retrieval consuming disproportionate time and tokens while polluting reasoning context with irrelevant files. The December 2024 launch demonstrates technical viability of RL-trained specialized retrieval policies outperforming generic approaches through optimization for dual metrics (precision finding relevant files, recall avoiding false negatives) that matter specifically to code understanding tasks.
The measured improvements—40% faster task completion, 70% context rot reduction—particularly significant for long-horizon tasks where context management becomes progressively more critical. The parallel multi-turn search architecture preventing sequential grep bottleneck reflects deep understanding of coding agent failure modes where traditional sequential approaches waste computational budget on ineffective queries compounding information retrieval inefficiency.
The MCP integration providing seamless Claude Code and compatible agent compatibility addresses practical adoption barrier enabling developers testing specialized retrieval without extensive integration work. The complementary embeddings and Fast Apply tools position Morph as comprehensive infrastructure layer for production-grade coding agents rather than single-point solution.
However, current speed deficit versus Cognition’s proprietary SWE-Grep, beta maturity with optimization ongoing, and pricing uncertainty prevent immediate universal recommendation. Organizations using Windsurf or Devin already benefit from integrated SWE-Grep. Teams building custom agents or using Claude Code benefit from WarpGrep’s open accessibility through MCP. The choice depends on compatibility, performance requirements, and willingness accepting beta maturity for access to open specialized retrieval infrastructure.
For organizations recognizing context retrieval as critical AI coding bottleneck, experimenting with agents at scale on large codebases, or building production agent systems, WarpGrep provides compelling infrastructure worth evaluating despite beta status and ongoing optimization. The RL-trained approach to specialized retrieval demonstrates promising direction for tackling domain-specific agent challenges through dedicated optimization rather than generic approaches, suggesting template for addressing other persistent agent bottlenecks through similar specialized training methodologies.